Abstract
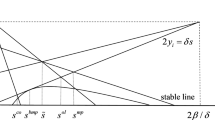
Along with the appearance of new optimization and control problems, novel paradigms emerge. A large number of them are based on behavioral ecology, where population dynamics play an important role. One of the most known models of population dynamics is the replicator equation, whose applications in optimization and control have increased in recent years. This fact motivates the study of the replicator dynamics’ properties that are related to the implementation of this method for solving optimization and control problems. This paper addresses implementation issues of the replicator equation in engineering problems. We show by means of the Lyapunov theory that the replicator dynamics model is robust under perturbations that make the state to leave the simplex (among other reasons, this phenomenon can emerge due to numerical errors of the solver employed to obtain the replicator dynamic’s response). A refinement of these results is obtained by introducing a novel robust dynamical system inspired by the replicator equation that allows to control and optimize plants under arbitrary initial conditions on the positive orthant. Finally, we characterize stability bounds of the replicator dynamics model in problems that involve N strategies that are subject to time delays. We illustrate our results via simulations.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maynard Smith J, Price G (1973) The logic of animal conflict. Nature 246:15–18
Maynard Smith J (1982) Evolution and the theory of games. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Thomas B (1984) Evolutionary stability: states and strategies. Theor Popul Biol 26(1):49–67
Taylor PD, Jonker LB (1978) Evolutionary stable strategies and game dynamics. Math Biosci 40(1):145–156
Weibull J (1997) Evolutionary game theory. The MIT press, Cambridge, MA, USA
Hofbauer J, Sigmund K (1998) Evolutionary games and population dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sandholm W (2010) Population games and evolutionary dynamics. The MIT press, Cambridge, MA, USA
Cressman R, Křivan V, Garay J (2004) Ideal free distributions, evolutionary games, and population dynamics in multiple-species environments. Am Nat 164(4):473–489
Fox MJ, Shamma JS (2013) Population games, stable games, and passivity. Games 4(4):561–583
Pais D, Caicedo-Núnez CH, Leonard NE (2012) Hopf bifurcations and limit cycles in evolutionary network dynamics. SIAM J Appl Dyn Syst 11(4):1754–1784
Leonard N (2014) Multi-agent system dynamics: bifurcation and behavior of animal groups. Annu Rev Control 38(4):171–183
Barreiro-Gomez J, Obando G, Quijano N (2016) Distributed population dynamics: optimization and control applications. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 99:1–11. doi:10.1109/TSMC.2016.2523934
Barreiro-Gomez J, Quijano N, Ocampo-Martinez C (2016) Constrained distributed optimization: a population dynamics approach. Automatica 69:101–116
Obando G, Pantoja A, Quijano N (2014) Building temperature control based on population dynamics. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 22(1):404–412
Ramírez-Llanos E, Quijano N (2010) A population dynamics approach for the water distribution problem. Int J Control 83(9):1947–1964
Bomze I, Pelillo M, Stix V (2000) Approximating the maximum weight clique using replicator dynamics. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11(6):1228–1241
Tembine H, Altman E, El-Azouzi R, Hayel Y (2010) Evolutionary games in wireless networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 40(3):634–646
Tembine H, Altman E, El-Azouzi R, Hayel Y (2011) Bio-inspired delayed evolutionary game dynamics with networking applications. Telecommun Syst 47(1–2):137–152
Poveda J, Quijano N (2012) Dynamic bandwidth allocation in wireless networks using a shahshahani gradient based extremum seeking control. In: Proceedings of the 2012 6th international conference on network games, control and optimization (NetGCooP), IEEE, pp 44–50
Pantoja A, Quijano N (2011) A population dynamics approach for the dispatch of distributed generators. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58:4559–4567
Poveda JI, Quijano N (2015) Shahshahani gradient-like extremum seeking. Automatica 58:51–59
Pantoja A, Quijano N (2012) Distributed optimization using population dynamics with a local replicator equation. In: Proceedings of the 51st IEEE conference on decision and control, IEEE, pp 3790–3795
Yi T, Zuwang W (1997) Effect of time delay and evolutionarily stable strategy. J Theor Biol 187(1):111–116
Alboszta J, Miekisz J (2004) Stability of evolutionarily stable strategies in discrete replicator dynamics with time delay. J Theor Biol 231(2):175–179
Menache I, Ozdaglar A (2011) Network games: theory, models, and dynamics, vol 4. Morgan & Claypool Publishers, San Rafael, CA, USA
Shahshahani S (1979) A new mathematical framework for the study of linkage and selection. Memoirs of the American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, USA
Poveda J, Quijano N (2012) A shahshahani gradient based extremum seeking scheme. In: Proceedings of the 51st IEEE conference on decision and control, IEEE, pp 5104–5109
Quijano N, Passino KM (2007) The ideal free distribution: theory and engineering application. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 37(1):154–165
Khalil HK (2002) Nonlinear systems. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Pantoja A, Quijano N, Leirens S (2011) A bioinspired approach for a multizone temperature control system. Bioinspir Biomim 6(1):016007
Teel AR, Peuteman J, Aeyels D (1999) Semi-global practical asymptotic stability and averaging. Syst Control Lett 37(5):329–334
Lobry C, Sari T (2005) Singular perturbation methods in control theory. Contrôle non linéaire et Applications 4(64):155–182
Barreiro-Gomez J, Quijano N, Ocampo-Martínez C (2014) Constrained distributed optimization based on population dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 53rd IEEE conference on decision and control, IEEE, pp 4260–4265
Iijima R (2012) On delayed discrete evolutionary dynamics. J Theor Biol 300:1–6
Chen C-T (1998) Linear system theory and design. Oxford University Press Inc, Oxford
Corless RM, Gonnet GH, Hare DE, Jeffrey DJ, Knuth DE (1996) On the lambert w function. Adv Comput Math 5(1):329–359
Yi S, Nelson PW, G U (2010) Time-delay systems: analysis and control using the Lambert W function. World Scientific, Singapore
Gu K, Kharitonov V, Chen J (2003) Stability of time-delay systems. Birkhauser, Cambridge, MA, USA
Sipahi R, Niculescu S, Abdallah C, Michiels W, Gu K (2011) Stability and stabilization of systems with time delay. IEEE Control Syst Mag 31(1):38–65
Engelborghs K, Luzyanina T, Samaey G (2001) Dde-biftool v. 2.00: a matlab package for bifurcation analysis of delay differential equations. tech. rep., Department of Computer Science, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium
Wright EM (1955) A non-linear difference-differential equation. J. Reine Angew. Math 194(1):66–87
Giraldo J, Quijano N (2012) Delay independent evolutionary dynamics for resource allocation with asynchronous distributed sensors. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IFAC workshop on distributed estimation and control in networked systems, pp 121–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research supported in part by ALTERNAR project, BPIN 20130001000089, Acuerdo 005 de 2013, OCAD-Fondo de CTel SGR, Colombia; and in part by Programa de becas doctorales Colciencias–Colfuturo Convocatoria 528 and Colciencias programa Jóvenes Investigadores 2012.
This work was done while J. I. Poveda was with the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Universidad de los Andes, Bogotá, Colombia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obando, G., Poveda, J.I. & Quijano, N. Replicator dynamics under perturbations and time delays. Math. Control Signals Syst. 28, 20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00498-016-0170-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00498-016-0170-9