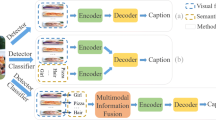
Abstract
Automatically describing the detail and content of the image is a meaningful but difficult task. In this paper, we propose a variety of optimization improvements to enhance the encoder and decoder for image captioning, called multi-channel weighted fusion. In the presented model, we propose multi-channel encoder which is able to extract different features of the same image by combining various models and algorithms. In order to avoid dimensional explosion caused by multi-channel encoder, we employ the reducing multilayer perceptron to reduce the dimension and discuss how to train the reducing multilayer perceptron. For the decoder part, we discuss how the decoder receives features from different channels and propose a technique for fusing independent and identically typed decoders. To get a better description generated by the decoder, we exploit the voting weight strategy for decoder fusion and explore the entropy function to choose the best distribution. The experiment on datasets Flickr-8k, Flickr-30k and MS COCO demonstrates that the proposed model is compatible with most features with low error rate. For instance, our model is specifically outstanding on METEOR score.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ojala, T., Pietikäinen, M., Harwood, D.: A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recognit. 29(1), 51–59 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-3203(95)00067-4
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 886–893 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.177
Mitchell, M., Dodge, J., Goyal, A., Yamaguchi, K., Stratos, K., Han, X., Mensch, A.C., Berg, A.C., Berg, T.L., III, H.D.: Midge: generating image descriptions from computer vision detections. In: Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 747–756 (2012)
Mason, R., Charniak, E.: Nonparametric method for data-driven image captioning. In: Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 592–598 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/p14-2097
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), pp. 1409–15566 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, L., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., Erhan, D.: Show and tell: a neural image caption generator. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3156–3164 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298935
Leng, L., Zhang, J.: Palmhash code vs. palmphasor code. Neurocomputing 108, 1–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2012.08.028
Leng, L., Li, M., Kim, C., Bi, X.: Dual-source discrimination power analysis for multi-instance contactless palmprint recognition. Multimed. Tools. Appl. 76(1), 333–354 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3058-7
Abbass, M.Y., Kwon, K., Kim, N., Abdelwahab, S.A.S., El-Samie, F.E.A., Khalaf, A.A.M.: Efficient object tracking using hierarchical convolutional features model and correlation filters. Vis. Comput. 37(4), 831–842 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01833-5
Asad, M., Yang, J., Jiang, H., Shamsolmoali, P., He, X.: Multi-frame feature-fusion-based model for violence detection. Vis. Comput. 37(6), 1415–1431 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01878-6
Hazgui, M., Ghazouani, H., Barhoumi, W.: Genetic programming-based fusion of HOG and LBP features for fully automated texture classification. Vis. Comput. 38(2), 457–476 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-02028-8
Ding, S., Qu, S., Xi, Y., Wan, S.: Stimulus-driven and concept-driven analysis for image caption generation. Neurocomputing 398, 520–530 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.04.095
Wei, H., Li, Z., Zhang, C., Ma, H.: The synergy of double attention: Combine sentence-level and word-level attention for image captioning. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 201, 103068 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2020.103068
Zhang, J., Li, K., Wang, Z., Zhao, X., Wang, Z.: Visual enhanced GLSTM for image captioning. Expert Syst. Appl. 184, 115462 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115462
Cao, P., Yang, Z., Sun, L., Liang, Y., Yang, M.Q., Guan, R.: Image captioning with bidirectional semantic attention-based guiding of long short-term memory. Neural Process. Lett. 50(1), 103–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-09973-5
Farhadi, A., Hejrati, S.M.M., Sadeghi, M.A., Young, P., Rashtchian, C., Hockenmaier, J., Forsyth, D.A.: Every picture tells a story: generating sentences from images. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), vol. 6314, pp. 15–29 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15561-1_2
Yao, B.Z., Yang, X., Lin, L., Lee, M.W., Zhu, S.-C.: I2T: image parsing to text description. Proc. IEEE 98(8), 1485–1508 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2010.2050411
Mao, J., Xu, W., Yang, Y., Wang, J., Huang, Z., Yuille, A.L.: Deep captioning with multimodal recurrent neural networks (m-RNN). In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), pp. 1412–66325 (2015)
Xu, K., Ba, J.L., Kiros, R., Cho, K., Courville, A.C., Salakhutdinov, R., Zemel, R.S., Bengio, Y.: Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), vol. 37, pp. 2048–2057 (2015)
Fu, K., Jin, J., Cui, R., Sha, F., Zhang, C.: Aligning where to see and what to tell: Image captioning with region-based attention and scene-specific contexts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2321–2334 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2642953
Jia, X., Gavves, E., Fernando, B., Tuytelaars, T.: Guiding the long-short term memory model for image caption generation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2407–2415 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.277
Jiang, T., Zhang, Z., Yang, Y.: Modeling coverage with semantic embedding for image caption generation. Vis. Comput. 35(11), 1655–1665 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1565-z
Feng, Y., Ma, L., Liu, W., Luo, J.: Unsupervised image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4120–4129 (2019)
Barlas, G., Veinidis, C., Arampatzis, A.: What we see in a photograph: content selection for image captioning. Vis. Comput. 37(6), 1309–1326 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01867-9
Zha, Z., Liu, D., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., Wu, F.: Context-aware visual policy network for fine-grained image captioning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(2), 710–722 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2909864
