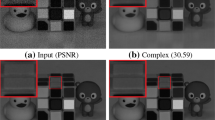
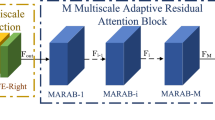
Abstract
Due to the instability of the hyperspectral imaging system and the atmospheric interference, hyperspectral images (HSIs) often suffer from losing the image information of areas with different shapes, which significantly degrades the data quality and further limits the effectiveness of methods for subsequent tasks. Although mainstream deep learning-based methods have achieved promising inpainting performance, the complicated ground object distributions increase the difficulty of HSIs inpainting in practice. In addition, spectral redundancy and complex texture details are two main challenges for deep neural network-based inpainting methods. To address the above issues, we propose a Global-Local Constraints-based Spectral Adaptive Network (GLCSA-Net) for HSI inpainting. To reduce the redundancy of spectral information, a multi-frequency channel attention module is designed to strengthen the essential channels and suppress the less significant ones, which calculates adaptive weight coefficients by converting feature maps to the frequency domain. Furthermore, we propose to constrain the generation of missing areas from both global and local perspectives, by fully leveraging the HSI texture information, so that the overall structure information and regional texture consistency of the original HSI can be maintained. The proposed method has been extensively evaluated on the Indian Pines and FCH datasets. The promising results indicate that GLCSA-Net outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in quantitative and qualitative assessments.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Indian Pines dataset is available online at http://www.ehu.eus/ccwintco/index.phptitle=Hyperspectral_Remote_Sensing_Scenes. If you want to use the FCH dataset, please contact the first author or corresponding author.
References
Zhang, X., Wang, T., Yang, Y.: Hyperspectral image classification based on multi-scale residual network with attention mechanism. Geosci. J. 13, 335 (2020)
Plaza, A., Benediktsson, J.A., Boardman, J.W., Brazile, J., Bruzzone, L., Camps-Valls, G., Chanussot, J., Fauvel, M., Gamba, P., Gualtieri, A., Marconcini, M., Tilton, J.C., Trianni, G.: Recent advances in techniques for hyperspectral image processing. Remote Sens. Environ. 113, 110–122 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.07.028
Eismann, M.T., Meola, J., Hardie, R.C.: Hyperspectral change detection in the presenceof diurnal and seasonal variations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 46(1), 237–249 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2007.907973
Goetz, A.F.H.: Three decades of hyperspectral remote sensing of the earth: a personal view. Remote Sens. Environ. 113, 5–16 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.12.014
Dua, Y., Singh, R.S., Kumar, V.: Compression of multi-temporal hyperspectral images based on rls filter. Vis. Comput. 38(1), 65–75 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-02000-6
Ma, A., Filippi, A.M., Wang, Z., Yin, Z.: Hyperspectral image classification using similarity measurements-based deep recurrent neural networks. Remote Sens. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020194
Sun, L., Zhang, J., Li, J., Wang, Y., Zeng, D.: SDFC dataset: a large-scale benchmark dataset for hyperspectral image classification. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 173 (2022)
Li, J., Liao, Y., Zhang, J., Zeng, D., Qian, X.: Semi-supervised degan for optical high-resolution remote sensing image scene classification. Remote Sens. (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174418
Li, J., Zeng, D., Zhang, J., Han, J., Mei, T.: Column-spatial correction network for remote sensing image destriping. Remote Sens. (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143376
Li, J., Zhang, J., Chen, F., Zhao, K., Zeng, D.: Adaptive material matching for hyperspectral imagery destriping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–20 (2022)
Cheng, X., Xu, Y., Zhang, J., Zeng, D.: Hyperspectral anomaly detection via low-rank decomposition and morphological filtering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2021.3126902
Hu, H., Shen, D., Yan, S., He, F., Dong, J.: Ensemble graph laplacian-based anomaly detector for hyperspectral imagery. Vis. Comput. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02775-4
Melgani, F.: Contextual reconstruction of cloud-contaminated multitemporal multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 44(2), 442–455 (2006)
Salberg, A.B.: Land cover classification of cloud-contaminated multitemporal high-resolution images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 49(1), 377–387 (2010)
Zhuang, L., Bioucas-Dias, J.M.: Fast hyperspectral image denoising and inpainting based on low-rank and sparse representations. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 11(99), 730–742 (2018)
Dan, Y., Zhuang, L., Gao, L., Bing, Z., Bioucas-Dias, J.M.: Hyperspectral image inpainting based on low-rank representation: A case study on tiangong-1 data. In: IGARSS 2017 - 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (2017)
Yang, Y., Cheng, Z., Yu, H., Zhang, Y., Cheng, X., Zhang, Z., Xie, G.: Mse-net: generative image inpainting with multi-scale encoder. Vis. Comput. 38(8), 2647–2659 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02143-0
Sidorov, O., Hardeberg, J.Y.: Deep hyperspectral prior: Denoising, inpainting, super-resolution. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW) (2019)
Faghih Niresi, K., Chi, C.-Y.: Robust hyperspectral inpainting via low-rank regularized untrained convolutional neural network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 20, 1–5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2023.3241161
