Abstract
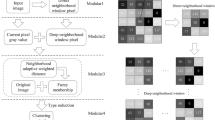
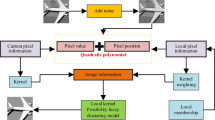
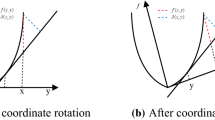
Interval type-2 fuzzy sets not only have stronger ability to deal with uncertainty, but also have low computational complexity than general type-2 fuzzy set, so they are widely used in fuzzy clustering methods. However, most existing interval type-2 fuzzy clustering methods are still sensitive to noise and lack a certain degree of robustness in segmenting images with noise. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel interval type-2 enhanced kernel possibilistic fuzzy local and non-local information c-means clustering method for segmenting images with high noise. Interval type-2 possibilistic fuzzy clustering with Lambert-W function is first extended to obtain a novel interval type-2 enhanced possibilistic fuzzy clustering with product partition. Then deep local neighborhood information including local and non-local information is used to constrain interval type-2 enhanced possibilistic fuzzy product partition c-means clustering, and a robust interval type-2 enhanced possibilistic fuzzy deep local information clustering with kernel metric is proposed. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the latest fuzzy clustering-related algorithms in the presence of high noise.





































Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Cai, Y., Zhang, Z., Cai, Z., Liu, X., Jiang, X., Yan, Q.: Graph convolutional subspace clustering: A robust subspace clustering framework for hyperspectral image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing. 59(5), 4191–4202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.3018135
Fan, T., Li, P., Qi, Z., Zhao, Z.: Borehole transient electromagnetic stereo imaging method based on horizontal component anomaly feature clustering. J. Appl. Geophys. 197, 104537 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2022.104537
Bezdek, J.C., Ehrlich, R., Full, W.: FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 10(2), 191–203 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-3004(84)90020-7
Dang, T.H., Mai, D.S., Ngo, L.T.: Multiple kernel collaborative fuzzy clustering algorithm with weighted super-pixels for satellite image land-cover classification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 85, 85–98 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2019.05.004
Cheng, H., Qian, Y., Wu, Y., Guo, Q., Li, Y.: Diversity-induced fuzzy clustering. Int. J. Approx. Reasoning. 106, 89–106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2018.12.010
Mittal, H., Saraswat, M.: A new fuzzy cluster validity index for hyperellipsoid or hyperspherical shape close clusters with distant centroids. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 29(11), 3249–3258 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3016339
Shirkhorshidi, A.S., Wah, T.Y., Shirkhorshidi, S.M.R., Aghabozorgi, S.: Evolving fuzzy clustering approach: an epoch clustering that enables heuristic postpruning. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 29(3), 560–568 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2956900
Daranyi, A., Dorgo, G., Ruppert, T., Abonyi, J.: Processing indoor positioning data by goal-oriented supervised fuzzy clustering for tool management. J. Manuf. Syst. 63, 15–22 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.02.010
Krishnapuram, R., Keller, J.M.: A possibilistic approach to clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1, 98–110 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/91.227387
Pal, N.R., Pal, K., Keller, J.M., Bezdek, J.C.: A possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 13(4), 517–530 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2004.840099
Szilágyi, L.: Fuzzy-possibilistic product partition: A novel robust approach to c-means clustering. Model. Decis. Artif. Intell.. 6820, 150–161 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22589-5_15
Cai, W., Chen, S., Zhang, D.: Fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms incorporating local information for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 40(3), 825–838 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2006.07.011
Zhou, Y., Zou, X., Lan, G., Dai, X., Wen, Y.: A local spatial information and lp-norm based fuzzy c-means clustering for image segmentation. In: 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Automation, Electronics and Electrical Engineering (AUTEEE), 2020, pp, 299–303. https://doi.org/10.1109/AUTEEE50969.2020.9315614
Krinidis, S., Chatzis, V.: A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(5), 1328–1337 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2040763
Gong, M., Zhou, Z., Ma, J.: Change detection in synthetic aperture radar images based on image fusion and fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(4), 2141–2151 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2011.2170702
Wu, C., Zhang, X.: A novel kernelized total Bregman divergence-based fuzzy clustering with local information for image segmentation. Int. J. Approx. Reasoning. 136, 281–305 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2021.06.004
Zare, A., Young, N., Suen, D., Nabelek, T., Galusha, A., Keller, J.: Possibilistic fuzzy local information c-means for sonar image segmentation. In: IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, 2017, pp, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI.2017.8285358
Gong, M., Liang, Y., Shi, J., Ma, W., Ma, J.: Fuzzy c-means clustering with local information and kernel metric for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(2), 53–584 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2219547
Memon, K.H., Memon, S., Qureshi, M.A., Alvi, M.B., Kumar, D., Shah, R.A.: Kernel possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering with local information for image segmentation. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(1), 321–332 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0537-9
Zhang, X., Sun, Y., Liu, H., Hou, Z., Zhao, F., Zhang, C.: Improved clustering algorithms for image segmentation based on non-local information and back projection. Inf. Sci. 550(6), 129–144 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.10.039
Ruiz-García, G., Hagras, H., Pomares, H., Ruiz, I.R.: Toward a fuzzy logic system based on general forms of interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 27(12), 2381–2395 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2898582
Shen, Y., Pedrycz, W., Wang, X.: Approximation of fuzzy sets by interval type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy sets. IEEE T. Cybern. 50(11), 4722–4734 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2886725
Hwang, C., Rhee, C.H.: Uncertain fuzzy clustering: interval type-2 fuzzy approach to c-means. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst 15, 107–120 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2006.889763
Ji, Z., Xia, Y., Sun, Q., Cao, G.: Interval-valued possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 253, 138–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2013.12.011
Sotudian, S., Zaradi, M.H.F.: Interval type-2 enhanced possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering for gene expression data analysis. https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2101/2101.00304.pdf.
