Abstract
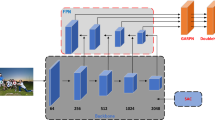
Center and scale prediction (CSP) is an anchor-free pedestrian detector with good performance. However, there are lots of parameters in the detector, which seriously limits the speed. In this paper, a new network is designed for the improvement of the detector speed, which contains less parameters, named Feature Fusion: Center and Scale Prediction (F-CSP). F-CSP fuses multi-scale feature maps with two efficient feature fusion networks: Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN) and Balanced Feature Pyramid (BFP). Specifically, FPN is used to reduce the channel of feature maps, and BFP is used to fuse multiple feature maps into a single one. This way, the proposed detector achieves competitive accuracy and higher speed on the challenging pedestrian detection benchmark. The performance of F-CSP is demonstrated on the Caltech dataset. Compared with CSP, under the premise of ensuring accuracy, the speed is increased from 45.1 to 32.9 ms/img.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For ResNet-50, its Conv layers can be divided into five stages, in which the output feature maps of the five stages are downsampled by 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 with respect to the input image, respectively. As regular [37, 38], the dilated convolutions are adopted in the last residual block to keep its output as 1/16 of the input image size.
Optionally, to slightly adjust the center location, an extra offset prediction branch can be appended in parallel with the above two branches.
References
Moya, S., Grau, S., Tost, D.: The wise cursor: assisted selection in 3D serious games. Vis. Comput. 29(6), 795 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-013-0831-3
Sherstyuk, A., Jay, C., Treskunov, A.: Impact of hand-assisted viewing on user performance and learning patterns in virtual environments. Vis. Comput. 27(3), 173 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-010-0516-0
Ballit, A., Mougharbel, I., Ghaziri, H., Dao, T.T.: Computer-aided parametric prosthetic socket design based on real-time soft tissue deformation and an inverse approach. Vis. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02059-9
Chen, G., Qin, H.: Class-discriminative focal loss for extreme imbalanced multiclass object detection towards autonomous driving. Vis. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02067-9
Fan, X., Pan, G., Mao, Y., He, W.: A personalized traffic simulation integrating emotion using a driving simulator. Vis. Comput. 36(6), 1203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01732-4
Musse, S.R., Cassol, V.J., Thalmann, D.: A history of crowd simulation: the past, evolution, and new perspectives. Vis. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02252-w
He, Z., Li, Q., Feng, H., Xu, Z.: Fast and sub-pixel precision target tracking algorithm for intelligent dual-resolution camera. Vis. Comput. 36(6), 1157 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01724-4
Bagheri Baba Ahmadi, S., Zhang, G., Wei, S., Boukela, L.: An intelligent and blind image watermarking scheme based on hybrid SVD transforms using human visual system characteristics. Vis. Comput. 37(2), 385 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01808-6
Vishwakarma, S., Agrawal, A.: A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. Vis. Comput. 29(10), 983 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-012-0752-6
Zhang, H., Hu, Z., Hao, R.: Joint information fusion and multi-scale network model for pedestrian detection. Vis. Comput. 37(8), 2433 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01997-0
Khan, S.D., Basalamah, S.: Scale and density invariant head detection deep model for crowd counting in pedestrian crowds. Vis. Comput. 37(8), 2127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01974-7
Silveira, R., Dapper, F., Prestes, E., Nedel, L.: Natural steering behaviors for virtual pedestrians. Vis. Comput. 26(9), 1183 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-009-0399-0
Li, Z., He, S., Hashem, M.: Robust object tracking via multi-feature adaptive fusion based on stability: contrast analysis. Vis. Comput. 31(10), 1319 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-014-1014-6
Liu, W., Liao, S., Ren, W., Hu, W., Yu, Y.: High-level semantic feature detection: A new perspective for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5187–5196 (2019)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 28, 91 (2015)
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S., Fu, C.Y., Berg, A.C.: Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 21–37. Springer (2016)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7263–7271 (2017)
Law, H., Deng, J.: Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 734–750 (2018)
Zhou, X., Zhuo, J., Krahenbuhl, P.: Bottom-up object detection by grouping extreme and center points. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 850–859 (2019)
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Pang, J., Chen, K., Shi, J., Feng, H., Ouyang, W., Lin, D.: Libra r-cnn: Towards balanced learning for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 821–830 (2019)
Singh, V.K., Kumar, N.: Saliency bagging: a novel framework for robust salient object detection. Vis. Comput. 36(7), 1423 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01750-2
Xu, J., Cao, W., Liu, B., Jiang, K.: Object restoration based on extrinsic reflective symmetry plane detection. Vis. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02192-5
Wang, B., Chen, S., Wang, J., Hu, X.: Residual feature pyramid networks for salient object detection. Vis. Comput. 36(9), 1897 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01779-3
Shu, C., Ding, X., Fang, C.: Histogram of the oriented gradient for face recognition. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 16(2), 216 (2011)
Yan, J., Lei, Z., Wen, L., Li, S.Z.: The fastest deformable part model for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2497–2504 (2014)
Rothe, R., Guillaumin, M., Van Gool, L.: Non-maximum suppression for object detection by passing messages between windows. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 290–306. Springer (2014)
Papageorgiou, C.P., Oren, M., Poggio, T.: A general framework for object detection. In: Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision (IEEE Cat. No. 98CH36271), pp. 555–562. IEEE (1998)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Girshick, R.B., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(9), 1627 (2009)
Liu, L., Ouyang, W., Wang, X., Fieguth, P., Chen, J., Liu, X., Pietikäinen, M.: Deep learning for generic object detection: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vision 128(2), 261 (2020)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 580–587 (2014)
Girshick, R.: Fast r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1440–1448 (2015)
Duan, K., Xie, L., Qi, H., Bai, S., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Corner proposal network for anchor-free, two-stage object detection. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part III 16, pp. 399–416. Springer (2020)
Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2980–2988 (2017)
Zeiler, M.D., Taylor, G.W., Fergus, R.: Adaptive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level feature learning. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2018–2025. IEEE (2011)
Liu, Y., Zhang, Y.M., Zhang, X.Y., Liu, C.L.: Adaptive spatial pooling for image classification. Pattern Recogn. 55, 58 (2016)
Wang, S., Cheng, J., Liu, H., Tang, M.: Pcn: Part and context information for pedestrian detection with cnns. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.04483 (2018)
Zhang, S., Yang, J., Schiele, B.: Occluded pedestrian detection through guided attention in cnns. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6995–7003 (2018)
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: Weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.01780 (2017)
Mao, J., Xiao, T., Jiang, Y., Cao, Z.: What can help pedestrian detection? In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3127–3136 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Cao, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Efficient feature fusion network based on center and scale prediction for pedestrian detection. Vis Comput 39, 3865–3872 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02528-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02528-9