Abstract
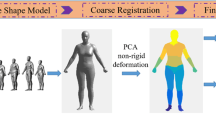
Nowadays, 3D human models are widely used in the garment industry where it is important to reconstruct compliant human model from scan of the body under partial dress for privacy reasons. A new 3D human construction method based on the combination of parametric and nonparametric reconstruction is proposed here. Inputs to the method include the raw scan and partial anthropometric parameters. The scan is divided into exposed area and clothing occluded area for modeling separately. The information of the clothing occluded area is restored by semantic parametric human modeling and pose fitting. The information of the exposed area is restored by the method of non-rigid registration. Then, the two types of information are fused to reconstruct the final human model. The experiment divided the human scan into three common situations: naked, partially clothed and highly clothed body scanning. The results of the qualitative and quantitative analyses show that the method is able to fit the parametric human model to the exposed area scan while matching the user input on the anthropometric parameters in the clothing occluded area. It is worth pointing out that the connection between the two areas is smooth. The performance is also better than previous related methods. The proposed method reduces the dressing requirements for reconstructing the human body from 3D scan and also demonstrates the validity, accuracy and versatility of the method for reconstructing human model.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Chen, D., et al.: 3D human body reconstruction based on SMPL model. The Vis. Comput. 39(5), 1893–1906 (2022)
Hasler, N., et al.: Estimating body shape of dressed humans. Comput. Graph. 33(3), 211–216 (2009)
Song, D., et al.: A Semantic Parametric Model for 3D Human Body Reshaping. Springer, Cham (2018)
Zeng, Y., Fu, J. and Chao, H.: 3D Human body reshaping with anthropometric modeling. In: International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, pp. 96–107. Springer Singapore, Singapore (2017)
Hu, P., et al.: Personalized 3D mannequin reconstruction based on 3D scanning. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 30(2), 159–174 (2018)
Haoyang, et al.: Structure-consistent customized virtual mannequin reconstruction from 3D scans based on optimization. Text. Res. J. 90(7–8), 937–950 (2019)
Li, X., et al.: Design of a multi-sensor information acquisition system for mannequin reconstruction and human body size measurement under clothes. Text. Res. J. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/00405175221093663
Anguelov, D., et al.: SCAPE: shape completion and animation of people. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(3), 408–416 (2005)
Loper, M., et al.: SMPL: a skinned multi-person linear model. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 34(6), 1–16 (2015)
Romero, J., Tzionas, D. and Black, M. J.: Embodied hands: modeling and capturing hands and bodies together. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.02610, 2022
Pavlakos, G. et al.: Expressive body capture: 3d hands, face, and body from a single image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2019.
Osman, A. A., Bolkart, T. and Black, M. J.: Star: sparse trained articulated human body regressor. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. 2020. Springer
Wang, Y., et al.: PanoMan: sparse localized components–based model for full human motions. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 40(2), 1–17 (2021)
Alldieck, T., Xu, H. and Sminchisescu, C.: Imghum: implicit generative models of 3d human shape and articulated pose. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021
Joo, H., Simon, T. and Sheikh, Y.: Total capture: a 3d deformation model for tracking faces, hands, and bodies. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018
Yang, Y. et al.: Semantic parametric reshaping of human body models. In: 2014 2nd International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 2014
Li, X., et al.: Remodeling of mannequins based on automatic binding of mesh to anthropometric parameters. The Vis. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02738-1
Chen, G., et al.: Reconstructing 3D human models with a Kinect. Comput. Anim. Virt. Worlds 27(1), 72–85 (2016)
Bogo, F. et al.: Keep it SMPL: automatic estimation of 3D human pose and shape from a single image. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Oct 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part V 14. 2016. Springer
Muller, L. et al.: On self-contact and human pose. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021
Omran, M. et al.: Neural body fitting: unifying deep learning and model-based human pose and shape estimation. In: International Conference on 3d Vision, 2018
Choutas, V. et al.: Monocular expressive body regression through body-driven attention. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020. Springer
Yu, T. et al.: DoubleFusion: real-time capture of human performances with inner body shapes from a single depth sensor. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018
Kolotouros, N. et al.: Learning to reconstruct 3D human pose and shape via model-fitting in the loop. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2019
Izadi, S. et al.: KinectFusion: real-time dynamic 3D surface reconstruction and interaction. In: Acm Siggraph. 2011
Wang, R., et al.: Capturing dynamic textured surfaces of moving targets. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. 2016. Springer
Tong, J., et al.: Scanning 3D full human bodies using kinects. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18(4), 643–650 (2012)
Yan, S., Wirta, J., and Kämäräinen, J. K.: Anthropometric clothing measurements from 3D body scans. Mach. Vis. Appl. 31(1–2), 7 (2020)
Blackwell, S. et al.: Civilian American and European surface anthropometry resource (CAESAR). Volume 2: Descriptions. 2002, SYTRONICS INC DAYTON OH
Saito S. et al.: Pifu: pixel-aligned implicit function for high-resolution clothed human digitization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2019
Xiu, Y. et al.: ICON: implicit clothed humans obtained from normals. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2022. IEEE
Chibane, J., Alldieck, T. and Pons-Moll, G.: Implicit functions in feature space for 3d shape reconstruction and completion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020.
Bhatnagar, B.L. et al.: Combining implicit function learning and parametric models for 3d human reconstruction. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, Aug 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 16. 2020. Springer
Bogo, F. et al.: FAUST: Dataset and evaluation for 3D mesh registration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2014
Sumner, R.W., Popović, J.: Deformation transfer for triangle meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 23(3), 399–405 (2004)
Alldieck, T. et al.: Learning to reconstruct people in clothing from a single RGB camera. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019
Lazova, V., Insafutdinov, E. and Pons-Moll, G.: 360-degree textures of people in clothing from a single image. In: 2019 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 2019. IEEE
Cao, Z. et al.: Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017
Yao, Y. et al.: Quasi-Newton solver for robust non-rigid registration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020
Sorkine, O. and Alexa, M.: As-rigid-as-possible surface modeling. In: Symposium on Geometry processing, 2007
Yang, L. et al.: Renovating parsing R-CNN for accurate multiple human parsing. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, Aug 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, PartXII. Springer (2020)
Zheng, Z., et al.: Pamir: parametric model-conditioned implicit representation for imagebased human reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 3170–3184 (2021)
Zhang, C., et al.: Detailed, accurate, human shape estimation from clothed 3D scan sequences. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Li, G., Li, T. et al. Human body construction based on combination of parametric and nonparametric reconstruction methods. Vis Comput 40, 5557–5573 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03122-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03122-3