Wang, Q., Wan, J., Chan, A.B.: On diversity in image captioning: Metrics and methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(2), 1035–1049 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3013834
Liu, A., Zhai, Y., Xu, N., Nie, W., Li, W., Zhang, Y.: Region-aware image captioning via interaction learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(6), 3685–3696 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3107035
Ben, H., Pan, Y., Li, Y., Yao, T., Hong, R., Wang, M., Mei, T.: Unpaired image captioning with semantic-constrained self-learning. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 24, 904–916 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3060948
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., Uszkoreit, J., Houlsby, N.: An image is worth 16 x 16 words: transformer for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), pp. 2010–119292 (2021)
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bernstein, M.S., Berg, A.C., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 115(3), 211–252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y
Zhou, B., Lapedriza, A., Khosla, A., Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Places: a 10 million image database for scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(6), 1452–1464 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2723009
Girshick, R.B.: Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1440–1448 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169
Wu, Y., Kirillov, A., Massa, F., Lo, W.-Y., Girshick, R.: Detectron2 (2019)
Chung, J., Gülçehre, Ç., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. In: Neural and Evolutionary Computing, pp. 1412–35551 (2014)
Micah, H., Young, P., Hockenmaier, J.: Framing image description as a ranking task: data, models and evaluation metrics. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 47, 853–899 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.3994
Young, P., Lai, A., Hodosh, M., Hockenmaier, J.: From image descriptions to visual denotations: New similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. In: Association for Computational Linguistics, vol. 2, pp. 67–78 (2014)
Lin, T., Maire, M., Belongie, S.J., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., Zitnick, C.L.: Microsoft coco: common objects in context. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), vol. 8693, pp. 740–755 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.-J.: BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 311–318 (2002). https://doi.org/10.3115/1073083.1073135
Lavie, A., Agarwal, A.: METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with high levels of correlation with human judgments. In: Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 228–231 (2005)
Lin, C., Och, F.J.: Automatic evaluation of machine translation quality using longest common subsequence and skip-bigram statistics. In: Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 605–612 (2004). https://doi.org/10.3115/1218955.1219032
Vedantam, R., Zitnick, C.L., Parikh, D.: CIDEr: consensus-based image description evaluation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4566–4575 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299087
Kingma, D.P., Bah, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), pp. 1412–69809 (2015)
Chen, L., Zhang, H., Xiao, J., Nie, L., Shao, J., Liu, W., Chua, T.: SCA-CNN: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6298–6306 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.667
Zhou, L., Zhang, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhang, T., Fan, W.: Re-caption: saliency-enhanced image captioning through two-phase learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 694–709 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2928144
Guo, L., Liu, J., Lu, S., Lu, H.: Show, tell, and polish: ruminant decoding for image captioning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 22(8), 2149–2162 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2951226
Zhang, J., Mei, K., Zheng, Y., Fan, J.: Integrating part of speech guidance for image captioning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 23, 92–104 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.2976552
Wu, L., Xu, M., Wang, J., Perry, S.W.: Recall what you see continually using gridlstm in image captioning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 22(3), 808–818 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2931815
do Carmo Nogueira, T., Vinhal, C.D.N., da Cruz Jr., G., Ullmann, M.R.D.: Reference-based model using multimodal gated recurrent units for image captioning. Multimed. Tools. Appl. 79(41-42), 30615–30635 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09539-5
Yang, L., Wang, H., Tang, P., Li, Q.: Captionnet: a tailor-made recurrent neural network for generating image descriptions. IEEE Trans. Multimed 23, 835–845 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.2990074
Yang, X., Zhang, H., Cai, J.: Auto-encoding and distilling scene graphs for image captioning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(5), 2313–2327 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3042192
Yu, L., Zhang, J., Wu, Q.: Dual attention on pyramid feature maps for image captioning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 24, 1775–1786 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3072479
Li, X., Zhang, W., Sun, X., Gao, X.: Without detection: two-step clustering features with local-global attention for image captioning. IET Comput. Vis. 16(3), 280–294 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1049/cvi2.12087
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology on Information System Engineering Laboratory [WDZC20205250410] and Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province under Grant [2019B111101001].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
The detail about Equation (8)
Let’s assume the linear layer is calculated by
the partial derivative of z with respect to w is
If there are v words in vocabulary, at time t, the probability of the ith word generated by softmax function is
If \(i = j\), we have
If \(i \ne j\), then
Let cross-entropy be the loss function, \({\varvec{p}}_{t}\) is the distribution which is not reduced. The loss function can be written as
Then,
Because there are v words in vocabulary, \({\varvec{q}}_{t}\) will generate different probabilities for different words,
Separate the two cases when \(k = i\) and \(k \ne i\), we have
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, J., Cao, Y., Zhu, Y. et al. Multi-channel weighted fusion for image captioning. Vis Comput 39, 6115–6132 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02716-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02716-7