Abstract
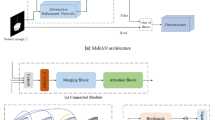
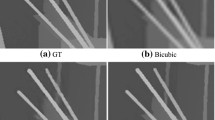
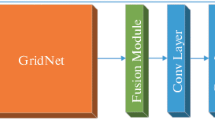
In recent years, deep learning networks have achieved prominent success in the field of multi-exposure image fusion. However, it is still challenging to prevent color distortion and blurry edges which leads to bad visual effects. In this paper, we present a multi-scale attention-guided network for multi-exposure image fusion in a coarse-to-fine manner. The network generates multi-scale enhanced attention weight maps of images in different sizes which possess vital details and can emphasize essential regions of interest from both sides. The multi-scale structure can extract features on different scales, and the bilayer structure can extract features from different image sizes. Moreover, we designed a coarse-to-fine attention module to finally generate the weight maps; the module combines channel attention with spatial attention. Fused results will be generated under the guidance of the weight maps. Qualitative and quantitative experiments are performed on a publicly available dataset which shows our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in visual effect and objective analysis. Also, ablation experiments prove each part of our method has a great advantage in generating images with significant details, prominent targets, and faithful color.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, X.-K. Shang, upon reasonable request.
References
Zhuang, P., Wu, J., Porikli, F., Li, C.: Underwater image enhancement with hyper-laplacian reflectance priors. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 5442–5455 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3196546
Jiang, Z., Li, Z., Yang, S., Fan, X., Liu, R.: Target oriented perceptual adversarial fusion network for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(10), 6584–6598 (2022)
Liu, J., Wu, Y., Huang, Z., Liu, R., Fan, X.: SMoA: searching a modality-oriented architecture for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 1818–1822 (2021)
Liu, R., Liu, J., Jiang, Z., Fan, X., Luo, Z.: A bilevel integrated model with data-driven layer ensemble for multi-modality image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 1261–1274 (2020)
Liu, J., Fan, X., Huang, Z., Wu, G., Liu, R., Zhong, W., Luo, Z.: Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5802–5811 (2022)
Goshtasby, A.A.: Fusion of multi-exposure images. Image Vis. Comput. 23(6), 611–618 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2005.02.004
Li, H., Manjunath, B., Mitra, S.: Multisensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Gr. Models Image Process. 57(3), 235–245 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1006/gmip.1995.1022
Ma, K., Wang, Z.: Multi-exposure image fusion: a patch-wise approach, pp. 1717–1721 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2015.7351094
Li, S., Yang, B., Hu, J.: Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion. Inf. Fus. 12(2), 74–84 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2010.03.002
Pajares, G., Manuel Cruz, J.: A wavelet-based image fusion tutorial. Pattern Recognit. 37(9), 1855–1872 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2004.03.010
Li, S., Kang, X., Hu, J.: Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(7), 2864–2875 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2013.2244222
Mo, Y., Kang, X., Duan, P., Sun, B., Li, S.: Attribute filter based infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fus. 75, 41–54 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.04.005
Shen, J., Zhao, Y., Yan, S., Li, X.: Exposure fusion using boosting Laplacian pyramid. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(9), 1579–1590 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2013.2290435
Wang, J., Liu, H., He, N.: Exposure fusion based on sparse representation using approximate k-svd. Neurocomputing 135, 145–154 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.12.042
Kuang, J., Johnson, G.M., Fairchild, M.D.: iCAM06: A refined image appearance model for HDR image rendering. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 18(5), 406–414 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2007.06.003
Harsanyi, J., Chang, C.-I.: Hyperspectral image classification and dimensionality reduction: an orthogonal subspace projection approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 32(4), 779–785 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/36.298007
Zhang, H., Xu, H., Tian, X., Jiang, J., Ma, J.: Image fusion meets deep learning: a survey and perspective. Inf. Fus. 76, 323–336 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.06.008
Li, C., et al.: Low-light image and video enhancement using deep learning: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(12), 9396–9416 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3126387
Liu, J., Fan, X., Jiang, J., Liu, R., Luo, Z.: Learning a deep multi-scale feature ensemble and an edge-attention guidance for image fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(1), 105–119 (2021)
Zhang, W., et al.: Underwater image enhancement via minimal color loss and locally adaptive contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 3997–4010 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3177129
Liu, R., Jiang, Z., Yang, S., Fan, X.: Twin adversarial contrastive learning for underwater image enhancement and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 4922–4936 (2022)
Cai, J., Gu, S., Zhang, L.: Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(4), 2049–2062 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2794218
Hou, X., Zhang, J., Zhou, P.: Reconstructing a high dynamic range image with a deeply unsupervised fusion model. IEEE Photonics J. 13(2), 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2021.3058740
