Abstract.
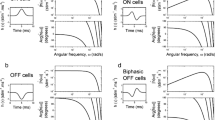
Pseudorandom white-noise stimulation followed by direct spectral estimation was used to obtain linear frequency response and coherence functions from paired, but dynamically different, spider mechanosensory neurons. The dynamic properties of the two neuron types were similar with either mechanical or electrical stimulation, showing that action potential encoding dominates the dynamics. Phase-lag data indicated that action potential initiation occurs more rapidly during mechanical stimulation, probably in the distal sensory dendrites. Total information capacity, calculated from coherence, as well as information per action potential, were both similar in the two types of neurons, and similar to the few available estimates from other spiking neurons. However, information capacity and information per action potential both depended strongly on neuronal firing rate, which has not been reported before.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 August 2000 / Accepted in revised form: 5 April 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
French, A., Höger, U., Sekizawa, Si. et al. Frequency response functions and information capacities of paired spider mechanoreceptor neurons. Biol Cybern 85, 293–300 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220100260
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220100260