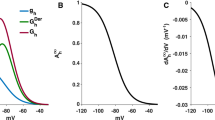
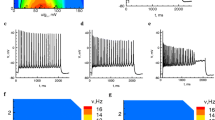
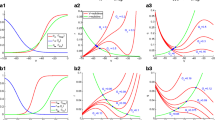
Abstract
The hyperpolarization-activated, inward, mixed cation current, I h, appears in a wide variety of cells in the nervous system, contributes to diverse neuronal properties, and is up-regulated by a number of important neurotransmitters. Up-regulation of I h is usually associated with an excitability-enhancing depolarization of resting membrane potential and an excitability-depressing shunting effect caused by a decrease in input resistance. In order to gain a better understanding of the interaction of these effects and their influence on excitability with I h modulation, we systematically analyze changes in neuronal properties associated with excitability during I h modulation in simplified, yet, biophysical neuron models based on a hippocampal pyramidal neuron. We simulate I h modulation by varying both its maximal conductance and its half-activation voltage, mimicking the effects of cAMP-linked neurotransmitters, through ranges of physiologically realistic parameter regimes. Of particular interest is the contribution of the different effects of I h up-regulation when membrane potentials are held at common levels and neuronal excitability is probed. Our modeling results suggest that, although holding potentials at common levels may compensate for changes in resting membrane potentials, this protocol may exaggerate the excitability-depressing influences of changes in input resistances with I h up-regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger T, Larkum ME, Luscher HR (2001) High I(h) channel density in the distal apical dendrite of layer V pyramidal cells increases bidirectional attenuation of EPSPs. J Neurophysiol 85: 855–868
Desjardins AE, Li YX, Reinker S, Miura RM, Neuman RS (2003) The influences of Ih on temporal summation in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: a modeling study. J Comput Neurosci 15: 131–142
DiFrancesco D (1993) Pacemaker mechanisms in cardiac tissue. Annu Rev Physiol 55: 455–472
Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen J, Morgan RJ, Foldy C, Soltesz I (2008) Upregulated H-current in hyperexcitable CA1 dendrites after febrile seizures. Front Cell Neurosci 2: 2
Edman A, Theander S, Grampp W (1992) Functional effects of a hyperpolarization-activated membrane current in the lobster stretch receptor neurone. Acta Physiol Scand 146: 221–232
Fernandez N, Andreasen M, Nedergaard S (2002) Influence of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current, I(h), on the electrotonic properties of the distal apical dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones. Brain Res 930: 42–52
Gasparini S, DiFrancesco D (1999) Action of serotonin on the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih) in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 11: 3093–3100
Golding NL, Mickus TJ, Katz Y, Kath WL, Spruston N (2005) Factors mediating powerful voltage attenuation along CA1 pyramidal neuron dendrites. J Physiol 568: 69–82
Izhikevich EM (2007) Dynamical systems in neuroscience: the geometry of excitability and bursting. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Jarsky T, Roxin A, Kath WL, Spruston N (2005) Conditional dendritic spike propagation following distal synaptic activation of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nat Neurosci 8: 1667–1676
Leung LS, Yu HW (1998) Theta-frequency resonance in hippocampal CA1 neurons in vitro demonstrated by sinusoidal current injection. J Neurophysiol 79: 1592–1596
Maccaferri G, McBain CJ (1996) The hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) and its contribution to pacemaker activity in rat CA1 hippocampal stratum oriens-alveus interneurons. J Physiol 497(Pt 1): 119–130
Magee JC (1998) Dendritic hyperpolarization-activated currents modify the integrative properties of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 18: 7613–7624
Magee JC (1999) Dendritic lh normalizes temporal summation in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Nat Neurosci 2: 508–514
McCormick DA, Pape HC (1990a) Noradrenergic and serotonergic modulation of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current in thalamic relay neurones. J Physiol 431: 319–342
McCormick DA, Pape HC (1990b) Properties of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current and its role in rhythmic oscillation in thalamic relay neurones. J Physiol 431: 291–318
McCormick DA, Huguenard JR (1992) A model of the electrophysiological properties of thalamocortical relay neurons. J Neurophysiol 68: 1384–1400
Nicoll A, Larkman A, Blakemore C (1993) Modulation of EPSP shape and efficacy by intrinsic membrane conductances in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons in vitro. J Physiol 468: 693–710
Nolan MF, Malleret G, Lee KH, Gibbs E, Dudman JT, Santoro B, Yin D, Thompson RF, Siegelbaum SA, Kandel ER, Morozov A (2003) The hyperpolarization-activated HCN1 channel is important for motor learning and neuronal integration by cerebellar Purkinje cells. Cell 115: 551–564
Nolan MF, Malleret G, Dudman JT, Buhl DL, Santoro B, Gibbs E, Vronskaya S, Buzsaki G, Siegelbaum SA, Kandel ER, Morozov A (2004) A behavioral role for dendritic integration: HCN1 channels constrain spatial memory and plasticity at inputs to distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Cell 119: 719–732
Pape HC (1996) Queer current and pacemaker: the hyperpolarization-activated cation current in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol 58: 299–327
Pike FG, Goddard RS, Suckling JM, Ganter P, Kasthuri N, Paulsen O (2000) Distinct frequency preferences of different types of rat hippocampal neurones in response to oscillatory input currents. J Physiol 529(Pt 1): 205–213
Poolos NP, Migliore M, Johnston D (2002) Pharmacological upregulation of h-channels reduces the excitability of pyramidal neuron dendrites. Nat Neurosci 5: 767–774
Robinson RB, Siegelbaum SA (2003) Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents: from molecules to physiological function. Annu Rev Physiol 65: 453–480
Rosenkranz JA, Johnston D (2006) Dopaminergic regulation of neuronal excitability through modulation of Ih in layer V entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci 26: 3229–3244
Rotstein HG, Pervouchine DD, Acker CD, Gillies MJ, White JA, Buhl EH, Whittington MA, Kopell N (2005) Slow and fast inhibition and an H-current interact to create a theta rhythm in a model of CA1 interneuron network. J Neurophysiol 94: 1509–1518
Stuart G, Spruston N (1998) Determinants of voltage attenuation in neocortical pyramidal neuron dendrites. J Neurosci 18: 3501–3510
Surges R, Freiman TM, Feuerstein TJ (2004) Input resistance is voltage dependent due to activation of Ih channels in rat CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurosci Res 76: 475–480
Tsay D, Dudman JT, Siegelbaum SA (2007) HCN1 channels constrain synaptically evoked Ca2+ spikes in distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neuron 56: 1076–1089
Ulrich D (2002) Dendritic resonance in rat neocortical pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol 87: 2753–2759
Williams SR, Stuart GJ (2000) Site independence of EPSP time course is mediated by dendritic I(h) in neocortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 83: 3177–3182
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lippert, A., Booth, V. Understanding effects on excitability of simulated I h modulation in simple neuronal models. Biol Cybern 101, 297–306 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-009-0337-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-009-0337-2