Ma, K., Duanmu, Z., Zhu, H., Fang, Y., Wang, Z.: Deep guided learning for fast multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 2808–2819 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2952716
Ma, K., Zeng, K., Wang, Z.: Perceptual quality assessment for multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(11), 3345–3356 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2442920
Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., Blum, R.S., Han, J., Tao, D.: Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: a review. Inf. Fus. 40, 57–75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.05.006
Debevec, P.E., Malik, J.: Recovering high dynamic range radiance maps from photographs, pp. 369-378 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1145/258734.258884
Shan, Q., Jia, J., Brown, M.S.: Globally optimized linear windowed tone mapping. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Gr. 16(4), 663–675 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2009.92
Ma, J., Yu, W., Liang, P., Li, C., Jiang, J.: Fusiongan: a generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fus. 48, 11–26 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.004
Liu, J., Wu, G., Luan, J., Jiang, Z., Liu, R., Fan, X.: HoLoCo: Holistic and local contrastive learning network for multi-exposure image fusion. Inf. Fus. 95, 237–249 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.02.027
Liu, J., Shang, J., Liu, R., Fan, X.: Attention-guided global-local adversarial learning for detail-preserving multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(8), 5026–5040 (2022)
Jiang, Z., Zhang, Z., Fan, X., Liu, R.: Towards all weather and unobstructed multi-spectral image stitching: algorithm and benchmark, pp. 3783–3791 (2022)
Prabhakar, K., Srikar, V., Babu, R.: Deepfuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs, pp. 4724–4732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.505https://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.505
Liu, Z., Yang, J., Yadid-Pecht, O.: Lightfuse: Lightweight CNN based dual-exposure fusion. CoRR abs/2107.02299 (2021). arXiv:2107.02299
Li, H., Wu, X.-J.: Densefuse: a fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(5), 2614–2623 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2887342
Xu, H., Ma, J., Zhang, X.-P.: MEF-GAN: multi-exposure image fusion via generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 7203–7216 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.2999855
Wu, K., Chen, J., Yu, Y., Ma, J.: ACE-MEF: adaptive clarity evaluation-guided network with illumination correction for multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3233299
Qu, L., Liu, S., Wang, M., Song, Z.: Transmef: A transformer-based multi-exposure image fusion framework using self-supervised multi-task learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 36(2), 2126–2134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20109
Qu, L., Liu, S., Wang, M., Song, Z.: Rethinking multi-exposure image fusion with extreme and diverse exposure levels: a robust framework based on fourier transform and contrastive learning. Inf. Fus. 92, 389–403 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2022.12.002
Ma, J., et al.: Swinfusion: cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 9(7), 1200–1217 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2022.105686
Chaudhari, S., Mithal, V., Polatkan, G., Ramanath, R.: An attentive survey of attention models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3465055
Wang, F., Tax, D. M.J.: Survey on the attention based RNN model and its applications in computer vision. CoRR abs/1601.06823 (2016). arXiv:1601.06823
Chorowski, J. K., Bahdanau, D., Serdyuk, D., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Attention-based models for speech recognition 28 (2015). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2015/file/1068c6e4c8051cfd4e9ea8072e3189e2-Paper.pdf
Wang, F. et al.: Residual attention network for image classification (2017)
Galassi, A., Lippi, M., Torroni, P.: Attention in natural language processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(10), 4291–4308 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3019893
Li, H., Wu, X.-J., Durrani, T.: NestFuse: an infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69(12), 9645–9656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2020.3005230
Ram Prabhakar, K., Sai Srikar, V., Venkatesh Babu, R.: DeepFuse: a deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs (2017)
Xu, H., Ma, J., Jiang, J., Guo, X., Ling, H.: U2Fusion: a unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(1), 502–518 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548
Zhang, Y., et al.: IFCNN: a general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fus. 54, 99–118 (2020)
Liu, J., Shang, J., Liu, R., Fan, X.: Halder: Hierarchical attention-guided learning with detail-refinement for multi-exposure image fusion, pp. 1–6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME51207.2021.9428192
Deng, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, M., Gu, S., Duan, Y.: Deep coupled feedback network for joint exposure fusion and image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 3098–3112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3058764
Horé, A., Ziou, D.: Image quality metrics: Psnr vs. ssim, pp. 2366–2369 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2010.579
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61906029.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Zheng, J., Shang, X. et al. Coarse-to-fine multi-scale attention-guided network for multi-exposure image fusion. Vis Comput 40, 1697–1710 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02880-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02880-4