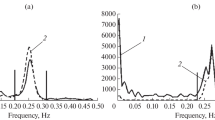
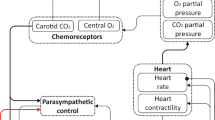
Abstract
The cardiac and respiratory rhythms in humans are known to be coupled by several mechanisms. In particular, the first rhythm is deeply modulated by the second. In this report we propose a simple operational model for heart rate variability which, taking such modulation into account, reproduces the main features of some experimental sequences of RR intervals recorded from healthy subjects in the resting condition. Also, peer analysis of the model performance allows us to answer the question whether the observed behaviour should be ascribed to phase synchronisation of the heart beating to the respiratory rhythm. Lastly, the changes of the model activity brought about by changing its relevant parameters are analysed and discussed
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babloyantz A, Maurer P (1996) A graphical representation of local correlations in time series – assessment of cardiac dynamics. Phys Lett A 221:43–55
Balocchi R, Menicucci D, Santarcangelo E, Sebastiani L, Gemignani A, Ghelarducci B, Varanini M (2004) Deriving the respiratory sinus arrhythmia from the heartbeat time series using empirical mode decomposition. Chaos Solitons Fractals 20:171–177
Barbi M, Chillemi S, Di Garbo A, Balocchi R, Carpeggiani C, Emdin M, Michelassi C, Santarcangelo E (1998) Predictability and nonlinearity of the heart rhythm. Chaos Solitons Fractals 9:507–515
Barbi M, Chillemi S, Di Garbo A, Balocchi R, Menicucci D (2004) Characterisation of cardiac tachograms. The 8th experimental chaos conference (Florence, 14–17 June 2004)
Ehlers CL, Havstad J, Prichard D, Theiler J (1998) Low doses of ethanol reduce evidence for nonlinear structure in brain activity. J Neurosci 18:7474–7486
Fitzurka MA, Tam DC (1999) A joint interspike interval difference stochastic spike train analysis: detecting local trends in the temporal firing patterns of single neurons. Biol Cybern 80:309–326
Glass L (2001) Synchronization and rhythmic processes in physiology. Nature 410:277–284
Glass L, Mackey MC (1979) A simple model for phase locking of biological oscillators. J Math Biol 7:339–352
Glass L, Graves C, Petrillo GA, Mackey MC (1980) Unstable dynamics of a periodically driven Oscillator in the Presence of Noise. J Theor Biol 86:455–475
McGuinness M, Hong Y, Galletly D, Larsen P (2004) Arnold Tongues in human cardiorespiratory systems. Chaos 14:1–6
Porta A, Montano N, Furlan R, Cogliati C, Guzzetti S, Gnecchi-Ruscone T, Malliani A, Chang H-S, Stares K, Gilbey MP (2004) Automatic classification of interference patterns in driver event series: application to single sympathetic neuron discharge forced by mechanical ventilation. Biol Cybern 91:258–273
Schafer C, Rosenblum MG, Kurths J (1998) Heartbeat synchronized with ventilation. Nature 392:239–240
Schafer C, Rosenblum MG, Abel H-H, Kurths J (1999) Synchronization in the human cardiorespiratory system. Phys Rev E 60: 857–870
Theiler J, Galdrikian B, Longtin A, Eubank A, Farmer JD (1992) Testing for nonlinearity in time series: the method of surrogate data. Physica D 58:77–94
Winfree AT (1980, 2001) The geometry of biological time. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbi, M., Chillemi, S., Garbo, A.D. et al. A Minimal Model for the Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia. Biol Cybern 94, 225–232 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-005-0043-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-005-0043-7