Abstract
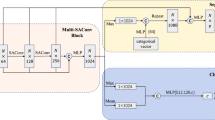
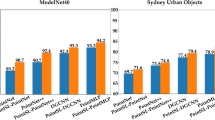
With the gradual growth of deep learning in machine vision, efficient extraction of 3D point clouds becomes significant. The raw data of the 3D point cloud are sparse, disordered, and immersed in noise, which makes it difficult to classify and segment. Whether 3D point clouds can be classified and segmented or not, the local feature is an essential ingredient. Therefore, this paper proposes a GateNet-based PointNet++ network (G-PointNet++). G-PointNet++ extracts local features more accurately than PointNet++ by suppressing irrelevant features and emphasizing important features. Meanwhile, it refines the feature adaptively. Besides, the SENet and attention mechanism are introduced into PointNet++. G-PointNet++ was evaluated on the public ModelNet dataset, ShapeNet dataset, and S3DIS dataset, and its effectiveness in classification and segmentation tasks was verified. In the classification task, G-PointNet++ achieves an overall classification accuracy (OA) of 95.5% on ModelNet10 and 93.3% on ModelNet40. In the segmentation task, the mIoU of G-PointNet++ reaches 85.5% on ShapeNet. These experiments show that G-PointNet++ achieves better performance and saves more time than PointNet++, and its overall accuracy is higher than that of PCT network on ModeNet40.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability statement
All data in the manuscript can be found at: https://modelnet.cs.princeton.edu/ and https://shapenet.org/. All other data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Cheraghian, A., Rahman, S., Petersson, L.: Zero-shot learning of 3D Point cloud objects. In: 2019 16th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA). IEEE (2019)
Mahdaoui, A., Sbai, E.H.: 3D point cloud simplification based on the clustering algorithm and introducing the Shannon’s entropy. In: 13th International Conference on Machine Vision. SPIE (2021)
Abbasi, R., Bashir, K., Alyamani, H.J., Amin, F., Doh, J., Chen, J.: Lidar point cloud compression, processing and learning for autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 24(1), 962–979 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3167957
Su, H., Maji, S., Kalogerakis, E., Learned-Miller, E.: Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE (2015)
Jiang, J., Bao, D., Chen, Z., Zhao, X., Gao, Y.: MLVCNN: multi-loop-view convolutional neural network for 3D shape retrieval. Proc. AAAI Confer. Artif. Intell. 33, 8513–8520 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018513
Maturana, D., Scherer, S.: VoxNet: a 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition. In: 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE (2015)
Klokov, R., Lempitsky, V.: Escape from Cells: Deep Kd-networks for the recognition of 3D point cloud models. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE (2017)
Zhirong, W., Song, S., Khosla, A., Fisher, Y., Linguang, Z., Xiaoou, T., et al.: 3D ShapeNets: a deep representation for volumetric shapes. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE (2015)
Chang, A.X., Funkhouser, T., Guibas, L., Hanrahan, P., Huang, Q., Li, Z., et al.: Shapenet: an information-rich 3d model repository. arXiv:1512.03012 (2015)
Charles, R.Q., Su, H., Kaichun, M., Guibas, L.J.: PointNet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE (2017)
Qi, C.R., Yi, L., Su, H., Guibas, L.J.: Pointnet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA
Xiao, B., Da, F.: Three-stage generative network for single-view point cloud completion. Vis. Comput. 38, 4373–4382 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02301-4
Song, Y., Shen, W., Peng, K.: A novel partial point cloud registration method based on graph attention network. Vis. Comput. 39, 1109–1120 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02391-0
Hurtado, J., Gattass, M., Raposo, A.: 3D point cloud denoising using anisotropic neighborhoods and a novel sharp feature detection algorithm. Vis. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02698-6
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE (2018)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Li, X., Wu, X., Lu, H., Liu, X., Meng, H.: Channel-wise gated Res2Net: towards robust detection of synthetic speech attacks. In: Interspeech 2021. ISCA (2021)
Te, G., Hu, W., Zheng, A., Guo, Z.: Rgcnn: regularized graph CNN for point cloud segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 746–754 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Rabbat, M.: A graph-CNN for 3d point cloud classification. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6279–6283. IEEE (2018)
Xu, Y., Fan, T., Xu, M., Zeng, L., Qiao, Y.: Spidercnn: deep learning on point sets with parameterized convolutional filters. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 87–102 (2018)
Li, Y., Bu, R., Sun, M., Wu, W., Di, X., Chen, B.: Pointcnn: convolution on x-transformed points. 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2018), Montréal, Canada
Hua, B.-S., Tran, M.-K., Yeung, S.-K.: Pointwise convolutional neural networks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE (2018)
Jiang, M., Wu, Y., Zhao, T., Zhao, Z., Lu, C.: Pointsift: a sift-like network module for 3d point cloud semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.00652 (2018)
Wu, W., Qi, Z., Fuxin, L.: PointConv: deep convolutional networks on 3D Point clouds. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE (2019)
Zhao, H., Jiang, L., Fu, C.-W., Jia, J.: PointWeb: enhancing local neighborhood features for point cloud processing. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE (2019)
Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Sarma, S.E., Bronstein, M.M., Solomon, J.M.: Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. 38(5), 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3326362
Zhang, Q., Cheng, J., Wang, S., Xu, C., Gao, X.: Point-selection and multi-level-point-feature fusion-based 3D point cloud classification. Electron. Lett. 56(6), 290–293 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2019.2856
Wang, H., Xu, H., Zhao, C., Liu, Y.: KC-PointNet: attentional network for 3D point cloud processing. In: 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC). IEEE (2021)
Chen, L., Zhang, Q.: DDGCN: graph convolution network based on direction and distance for point cloud learning. Vis. Comput 39, 863–873 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02351-8
Xu, S., Zhou, X., Ye, W., Ye, Q.: Classification of 3-D point clouds by a new augmentation convolutional neural network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2022.3141073
Guo, M.H., Cai, J.X., Liu, Z.N., et al.: Pct: point cloud transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 7, 187–199 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-021-0229-5
Engel, N., Belagiannis, V., Dietmayer, K.: Point transformer. IEEE Access 9, 134826–134840 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3116304
Zhao, M., Zhong, S., Fu, X., Tang, B., Pecht, M.: Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 16(7), 4681–4690 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2019.2943898
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The manuscript has no relevant conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Under Grant: 62176018).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Tian, S. Deep 3D point cloud classification and segmentation network based on GateNet. Vis Comput 40, 971–981 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02826-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02826-w