Wong, R., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Chen, F., Zeng, D.: Hsi-ipnet: hyperspectral imagery inpainting by deep learning with adaptive spectral extraction. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 13, 4369–4380 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3012443
Bertalmio, M., Sapiro, G., Caselles, V., Ballester, C.: Image inpainting. Siggraph (2000)
Ballester, C., Bertalmio, M., Caselles, V., Sapiro, G., Verdera, J.: Filling-in by joint interpolation of vector fields and gray levels. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10, 1200 (2001)
Barnes, C., Shechtman, E., Finkelstein, A., Dan, B.G.: Patchmatch: a randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing. ACM Trans. Graph 28, 24 (2009)
Xu, Z., Sun, J.: Image inpainting by patch propagation using patch sparsity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(5), 1153–1165 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2042098
Pathak, D., Krahenbuhl, P., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Efros, A.A.: Context Encoders: Feature Learning by Inpainting. IEEE (2016)
Iizuka, S., Simo-Serra, E., Ishikawa, H.: Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Trans. Gr. 36, 107–110714 (2017)
Yu, J., Lin, Z., Yang, J., Shen, X., Lu, X., Huang, T.S.: Generative Image Inpainting with Contextual Attention. IEEE (2018)
Liu, H., Jiang, B., Xiao, Y., Yang, C.: Coherent semantic attention for image inpainting. IEEE (2019)
Yu, J., Lin, Z., Yang, J., Shen, X., Huang, T.: Free-form image inpainting with gated convolution. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
Zeng, Y., Fu, J., Chao, H., Guo, B.: Aggregated contextual transformations for high-resolution image inpainting (2021)
Cai, N., Su, Z., Lin, Z., Wang, H., Yang, Z., Ling, B.W.: Blind inpainting using the fully convolutional neural network. Vis. Comput. 33(2), 249–261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-015-1190-z
Zhu, X., Lu, J., Ren, H., Wang, H., Sun, B.: A transformer-cnn for deep image inpainting forensics (2022)
Liang, M., Zhang, Q., Wang, G., Xu, N., Wang, L., Liu, H., Zhang, C.: Multi-scale self-attention generative adversarial network for pathology image restoration. The Visual Computer, 1–17 (2022)
Shen, H., Li, X., Zhang, L., Tao, D., Zeng, C.: Compressed sensing-based inpainting of aqua moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer band 6 using adaptive spectrum-weighted sparse bayesian dictionary learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52(2), 894–906 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2013.2245509
Rakwatin, P., Takeuchi, W., Yasuoka, Y.: Restoration of aqua modis band 6 using histogram matching and local least squares fitting. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 47(2), 613–627 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2008.2003436
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. Enhua (2019)
Zhao, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Shi, J., Loy, C.C., Lin, D., Jia, J.: Psanet: Point-wise spatial attention network for scene parsing. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (2018)
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Selective kernel networks, pp. 510–519 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00060
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision - ECCV 2018, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018)
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Zhu, P., Li, P., Zuo, W., Hu, Q.: Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks (2019)
Qin, Z., Zhang, P., Wu, F., Li, X.: FcaNet: Frequency Channel Attention Networks (2020)
Fang, B., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Chan, J.C.-W.: Hyperspectral images classification based on dense convolutional networks with spectral-wise attention mechanism. Remote Sens. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020159
Qing, Y., Liu, W.: Hyperspectral image classification based on multi-scale residual network with attention mechanism. Remote Sens. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030335
Huang, L.: Hybrid dense network with dual attention for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. 13, 4921 (2021)
Zhao, Y., Zhai, D., Jiang, J., Liu, X.: Adrn: Attention-based deep residual network for hyperspectral image denoising. In: ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2668–2672 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054658
Wang, Z., Shao, Z., Huang, X., Wang, J., Lu, T.: Sscan: a spatial-spectral cross attention network for hyperspectral image denoising. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2021.3112038
Shi, Z., Chen, C., Xiong, Z., Liu, D., Zha, Z.-J., Wu, F.: Deep residual attention network for spectral image super-resolution. In: Leal-Taixé, L., Roth, S. (eds.) Computer Vision - ECCV 2018 Workshops, pp. 214–229. Springer, Cham (2019)
Phaphuangwittayakul, A., Ying, F., Guo, Y., Zhou, L., Chakpitak, N.: Few-shot image generation based on contrastive meta-learning generative adversarial network. Vis. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02566-3
Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. IEEE (2017)
Esedoglu, S.: Digital inpainting based on the mumford-shah-euler image model. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 13(4), 353–370 (2003)
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (No.62202283).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HC and JL designed the experiments. YF participated in the experiments. DZ, JZ and CY guided the research. All authors wrote the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Li, J., Zhang, J. et al. GLCSA-Net: global–local constraints-based spectral adaptive network for hyperspectral image inpainting. Vis Comput 40, 3331–3346 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03036-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03036-0