Zhang, A., Jiang, G., Zhang, Y.: Remote sensing image change detection based on an adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy clustering. J. Geomatics Sci. Technol. 35(4), 376–382 (2018)
Hu, F., Chen, H., Wang, X.: An intuitionistic kernel-based fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm with local information for power equipment image segmentation. IEEE Access. 8, 4500–4514 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963444
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Inf. Sci. 8(3), 199–249 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-0255(75)90036-5
Mendel, J.M.: Computing derivatives in interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 12(1), 84–98 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2003.822681
Karnik, N.N., Mendel, J.M.: Centroid of a type-2 fuzzy set. Inf. Sci. 132(1), 195–220 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-0255(01)00069-X
Lv, G., Chi, Q., Awrangjeb, M., Li, J.: Robust registration of multispectral satellite images based on structural and geometrical similarity. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2021.3093502
Tang, Y.M., Ren, F.J., Pedrycz, W.: Fuzzy C-means clustering through SSIM and patch for image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 87, 105928 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105928
Maji, P., Garai, P.: Rough hypercuboid based generalized and robust IT2 fuzzy c-means algorithm. IEEE T. Cybern. 51(7), 3641–3652 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2925130
Wu, C., Guo, X.: A novel interval-valued data driven type-2 possibilistic local information c-means clustering for land cover classification. Int. J. Approx. Reasoning. 148, 80–116 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2022.05.007
Alruwaili, M., Siddiqi, M.H., Javed, M.A.: A robust clustering algorithm using spatial fuzzy c-means for brain MR images. Egypt. Inform. J. 21(1), 51–66 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2019.10.005
Zhang, J., Qi, J., Zheng, Z., Sun, L.: A robust image segmentation framework based on total variation spectral transform. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 153, 159–167 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2021.12.001
Shen, L., Zhu, W., Wang, X., Xing, L., Pauly, J.M.: Multi-Domain image completion for random missing input data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 40(4), 1113–1122 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3046444
Yuan, Y., Lo, Y.C.: Improving dermoscopic image segmentation with enhanced convolutional-deconvolutional networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 23(2), 519–526 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2017.2787487
Li, H., Li, Y., Zhang, G., Liu, R., Huang, H., Zhu, Q., Tao, C.: Global and local contrastive self-supervised learning for semantic segmentation of HR remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing. 60, 5618014 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3147513
https://www2.eecs.berkeley.edu/Research/Projects/CS/vision/bsds/
Wang, Q., Wang, X., Fang, C., Jiao, J.: Fuzzy image clustering incorporating local and region-level information with median memberships, Appl. Soft. Comput. 105 (2021) 107245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107245
Wang, Q., Wang, X., Fang, C., Yang, W.: Robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm with adaptive spatial and intensity constraint and membership linking for noise image segmentation. Appl. Soft. Comput. 92, 106318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106318
Lei, T., Jia, X., Zhang, Y.: Significantly fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm based on morphological reconstruction and membership filtering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(5), 3027–3041 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2796074
Tang, Y., Ren, F., Pedrycz, W.: Fuzzy c-means clustering through SSIM and patch for image segmentation. Appl. Soft. Comput. 87, 105928 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105928
Nawaz, M., Yan, H.: Saliency detection via multiple-morphological and superpixel based fast fuzzy c-mean clustering network. Expert Syst. Appl. 161 (15), 113654 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113654
Chui, K.T., Lytras, M.D., Vasant, P.: Combined generative adversarial network and fuzzy C-means clustering for multi-class voice disorder detection with an imbalanced dataset. Appl. Sci. 10(13), 4571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134571
Nguyen, R., Singh, S.K., Rai, R.: FuzzyGAN: Fuzzy generative adversarial networks for regression tasks. Neurocomputing 525, 88–110 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.015
Tan, J., Liao, X., Liu, J., Cao, Y., Jiang, H.: Channel attention image steganography with generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 9(2), 888–903 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSE.2021.3139671
Li, Y., You, J., Zhou, J., Wang, W., Liao, X., Li, X.: Image operation chain detection with machine translation framework. IEEE Trans. Multimedia. (2022) (online), https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3215000
Liao, X., Huang, Z., Peng, L., Qiao, T.: First step towards parameters estimation of image operator chain. Inf. Sci. 575, 231–247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.06.045
Barni, B., Costanzo, A.: A fuzzy approach to deal with uncertainty in image forensics. Image Commun. 27(9), 998–1010 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2012.07.006
Sushir, R.D., Wakde, D.G.: An improved detection of blind image forgery using hybrid deep belief network and adaptive fuzzy clustering. Multimed. Tools Appl. 81, 29177–29205 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12923-y
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62071378), and the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation of China (2022JM-370). The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions to improve the overall quality of the paper. Besides, the authors would like to thank the School of Electronic Engineering, Xi’an University of Posts & Telecommunications, Xi’an, China for financially support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization. SP: Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. XZ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing-review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Peng, S. & Zhang, X. Robust interval type-2 kernel-based possibilistic fuzzy deep local information clustering driven by Lambert-W function. Vis Comput 40, 2161–2201 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02910-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02910-1