Abstract.
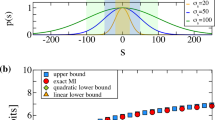
How does the information about a signal in neural threshold crossings depend on the noise acting upon it? Two models are explored, a binary McCulloch and Pitts (threshold exceedance) model and a model of waiting time to exceedance – a discrete-time version of interspike intervals. If noise grows linearly with the signal, we find the best identification of the signal in terms of the Fisher information is for signals that do not reach the threshold in the absence of noise. Identification attains the same precision under weak and strong signals, but the coding range decreases at both extremes of signal level. We compare the results obtained for Fisher information with those using related first and second moment measures. The maximum obtainable information is plotted as a function of the ratio of noise to signal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ED Adrian (1928) The basis of sensation: the action of the sense organs Norton New York
N Brunel JP Nadal (1998) ArticleTitleMutual information, Fisher information, and population coding Neural Comput 10 1731–1757
AR Bulsara TC Elston CR Doering SB Lowen K Lindberg (1996) ArticleTitleCooperative behavior in periodically driven noisy integrate-and-fire models of neuronal dynamics Phys Rev E 53 3958–3969
GA Cecchi M Sigman J-M Alonso L Martinez DR Chialvo MO Magnasco (2000) ArticleTitleNoise in neurons is message dependent Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 5557–5561
C Christodoulou G Bugmann (2000) ArticleTitleNear Poisson-type firing produced by concurrent excitation and inhibition Biosystems 58 41–48
JA Freund L Schimansky-Geier B Beisner A Neiman DF Russell T Yakusheva F Moss (2002) ArticleTitleBehavioral stochastic resonance: how the noise from a Daphnia swarm enhances individual prey capture by juvenile paddlefish J Theor Biol 214 71–83
W Gerstner W Kistler (2002) Spiking neuron models Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK
WM Getz P Lańský (2001) ArticleTitleLigand concentration coding and optimal Michaelis-Menten parameters in multivalent and heterogeneous receptor membranes Chem Senses 26 95–104
PE Greenwood LM Ward W Wefelmeyer (1999) ArticleTitleStatistical analysis of stochastic resonance in a simple setting Phys Rev E 60 4687–4695
PE Greenwood LM Ward DF Russel A Neiman F Moss (2000) ArticleTitleStochastic resonance enhances the electrosensory information available to paddlefish for prey capture Phys Rev Lett 84 4773–4776
BS Gutkin CE Smith (2000) ArticleTitleConditions for noise reduction and stable encoding of spatial structure by cortical neural networks Biol Cybern 82 469–475
J Kroller OJ Grusser LR Weiss (1988) ArticleTitleSuperimposing noise linearizes the responses of primary muscle-spindle afferents to sinusoidal muscle stretch Biol Cybern 60 131–137
D Laming (1986) Sensory analyses Academic London
P Lansky WM Getz (2001) ArticleTitleSensitivity and coding range in olfactory sensory neuron. Role of heterogeneity of receptors Bull Math Biol 63 885–908
P Lansky L Sacerdote (2001) ArticleTitleThe Ornstein-Uhlenbeck neuronal model with signal-dependent noise Phys Lett A 285 132–140
P Lansky L Sacerdote F Tomassetti (1995) ArticleTitleOn the comparison of Feller and Ornstein-Uhlenbeck models for neural activity Biol Cybern 73 457–465
P Lansky R Rodriguez L Sacerdote (2004) ArticleTitleMean instantaneous firing frequency is always higher than the firing rate Neural Comput 16 477–489
B Lindner J Garcia-Ojalvo A Neiman (2004) ArticleTitleEffects of noise in excitable systems Phys Rep Rev Sect Phys Lett 392 321–424
A Longtin B Doiron AR Bulsara (2002) ArticleTitleNoise-induced divisive gain control in neuron models Biosystems 67 147–156
KD Miller TW Troyer (2002) ArticleTitleNeural noise can explain expansive, power-law nonlinearities in neural response functions J Neurophysiol 87 653–659
WS McCulloch WH Pitts (1943) ArticleTitleA logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity Bull Math Biophys 5 115–133
WJ McGill MC Teich (1995) ArticleTitleAlerting signals and detection in a sensory network J Math Psychol 39 146–163
Moss F, Bulsara A, Shlesinger MF (eds) (1993) Proceedings of the NATO ARW on stochastic resonance in physics and biology. J Stat Phys 70
F Moss LM Ward WG Sannita (2004) ArticleTitleStochastic resonance and sensory information processing: a tutorial and review of application Clin Neurophysiol 115 267–281
K Pakdaman D Mestivier (2004) ArticleTitleNoise induced synchronization in a neuronal oscillator Physica D 192 123–137
HE Plesser S Tanaka (1997) ArticleTitleStochastic resonance in a model neuron with reset Phys Lett A 225 228–234
CR Rao (2001) Linear statistical inference and its application EditionNumber2 Wiley New York
R Rodriguez P Lansky (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of spatial extension on noise-enhanced phase locking in a leaky integrate-and-fire model of a neuron Phys Rev E 62 8427–8437
J Segundo J-F Vibert K Pakdaman M Stiber O Diez Martinez (1994) Noise and the neuroscience: a long history, a recent revival and some theory KH Pribram (Eds) Origins: brain & self organization Erlbaum Hillsdale, NJ
T Shimokawa K Pakdaman S Sato (1999) ArticleTitleTime-scale matching in the response of a leaky integrate-and-fire neuron model to periodic stimulus with additive noise Phys Rev E 59 3427–3443
T Shimokawa K Pakdaman T Takahata S Tanabe S Sato (2000) ArticleTitleA first-passage-time analysis of the periodically forced leaky integrate-and-fire model Biol Cybern 83 327–340
M Stemmler (1996) ArticleTitleA single spike suffices: the simplest form of stochastic resonance in model neurons Network 7 687–716
HC Tuckwell (1988) Introduction to theoretical neurobiology Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK
LM Ward A Neiman F Moss (2002) ArticleTitleStochastic resonance in psychophysics and in animal behavior Biol Cybern 87 91–101
K Wiesenfeld F Moss (1995) ArticleTitleStochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: from ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs Nature 375 33–36
SD Wilke CW Eurich (2002) ArticleTitleRepresentational accuracy of stochastic neural populations Neural Comput 14 155–189
S Wu S Amari H Nakahara (2004) ArticleTitleInformation processing in a neuron ensemble with the multiplicative correlation structure Neural Netw 17 205–214
XL Yu ER Lewis (1989) ArticleTitleStudies with spike initiators – linearization by noise allows continuous signal modulation in neural networks IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 36 36–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greenwood, P., Lánský, P. Optimum signal in a simple neuronal model with signal-dependent noise. Biol Cybern 92, 199–205 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-005-0545-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-005-0545-3