Abstract
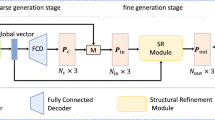
Diffusion models have been successfully applied to point cloud generation tasks recently. The main notion is using a forward process to progressively add noises into point clouds and then use a reverse process to generate point clouds by denoising these noises. However, since point cloud data is high-dimensional and exhibits complex structures, it is challenging to adequately capture the surface distribution of point clouds. Moreover, point cloud generation methods often resort to sampling methods and local operations to extract features, which inevitably ignores the global structures and overall shapes of point clouds. To address these limitations, we propose a latent diffusion model based on Transformers for point cloud generation. Instead of directly building a diffusion process based on the points, we first propose a latent compressor to convert original point clouds into a set of latent tokens before feeding them into diffusion models. Converting point clouds as latent tokens not only improves expressiveness, but also exhibits better flexibility since they can adapt to various downstream tasks. We carefully design the latent compressor based on an attention-based auto-encoder architecture to capture global structures in point clouds. Then, we propose to use transformers as the backbones of the latent diffusion module to maintain global structures. The powerful feature extraction ability of transformers guarantees the high quality and smoothness of generated point clouds. Experiments show that our method achieves superior performance in both unconditional generation on ShapeNet and multi-modal point cloud completion on ShapeNet-ViPC. Our code and samples are publicly available at https://github.com/Negai-98/LDT.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aiello, E., Valsesia, D., Magli, E.: Cross-modal learning for image-guided point cloud shape completion. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 37349–37362 (2022)
Cai, R., Yang, G., Averbuch-Elor. H., et al.: Learning gradient fields for shape generation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 364–381 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58580-8_22
Chai, S., Zhuang, L., Yan, F.: Layoutdm: transformer-based diffusion model for layout generation, pp. 18349–18358 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01760
Chang, A.X., Funkhouser, T., Guibas, L. et al.: Shapenet: an information-rich 3d model repository (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03012
Chang, H., Zhang, H., Jiang, L. et al.: Maskgit: masked generative image transformer, pp. 11305–11315 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01103
Chen, R., Han, S., Xu, J. et al.: Point-based multi-view stereo network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1538–1547 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00162
Chen, Z., Qiu, J., Sheng, B., et al.: Gpsd: generative parking spot detection using multi-clue recovery model. Vis. Comput. 37(9–11), 2657–2669 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00371-021-02199-Y
Chen, Z., Qiu, G., Li, P., et al.: Mngnas: distilling adaptive combination of multiple searched networks for one-shot neural architecture search. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(11), 13489–13508 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3293885
Cheng, A.C., Li, X., Liu, S., et al.: Autoregressive 3d shape generation via canonical mapping. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 89–104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20062-5_6
Cho, J., Zala, A., Bansal, M.: Dall-eval: probing the reasoning skills and social biases of text-to-image generation models. pp 3020–3031 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00283
Dhariwal, P., Nichol, A.: Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 8780–8794 (2021)
Dinh, L., Krueger, D., Bengio, Y.: Nice: Non-linear independent components estimation. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2015)
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021). https://openreview.net/forum?id=YicbFdNTTy
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
Groueix, T., Fisher, M., Kim, V.G., et al.: Atlasnet: a papier-mache approach to learning 3d surface generation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 216–224 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00030
Harvey, W., Naderiparizi, S., Masrani, V., et al.: Flexible diffusion modeling of long videos. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 27953–27965 (2022)
Ho, J., Jain, A., Abbeel, P.: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 6840–6851 (2020)
Ho, J., Saharia, C., Chan, W., et al.: Cascaded diffusion models for high fidelity image generation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 23, 2249–2281 (2022)
Huang, R., Lam, M.W., Wang, J. et al.: Fastdiff: a fast conditional diffusion model for high-quality speech synthesis. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 4157–4163 (2022). https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2022/577
Huang, R., Zhao, Z., Liu, H. et al.: Prodiff: Progressive fast diffusion model for high-quality text-to-speech. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 2595–2605, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3503161.3547855
Jiang, N., Sheng, B., Li, P., et al.: Photohelper: portrait photographing guidance via deep feature retrieval and fusion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, 2226–2238 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3144890
Kim, H., Lee, H., Kang, W.H., et al.: Softflow: probabilistic framework for normalizing flow on manifolds. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 16388–16397 (2020)
Kim, J., Yoo, J., Lee, J. et al.: Setvae: learning hierarchical composition for generative modeling of set-structured data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 15059–15068 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01481
Klokov, R., Boyer, E., Verbeek, J.: Discrete point flow networks for efficient point cloud generation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 694–710 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58592-1_41
Lai, X., Liu, J., Jiang, L. et al.: Stratified transformer for 3d point cloud segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8500–8509 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00831
Lee, J., Lee, Y., Kim, J. et al.: Set transformer: a framework for attention-based permutation-invariant neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 3744–3753 (2019)
Li, J., Chen, J., Sheng, B., et al.: Automatic detection and classification system of domestic waste via multimodel cascaded convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 18(1), 163–173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3085669
