Abstract
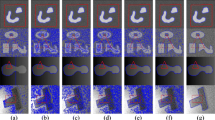
Highly accurate active contour models are widely used in various image segmentation methods. In this paper, we propose an image segmentation model based on Hellinger distance for local region intensity fitting (HD-LRIF). The method defines two different metrics based on the Hellinger distance and constructs a new data fitting term to segment the image efficiently by minimizing the energy function. In addition, our method is independent of the initial contour and the segmentation results consistently obtain high accuracy. The experimental results show that the HD-LRIF model is far superior to state-of-the-art segmentation methods in terms of accuracy and efficiency. Specifically, it can effectively filter the noise interference, thus enhancing robustness and improving the accuracy of image segmentation in general.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models[J]. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1(4), 321–331 (1988)
Li, C.M., Xu, C.Y., Gui, C.F.: Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation[J]. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(12), 3243–3254 (2010)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours[J]. Int. J. Comput. Vision 22, 61–79 (1997)
Li, C., Liu, J., Fox, M.D.: Segmentation of external force field for automatic initialization and splitting of snakes[J]. Pattern Recogn. 38(11), 1947–1960 (2005)
Li, C., Kao, C. Y., Gore, J. C., et al.: Implicit active contours driven by local binary fitting energy[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (2007)
Pan, H.Z., Liu, W.Q., Zhou, G.L.: A novel level set approach for image segmentation with landmark constraints[J]. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 182, 257–268 (2019)
Zhang, K.H., Song, H., Zhang, L.: Active contours driven by local image fitting energy[J]. Pattern Recogn. 43(4), 1199–1206 (2010)
Min, H., Lu, J.T., Jia, W., et al.: An effective local regional model based on salient fitting for image segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing 311, 245–259 (2018)
Wang, L., Chang, Y., Wang, H.: An active contour model based on local fitted images for image segmentation[J]. Inf. Sci. 418, 61–73 (2017)
Canny, J.: A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 6(8), 679–698 (1986)
Sobel, I.: Camera models and machine perception[J]. Dissertation Stanford University, (1970)
Liu, C., Liu, W., Xing, W.: A weighted edge-based level set method based on multi-local statistical information for noisy image segmentation[J]. J. Vis. Commun. Image Rep. 59, 89–107 (2019)
Zhi, X., Shen, H.B.: Saliency driven region-edge-based top down level set evolution reveals the asynchronous focus in image segmentation[J]. Pattern Recogn. J. Pattern Recogn. Soc. 80, 241–255 (2018)
Chan, T., Vese, L.: Active contour without edges[J]. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(2), 266–277 (2001)
Mumford, D., Shah, J.: Optimal approximations by piecewise smooth functions and associated variational problems[J]. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 42(5), 577–685 (1989)
Ma, C., He, T., Gao, J.: Skin scar segmentation based on saliency detection[J]. Vis. Comput. 1–13 (2022)
Chen, L. C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., et al.: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations, (2014)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., et al.: DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 4(40), 834–848 (2018)
Chen, L. C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., et al.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J]. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017, 851–859
Ouyang, S., Li, Y.: Combining deep semantic segmentation network and graph convolutional neural network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing Imagery[J]. Remote Sens. 1(13), 119–140 (2020)
Wang, D., Hu, G., Lyu, C.: FRNet: an end-to-end feature refinement neural network for medical image segmentation[J]. Vis. Comput. 5(37), 1101–1112 (2021)
Basu, A., Mandal, A., Pardo, L.: Hypothesis testing for two discrete populations based on the Hellinger distance[J]. Statist. Probab. Lett. 80, 206–214 (2010)
Merabet, Y. E., Ruichek, Y., Ghaffarian, S., et al.: Hellinger Kernel-based distance and local image region descriptors for sky region detection from fisheye images[C]. International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, 2017.
Bouhlel, N., Meric, S.: Multilook polarimetric SAR change detection using stochastic distances between Matrix-Variate G(d)(0) distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 1–21.
Wang, B., Tao, D., Dong, R., et al.: A contour co-tracking method for image pairs[J]. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 99, 5402–5412 (2021)
Arbelaez, P., Maire, M., Fowlkes, C., et al.: Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33, 898–916 (2011)
Liu, X.G., Liu, G.J., Wang, Y.Z., Li, G.S., Zhang, R., Peng, W.C.: A variational level set image segmentation method via fractional differentiation[J]. Fractal Fract. 6(9), 462 (2022)
Ma, D., Liao, Q., Chen, Z., et al.: Adaptive local-fitting-based active contour model for medical image segmentation[J]. Signal Process. Image Commun. 76, 201–213 (2019)
Zhang, K.H., Liu, Q.S., Song, H.: A variational approach to simultaneous image segmentation and bias correction[J]. Trans. Cybern. 45(8), 1426–1437 (2014)
Wang, L., He, L., Mishra, A.: Active contours driven by local Gaussian distribution fitting energy[J]. Signal Process. 89(12), 2435–2447 (2009)
Samad, W., Chunming, L., Mudassar, I., et al.: Level-set evolution for medical image segmentation with alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Signal Process. 211, 109105 (2023)
Weng, G.R., XiaoL, F., Ding, K.Y.: Active contours driven by region-scalable fitting and optimized Laplacian of Gaussian energy for image segmentation[J]. Signal Process. 134, 224–233 (2017)
Ding, K., Xiao, L., Weng, G.: Active contours driven by local pre-fitting energy for fast image segmentation[J]. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 104, 29–36 (2018)
Fang, J., Liu, H., Zhang, L., et al.: Fuzzy region-based active contours driven by weighting global and local fitting energy[J]. IEEE Access 99, 1–19 (2019)
Weng, G., Dong, B., Lei, Y.: A level set method based on additive bias correction for image segmentation[J]. Expert Syst. Appl. 185, 1–13 (2021)
Wan, M., Huang, Q., Xu, Y., Gu, G., et al.: Global and local multi-feature fusion-based active contour model for infrared image segmentation[J]. Displays 78, 102452 (2023)
Liu, X., Liu, G., Wang, Y., Li, G., Zhang, R., Peng, W.: A variational level set image segmentation method via fractional differentiation[J]. Fractal Fract. 6, 462 (2022)
Pritpal, S., Surya, S.B.: A quantum-clustering optimization method for COVID-19 CT scan image segmentation[J]. Expert Syst. Appl. 186, 1–21 (2021)
Shu, X., Yang, Y., Wu, B.: Adaptive segmentation model for liver CT images based on neural network and level set method[J]. Neurocomputing 4532021, 438–452 (2021)
Saman, S., Narayanan, S.J.: Active contour model driven by optimized energy functionals for MR brain tumor segmentation with intensity inhomogeneity correction[J]. Multim. Tools Appl. 80, 21925–21954 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62061040, 12162029), in part by the Scientific Research Fund of Ningxia University (Grant No. NYG2022018), and in part by the Key Research and Development Plan in Ningxia District under Grant 2019BEG03056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Guo, J., Wang, Y. et al. Local image segmentation model via Hellinger distance. Vis Comput 40, 7871–7885 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03213-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03213-1