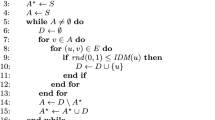Abstract
The diffusion of influence in a social network has been recently investigated in various fields. In this paper, we study the problem of minimizing the expected complete influence time of a social network under the resource constraint. We focus on the case where the budget for influencing the initial target set of individuals is limited. The incremental chance model is adopted to characterize the diffusion of influence, and a lower bound for the expected complete influence time is presented. In order to solve the problem effectively, we modify the well-known heuristic search approach, the A* algorithm, and provide a series of strategies for designing the heuristic functions. Finally, we perform experiments to show that the proposed algorithm generally performs better than widely used trivial heuristic methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Albert R, Jeong H, Barabasi A (2000) Error and attack tolerance of complex networks. Nature 406:378–382
Berger N, Borgs C, Chayes JT, Saberi A (2005) On the spread of viruses on the internet. In: Proceedings of the sixteenth annual ACM-SIAM symposium on discrete algorithms, SODA’05, Vancouver, British Columbia, pp 301–310
Brown J, Reinegen P (2007) Social ties and word-of-mouth referral behavior. J Consumer Res 14(3):350–362
Chen N (2008) On the approximability of influence in social networks. In: Proceedings of the fourteenth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD’08, San Francisco, California, pp 1029–1037
Cormen TH, Leiserson CE, Rivest RL, Stein C (2001) Introduction to algorithms. MIT press, Cambridge
Dezso Z, Barabasi AL (2002) Halting viruses in scale-free networks. Phys Rev E 65
Domingos P, Richardson M (2001) Mining the network value of customers. In: Proceedings of the seventh ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD’01, San Francisco, California, pp 57–66
Even-Dar E, Shapira A (2007) A note on maximizing the spread of influence in social networks. In: Proceedings of the third international workshop on internet and network economics (WINE)
Fishman GS (1995) Monte Carlo: concepts, algorithms, and applications. Springer, New York
Ganesh A, Massouli L, Towsley D (2005) The effect of network topology on the spread of epidemics. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2005. 24th annual joint conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, pp 1455–1466
Goldenberg J, Libai B, Muller E (2001) Talk of the network: a complex systems look at the underlying process of word-of-mouth. Market Lett 12(3):211–223
Granovetter M (1978) Threshold models of collective behavior. Am J Sociol 83:1420–1443
Hart PE, Nilsson NJ, Raphael B (1968) A formal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths in graphs. IEEE Trans Syst Sci Cybern (SSC) 4(2):100–107
Holland JH (1992) Adaptation in natural and artificial system. MIT Press, Cambridge
Immorlica N, Kleinberg JM, Mahdian M, Wexler T (2007) The role of compatibility in the diffusion of technologies through social networks. In: Proceedings of the eighth ACM conference on electronic commerce, EC’07, San Diego, California, pp 75–83
Kearns M, Ortiz L (2003) Algorithms for interdependent security games. In: Proceedings of the seventeenth annual conference on neural information processing systems, NIPS’03, Vancouver and Whistler, pp 288–297
Kempe D, Kleinberg J, Tardos É (2003) Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network. In: Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD’03, Washington, D.C., pp 137–146
Kempe D, Kleinberg J, Tardos É (2005) Influential nodes in a diffusion model for social networks. In: Proceedings of the 32nd international colloquium on automata, languages and programming, ICALP’05, Lisbon, Portugal, pp 1127–1138
Lee J, Mirrokni VS, Nagarajan V, Sviridenko M (2009) Non-monotone submodular maximization under matroid and knapsack constraints. In: Proceedings of the 41st ACM symposium on theory of computing, STOC’09, Bethesda, Maryland, pp 323–332
Morris S (2000) Contagion. Rev Econ Stud 67:57–78
Mossel E, Roch S (2007) On the submodularity of influence in social networks. In: Proceedings of the 39th ACM symposium on theory of computing, STOC’07, San Diego, California, pp 128–134
Ni Y, Liu ZQ (2008) Minimizing the expected time of complete influence through a social network. In: Proceedings of the seventh international conference on information and management sciences, IMS’08, Urumchi, China, pp 447–454
Richardson M, Domingos P (2002) Mining knowledge-sharing sites for viral marketing. In: Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD’02, Edmonton, Alberta, pp 61–70
Rogers E (1995) Diffusion of innovations. Free Press
Sviridenko M (2004) A note on maximizing a submodular set function subject to a knapsack constraint. Oper Res Lett 32:41–43
Valente T (1995) Network models of the diffusion of innovations. Hampton Press
Wasserman S, Faust K (1994) Social network analysis. Cambridge University Press
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393:440–442
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Hong Kong RGC General Research Fund (GRF) 9041369 (CityU 118608) and Project 211, Phase 3 of University of International Business and Economics (project no. 73100042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Y., Liu, ZQ. