Abstract.
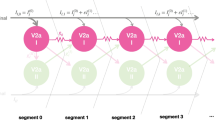
The aim of this study is to produce travelling waves in a planar net of artificial spiking neurons. Provided that the parameters of the waves – frequency, wavelength and orientation – can be sufficiently controlled, such a network can serve as a model of the spinal pattern generator for swimming and terrestrial quadruped locomotion. A previous implementation using non-spiking, sigmoid neurons lacked the physiological plausibility that can only be attained using more realistic spiking neurons. Simulations were conducted using three types of spiking neuronal models. First, leaky integrate-and-fire neurons were used. Second, we introduced a phenomenological bursting neuron. And third, a canonical model neuron was implemented which could reproduce the full dynamics of the Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. The conditions necessary to produce appropriate travelling waves corresponded largely to the known anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord. Especially important features for the generation of travelling waves were the topology of the local connections – so-called off-centre connectivity – the availability of dynamic synapses and, to some extent, the availability of bursting cell types. The latter were necessary to produce stable waves at the low frequencies observed in quadruped locomotion. In general, the phenomenon of travelling waves was very robust and largely independent of the network parameters and emulated cell types.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S Alford J Christenson S Grillner (1991) ArticleTitlePresynaptic GABAA and GABAB receptor-mediated phasic modulation in axons of spinal motor interneurons Eur J Neurosci 3 IssueID2 107–11
Batueva SuffixIV JT Buchanan NP Veselkin EI Suderevskaya EA Tsetkov (2002a) ArticleTitleThe effects of serotonin on functionally diverse isolated lamprey spinal cord neurons Neurosci Behav Physiol 32 IssueID1 99–101
Batueva SuffixIV JT Buchanan NP Veselkin EI Suderevskaya EA Tsetkov (2002b) ArticleTitleSerotonin modulates oscillations of the membrane potential in isolated spinal neurons from lampreys Neurosci Behav Physiol 32 IssueID2 195–203
RD Beer HJ Chiel JC Gallagher (1999) ArticleTitleEvolution and analysis of model CPGs for walking: General principles and individual variability J Comput Neurosci 7 IssueID2 119–147
A Bekkof (1985) Development of locomotion in vertebrates: a comparative perspective ES Gallin (Eds) Comparative development of adaptive skills: evolutionary implication Earlsbaum Hillsdale, NJ 57–94
T Bem JM Cabelguen Ö Ekeberg S Grillner (2003) ArticleTitleFrom swimming to walking: a single basic network for two different behaviors Biol Cybern 88 79–90 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00422-002-0340-3 Occurrence Handle12567223
WO Bennet RS Simons EL Brainerd (2001) ArticleTitleTwisting and bending: the functional role of salamander lateral hypaxial musculatire during locomotion J Exp Biol 204 1979–1989
Bonnot A, Whelan PJ, Mentis GZ, O’Donavan M (2002) Spatiotemporal pattern of motoneuron activation in the rostral lumbar and the sacral segments during locomotor-like activity in the neonatal mouse spinal cord. J Neurosci 22:RC203 (1–6)
G Bowtell TL Williams (1991) ArticleTitleAnguilliform body dynamics: modeling the interaction between muscle activation and body curvature Phil Trans Biol Sci 334 385–390
JT Buchanan (1982) ArticleTitleIdentification of interneurons with contralateral, caudal axons in the lamprey spinal cord: synaptic interactions and morphology J Neurophysiol 47 IssueID5 961–975
JT Buchanan S Grillner S Cullheim M Risling (1989) ArticleTitleIdentification of excitatory interneurons contributing to generation of locomotion in lamprey: structure, pharmacology, and function J Neurophysiol 62 IssueID1 59–69
J Christenson F Bongianni S Grillner T Hökfelt (1991) ArticleTitlePutative GABAergic input to axons of spinal interneurons and primary sensory neurons in the lamprey spinal cord as shown by intracellular Luzifer yellow and GABA immunohistochemistry Brain Res 538 IssueID2 313–318
J Christenson O Shupliakov S Cullheim S Grillner (1993) ArticleTitlePossible morphological substrates for GABA-mediated presynaptic inhibition in the lamprey spinal cord J Comp Neurol 328 IssueID4 463–472
C Cina S Hochman (2000) ArticleTitleDiffuse distribution of sulphorhodamine-labeled neurons during serotonin-evoked locomotion in the neonatal rat thoracolumbal spinal cord J Comp Neurol 423 IssueID4 590–602
AH Cohen (1988) Evolution of the vertebrate central pattern generator for locomotion AH Cohen S Rossignol S Grillner (Eds) Neural control of rhythmic movements in vertebrates Wiley New York 129–166
JJ Collins (1995) ArticleTitleThe redundant nature of locomotor optimization laws J Biomech 28 IssueID3 251–267
Devolve’I T Bem JM Cabelgruen (1997) ArticleTitleEpaxial and limb muscle actitivty during swimming and terrestrial stepping in the adult newt, Pleurodeles waltl J Neurophysiol 78 638–650
Manira A El J Tegner S Grillner (1997) ArticleTitleLocomotor-related presynaptic modulation of primary afferents in lamprey Eur J Neurosci 9 IssueID4 696–705
CT Farley TC Ko (1997) ArticleTitleMechanics of locomotion in lizards J Exp Biol 200 2177–2188
LM Frolich AA Biewener (1992) ArticleTitleKinematic and electromyographic analysis of the functional role of the body axis during terrestrial and aquatic locomotion in the salamader Ambystoma tigrinum J Exp Biol 162 107–130
C Gans (1975) ArticleTitleTetrapod limblessness: evolution and functional corrolaries Am Zool 15 455–467
G Gerber J Zhong D Young M Randic (2000) ArticleTitleGroup II and group III metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists depress synaptic transmission in the rat spinal cord dorsal horn Neuroscience 100 IssueID2 393–406
J Gerhart M Kirschner (1997) Cells, embryos and evolution Blackwell Oxford
D Golomb Y Amitai (1997) ArticleTitlePropagating neuronal discharges in neocortical slices: computational and experimental study J Neurophysiol 78 1199–1211
D Golomb GB Ermentrout (1999) ArticleTitleContinous and lurching traveling pulses in neuronal networks with delay and spatially decaying connectivity Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96 IssueID23 13480–13485
D Golomb GB Ermentrout (2001) ArticleTitleBistability in pulse propagation in networks of excitatory and inhibitory populations Phys Rev Lett 86 IssueID18 4179–4182
M Golubitsky I Stewart PL Buono JJ Collins (1999) ArticleTitleSymmetry in locomotor central pattern generators and animal gaits Nature 401 IssueID6754 693–695 Occurrence Handle10.1038/44416 Occurrence Handle10537106
A Gupta Y Wang H Markram (2000) ArticleTitleOrganizing principles for a diversity of gabaergic interneurons and synapses in the neocortex Science 287 273–279
JS Gustafsson A Birinyi J Crum M Ellisman L Brodin O Shupliakov (2002) ArticleTitleUltrastructural organization of lamprey reticulospinal synapses in three dimensions J Comp Neurol 450 IssueID2 167–182
FC Hoppensteadt EM Izhikevich (2002) Canonical Neural Models MA Arbib (Eds) Brain Theory and Neural Networks EditionNumberSecond The MIT press Cambridge, MA 181–186
BS Gutkin GB Ermentrout (1998) ArticleTitleDynamics of membrane excitability determine interspike interval variability: a link between spike generation mechanism and cortical spike train statistics Neural Comput 19 IssueID5 1047–1065
AJ Ijspeert (2001) ArticleTitleA connectionist central pattern generator for the aquatic and terrestrial gaits of a simulated salamander Biol Cybern 84 IssueID5 331–348
E Izhikevich (2003) ArticleTitleSimple model of spiking neurons IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14 1569–1572
N Kafkafi I Golani (1998) ArticleTitleA travelling wave of lateral movement coordinates both turning and forward walking un the ferret Biol Cybern 78 441–453
A Kaske G Winberg J Coster (2003) ArticleTitleEmergence of coherent traveling waves controlling quadruped gaits in a two dimensional spinal cord model Biol Cybern 88 20–32
WM Kistler (2000) ArticleTitleStability properties of solitary waves and periodic wave trains in a two-dimensional network of spiking neurons Phys Rev E 62 IssueID6 8834–8837
