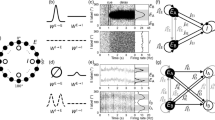
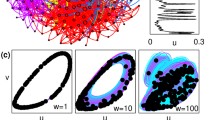
Abstract
The brain operates in a highly oscillatory environment. We investigate here how such an oscillating background can create stable organized behavior in an array of neuro-oscillators that is not observable in the absence of oscillation, much like oscillating the support point of an inverted pendulum can stabilize its up position, which is unstable without the oscillation. We test this idea in an array of electronic circuits coming from neuroengineering: we show how the frequencies of the background oscillation create a partition of the state space into distinct basins of attraction. Thus, background signals can stabilize persistent activity that is otherwise not observable. This suggests that an image, represented as a stable firing pattern which is triggered by a voltage pulse and is sustained in synchrony or resonance with the background oscillation, can persist as a stable behavior long after the initial stimulus is removed. The background oscillations provide energy for organized behavior in the array, and these behaviors are categorized by the basins of attraction determined by the oscillation frequencies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buzsaki G (2006) Rhythms of the brain. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Carrillo H, Hoppensteadt F (2009) Unfolding an electronic integrate-and-fire circuit (submitted)
Feynman R (1965) Lectures in physics. Addison-Wesley, Menlo Park
Guttman R et al (1980) J Membr Physiol 56: 9–18
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol 1: 500–544
Hoppensteadt FC (2000) Analysis and simulation of chaotic systems. Springer, New York
Hoppensteadt F (2006) Voltage-controlled oscillations in neurons. Scholarpedia 1(11): 1599
Hoppensteadt FC, Izhikevich EM (1997) Weakly connected neural networks. Springer, New York
Hoppensteadt FC, Izhikevich EM (1999) Oscillatory neurocomputers with dynamic connectivity. Phys Rev Lett 82: 2983–2986
Kiehl RA, Yang T, Chua LO (2001) Tunneling-phase logic based cellular nonlinear networks. In: 15th European conference circuit theory and design
McAdams ET, Jossinet J (1995) Tissue impedance: a historical overview. Physiol Meas 16: A1–A13
Nuñez P (1995) Neocortical dynamics and human EEG rhythms. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Singer W (2007) Binding by synchrony. Scholarpedia 2(12): 1657
van der Pol B, van der Mark J (1928) The heartbeat considered as a relaxation oscillation, and an electrical model of the heart. J Sci Ser 7 6: 763–775
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by FENA/FCRP Grant No. 0160-G-FD211.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoppensteadt, F. Activity patterns in networks stabilized by background oscillations. Biol Cybern 101, 43–47 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-009-0314-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-009-0314-9