Lin, X., Sun, S., Huang, W., et al.: Eapt: efficient attention pyramid transformer for image processing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, 50–61 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3120873
Liu, Q., Zhao, J., Cheng, C., et al.: Pointalcr: adversarial latent GAN and contrastive regularization for point cloud completion. Vis. Comput. 38(9), 3341–3349 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00371-022-02550-X
Liu, Z., Tang, H., Lin, Y., et al.: Point-voxel cnn for efficient 3d deep learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32, 963–973 (2019)
Luo, S., Hu, W.: Diffusion probabilistic models for 3d point cloud generation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2837–2845 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00286
Lyu, Z., Kong, Z., Xu, X. et al.: A conditional point diffusion-refinement paradigm for 3d point cloud completion. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2022)
Ma, B., Liu, Y.S., Han, Z.: Reconstructing surfaces for sparse point clouds with on-surface priors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6315–6325 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00621
Peebles, W., Xie, S.: Scalable diffusion models with transformers, pp. 4172–4182 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00387
Peng, S., Jiang, C., Liao, Y., et al.: Shape as points: a differentiable poisson solver. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 13032–13044 (2021)
Qin, Z., Yin, M., Lin, Z., et al.: Three-view generation based on a single front view image for car. Vis. Comput. 37(8), 2195–2205 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00371-020-01979-2
Ramasinghe, S., Khan, S., Barnes, N., et al.: Spectral-gans for high-resolution 3d point-cloud generation. In: 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 8169–8176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS45743.2020.9341265
Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D. et al.: High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 10684–10695 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01042
Ruan, L., Ma, Y., Yang, H. et al.: Mm-diffusion: learning multi-modal diffusion models for joint audio and video generation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10219–10228 (2023)
Sheng, B., Andge Riaz Ali, P.L., Chen, C.L.P.: Improving video temporal consistency via broad learning system. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 52(7), 6662–6675 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3079311
Shu, D.W., Park, S.W., Kwon, U.: 3d point cloud generative adversarial network based on tree structured graph convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3859–3868 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00396
Tchapmi, L.P., Kosaraju, V., Rezatofighi, H. et al.: Topnet: structural point cloud decoder. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 383–392, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00047
Vahdat, A., Kreis, K., Kautz, J.: Score-based generative modeling in latent space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 11287–11302 (2021)
Wu, J., Zhang, C., Xue, T., et al.: Learning a probabilistic latent space of object shapes via 3d generative-adversarial modeling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 29, 82–90 (2016)
Xiang, M., Ye, H., Yang, B., et al.: Multi-space and detail-supplemented attention network for point cloud completion. Appl. Intell. 53(12), 14971–14985 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04219-3
Xiang, P., Wen, X., Liu, Y.S. et al.: Snowflakenet: point cloud completion by snowflake point deconvolution with skip-transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5499–5509 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00545
Xu, F., Wang, Z., Wang, H., et al.: Dynamic vehicle pose estimation and tracking based on motion feedback for lidars. Appl. Intell. 53(2), 2362–2390 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03576-3
Xu, Q., Xu, Z., Philip, J., et al.: Point-nerf: point-based neural radiance fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5438–5448 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00536
Yang, G., Huang, X., Hao, Z. et al.: Pointflow: 3d point cloud generation with continuous normalizing flows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4541–4550 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00464
Yang, Y., Feng, C., Shen, Y. et al.: Foldingnet: point cloud auto-encoder via deep grid deformation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 206–215, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00029
Yu, X., Rao, Y., Wang, Z., et al.: Pointr: diverse point cloud completion with geometry-aware transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12498–12507 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01227
Yuan, W., Khot, T., Held, D. et al.: Pcn: point completion network. In: International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 728–737 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/3DV.2018.00088
Zeng, X., Vahdat, A., Williams, F., et al.: Lion: latent point diffusion models for 3d shape generation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 10021–10039 (2022)
Zhang, B., Gu, S., Zhang, B. et al.: Styleswin: transformer-based gan for high-resolution image generation, pp. 11294–11304 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01102
Zhang, X., Feng, Y., Li, S., et al.: View-guided point cloud completion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 15890–15899 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01563
Zhou, L., Du, Y., Wu, J.: 3d shape generation and completion through point-voxel diffusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5826–5835 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00577
Zhu, Z., Nan, L., Xie, H., et al.: Csdn: cross-modal shape-transfer dual-refinement network for point cloud completion. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Gr. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2023.3236061
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 4222020), and in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62241601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JJ involved in methodology and conceptualization; RZ involved in methodology, writing draft, results analysis, and visualization; ML involved in methodology, writing draft, and results analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical and informed consent for data used
Not applicable. The current study does not involve humans and animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, J., Zhao, R. & Lei, M. Latent diffusion transformer for point cloud generation. Vis Comput 40, 3903–3917 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03396-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03396-1