N Kopel GB Ermentrout (1986) ArticleTitleSymmetry and phase locking in chains of weakly coupled oscillators Commun Pure Appl Math 39 623–660
JH Kotaleski S Grillner A Lansner (1999) ArticleTitleNeural mechanisms potentially contributing to the intersegmental phase lag in lamprey Biol Cybern 81 317–330
WC Li R Perrins A Walford A Roberts (2002) ArticleTitleThe neuronal targets for GABAergic reticulospinal inhibition that stops swimming in hatchling frog tadpoles J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 189 IssueID1 29–37
Y Li RE Burke (2002) ArticleTitleDevelopmental changes in short-term synaptic depression in the neonatal mouse spinal cord J Neurophysiol 88 IssueID6 3218–3231
W Maass T Natschläger (2002) ArticleTitleReal-time computing without stable states: a new framework for neural computation based on perturbations Neural Comput 14 IssueID11 2531–2560
JN MacLean BJ Schmidt (2001) ArticleTitleVoltage-sensitivity of motoneuron NMDA receptor channels is modulated by serotonin in the neonatal rat spinal cord J Neurophysiol 86 IssueID3 1131–1138
H Markram Y Wang M Tsodyks (1998) ArticleTitleDifferential signalling via the same axon of neocortical pyramidal neurons Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 5323–5328
T Matsushimi S Grillner (1990) ArticleTitleIntersegmental coordination of undulatory movements – a “trailing oscillator” hypothesis Neuroreport 1 54–65
T Natschläger W Maass (2001) ArticleTitleComputing the optimally fitted spike train for a synapse Neural Comput 13 IssueID11 2377–2394
M O’Donovan S Ho W Yee (1994) ArticleTitleCalcium imaging of rhythmic network activity in the developing spinal cord of the chick embryo J Neurosci 14 6354–6369
GN Orlovsky TG Deliagina S Grillner (1999) Neuronal control of locomotion Oxford University Press Oxford
R Osan B Ermentrout (2001) ArticleTitleTwo dimensional synaptically generated traveling waves in a theta-neuron neural network Neurocomputing 38–40 789–795
R Osan B Ermentrout (2002) ArticleTitleThe evolution of synaptically generated waves in one- and two-dimensional domains Physica D 163 217–235
Z Puskar M Antal (1997) ArticleTitleLocalisation of last-order premotor interneurons in the lumbar spinal cord of rats J Comp Neurol 389 IssueID3 377–389
B Rexed (1952) ArticleTitleThe cytoarchitectonic organization of the spinal cord in the cat J Comp Neurol 96 415–496
J Rinzel D Terman XJ Wang Ermentrout (1998) ArticleTitlePropagating activity patterns in large-scale inhibitory neuronal networks Science 279 1351–1355
D Ritter (1992) ArticleTitleLateral bending during lizard locomotion J Exp Biol 173 1–10
D Ritter (1996) ArticleTitleAxial muscle function during lizard locomotion J Exp Biol 199 2499–2510
A Roberts SR Soffe ES Wolf M Yoshida FY Zhao (1998) ArticleTitleCentral circuits controlling locomotion in young tadpoles Ann NY Acad Sci 860 19–34
PJ Roos (1964) ArticleTitleLateral bending in newt locomotion Proc Ned Acad Wetten C 67 223–232
M Tanabe T Kaneko (1996) ArticleTitlePaired pulse facilitation of GABAergic IPSCs in ventral horn neurons in neonatal rat spinal cord Brain Res 716 IssueID1–2 101–106
JJ Tyson (1994) ArticleTitleWhat evertone should know about the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction Lect Notes Biomath 100 569–587
P Wallen O Shupliakov RH Hill (1993) ArticleTitleOrigin of phasic synaptic inhibition in myotomal motoneurons during fictive locomotion in lamprey Exp Brain Res 96 IssueID2 194–202
M Wheatley M Edamura RB Stein (1992) ArticleTitleA comparison of intact and in-vitro locomotion in an adult amphibian Exp Brain Res 88 IssueID3 609–614
S Yakovenko V Mushawar V VanderHorst G Holstege A Prochazka (2002) ArticleTitleSpatiotemporal activation of lumbosacral motoneurons in the locomotor step cycle J Neurophys 87 1542–1553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaske, A., Bertschinger, N. Travelling wave patterns in a model of the spinal pattern generator using spiking neurons. Biol Cybern 92, 206–218 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-005-0540-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-005-0540-8