Abstract.
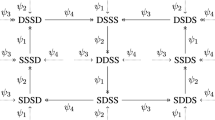
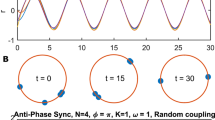
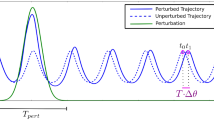
Canavier et al. (1997) used phase response curves (PRCs) of individual oscillators to characterize the possible modes of phase-locked entrainment of an N-oscillator ring network. We extend this work by developing a mathematical criterion to determine the local stability of such a mode based on the PRCs. Our method does not assume symmetry; neither the oscillators nor their connections need be identical. To use these techniques for predicting modes and determining their stability, one need only determine the PRC of each oscillator in the ring either experimentally or from a computational model. We show that network stability cannot be determined by simply testing the ability of each oscillator to entrain the next. Stability depends on the number of neurons in the ring, the type of mode, and the slope of each PRC at the point of entrainment of the respective neuron. We also describe simple criteria which are either necessary or sufficient for stability and examine the implications of these results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 April 1998 / Accepted in revised form: 2 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dror, R., Canavier, C., Butera, R. et al. A mathematical criterion based on phase response curves for stability in a ring of coupled oscillators. Biol Cybern 80, 11–23 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220050501
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220050501