Abstract
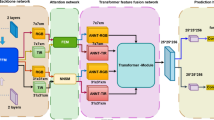
The existing model’s representation and fusion of features is inadequate in TIR scenarios. Our design of a new infrared tracking algorithm is based on this problem. Specifically, we use the transformer structure for feature extraction in our model, which captures global information and establishes long-distance dependencies between features. Additionally, convolutional projection is adopted to replace linear projection in the basic transformer module, which enriches local information and reduces computational complexity. For feature fusion, we associate the global spatiotemporal information between the template and search feature using the global information association module, which helps us get more accurate target positions. Finally, we utilize a new prediction head to further increase the stability of the prediction box and improve model performance. Our method achieved excellent performance on multiple infrared datasets.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study have been deposited in the https://github.com/QiaoLiuHit/LSOTB-TIR.
References
Wan, M., Gu, G., Qian, W., et al.: Unmmanned aerial vehicle video-based target tracking algorithm using sparse representation. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 9689–9706 (2019)
Shirmohammadi, S., Ferrero, A.: Camera as the instrument: the rising trend of vision based measurement. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag 17(3), 41–47 (2014)
Ojha, S., Sakhare, S.: Image processing techniques for object tracking in video surveillance-A survey. In: 2015 International Conference on Pervasive Computing (ICPC), pp. 1–6 (2015)
Khanafer, M., Shirmohammadi, S.: Applied AI in instrumentation and measurement: the deep learning revolution. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag 23(6), 10–17 (2020)
Gundogdu, E., Ozkan, H., Demir, H.S., et al: Comparison of infrared and visible imagery for object tracking: Toward trackers with superior IR performance. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 1–9 (2015)
Bolme, D.S., Beveridge, J.R., Draper, B.A., et al: Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2544–2550 (2010)
Li, Y., Li, P., Shen, Q.: Real-time infrared target tracking based on minimization and compressive features. Appl. Optics 53(28), 6518–6526 (2014)
Gao, J. S, Jhang, T. S: Infrared target tracking using multi-feature joint sparse representation. Proceedings of the International Conference on Research in Adaptive and Convergent Systems, 40–45 (2016)
Yu, X., Yu, Q., Shang, Y., et al.: Dense structural learning for infrared object tracking at 200+ frames per second. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 100, 152–159 (2017)
Hare, S., Golodetz, S., Saffari, A., et al.: Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(10), 2096–2109 (2016)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), vol. 1, pp. 886–8931 (2005)
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Henriques, J.F., et al: Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: Computer Vision – ECCV 2016 Workshops, pp. 850–865. Springer, Cham (2016)
Li, B., Yan, J., Wu, W., et al: High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8971–8980 (2018)
Li, B., Wu, W., Wang, Q., et al: SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4277–4286 (2019)
Guo, D., Wang, J., Cui, Y., et al: SiamCAR: Siamese fully convolutional classification and regression for visual tracking. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6268–6276 (2020)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, E.: G: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016)
Liu, Q., Li, X., He, Z., et al.: Multi-task driven feature models for thermal infrared tracking. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 34(07), 11604–11611 (2020)
Liu, Q., Li, X., He, Z., Fan, N., Yuan, D., Wang, H.: Learning deep multi-level similarity for thermal infrared object tracking. IEEE Trans. Multim. 23, 2114–2126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.3008028
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., et al: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst.30 (2017)
Liu, Q., He, Z., Li, X., et al.: PTB-TIR: a thermal infrared pedestrian tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans. Multim. 22(3), 666–675 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2932615
Liu, Q., Li, X., Yuan, D., Yang, C., Chang, X., He, Z.: LSOTB-TIR: A large-scale high-diversity thermal infrared single object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3236895
Fan, C., Zhang, R., Ming, Y.: MP-LN: motion state prediction and localization network for visual object tracking. Vis Comput 38, 4291–4306 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02296-y
Yang, S., Chen, H., Xu, F., et al.: High-performance UAVs visual tracking based on Siamese network. Vis. Comput. 38, 2107–2123 (2022)
Zhang, C.: Extremeformer: a new framework for accurate object tracking by designing an efficient head prediction module. Vis. Comput. (2023)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., et al: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In:Computer Vision-ECCV, 213–229 (2020)
Zhu, X., Su, W., Lu, L., et al: Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.04159 (2020)
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., et al: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., et al: Training data-efficient image transformers and distillation through attention. In: International conference on machine learning, 10347–10357 (2021)
Chen, C.-F.R., Fan, Q., Panda, R.: CrossViT: cross-attention multi-scale vision transformer for image classification. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 347–356 (2021)
Li, Y., Zhang, K., Cao, J., et al: Localvit: Bringing locality to vision transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.05707 (2021)
Zhou, D., Kang, B., Jin, X., et al: Deepvit: Towards deeper vision transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.11886 (2021)
Wang, N., Zhou, W., Wang, J., Li, H.: Transformer meets tracker: exploiting temporal context for robust visual tracking. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1571–1580 (2021)
Fu, Z., Liu, Q., Fu, Z., Wang, Y.: Stmtrack: Template-free visual tracking with space-time memory networks. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 13769–13778 (2021)
Gu, F., Lu, J., Cai, C., et al.: Repformer: a robust shared-encoder dual-pipeline transformer for visual tracking. Neural Comput. Appl. 35, 20581–20603 (2023)
Gu, F., Lu, J., Cai, C., et al.: Eantrack: An efficient attention network for visual tracking. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2023.3319676
Forsyth, A. D, Mundy, L. J, et al: Object recognition with gradient-based learning. Shape, contour and grouping in computer vision, 1251–1258 (2017)
Chollet, F.: Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1800–1807 (2017)
Wu, Y., Chen, Y., Yuan, L., Liu, Z., Wang, L., Li, H., Fu, Y.: Rethinking classification and localization for object detection. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10183–10192 (2020)
Rezatofighi, H., Tsoi, N., Gwak, J., et al: Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 658–666 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00075
Li, X., Ma, C., Wu, B., et al: Target-aware deep tracking. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1369–1378 (2019)
Danelljan, M., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M.: Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4310–4318 (2015)
Galoogahi, H.K., Fagg, A., Lucey, S.: Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1144–1152 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.129
Song, Y., Ma, C., Wu, X., et al: Vital: Visual tracking via adversarial learning. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8990–8999 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00937
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Golodetz, S., et al: Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1401–1409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.156
Danelljan, M., Khan, F., et al: Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In: British Machine Vision Conference (2014)
Liu, Q., Lu, X., He, Z., et al.: Deep convolutional neural networks for thermal infrared object tracking. Knowl. Based Syst. 134, 189–198 (2017)
Ma, Z., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Lu, W., Yin, J.: Rpt: Learning point set representation for Siamese visual tracking. In: Bartoli, A., Fusiello, A. (eds.) Computer Vis. ECCV 2020 Workshops, pp. 653–665. Springer, Cham (2020)
Valmadre, J., Bertinetto, L., Vedaldi, A., et al: End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5000–5008 (2017)
Wang, N., Zhou, W., Tian, Q., et al: Multi-cue correlation filters for robust visual tracking. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4844–4853 (2018)
Danelljan, M., Bhat, G., Khan, F.S., et al: Eco: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6931–6939 (2017)
Danelljan, M., Bhat, G., Khan, F.S., et al: Atom: Accurate tracking by overlap maximization. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4655–4664 (2019)
Wang, N., Song, Y., Ma, C., et al: Unsupervised deep tracking. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1308–1317 (2019)
Qi, Y., Zhang, S., Qin, L., et al: Hedged deep tracking. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4303–4311 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.466
Li, X., Liu, Q., Fan, N., et al.: Hierarchical spatial-aware Siamese network for thermal infrared object tracking. Knowl. Based Syst. 166, 71–81 (2019)
Song, Y., Ma, C., Gong, L., et al: Crest: Convolutional residual learning for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2555–2564 (2017)
Nam, H., Han, B.: Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4293–4302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.465
Fan, H., Lin, L., Yang, F., et al: Lasot: A high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5374–5383 (2019)
Huang, L., Zhao, X., Huang, K.: Got-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(5), 1562–1577 (2019)
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101 (2017)
Funding
This research was supported by the Special Project of Science and Technology Strategic Cooperation between Nanchong City and Southwest Petroleum University, Grant/Award Number: SXJBS002, SXHZ053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that we have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Z., Shen, H., Yu, P. et al. Infrared tracking for accurate localization by capturing global context information. Vis Comput 41, 331–343 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03328-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03328-z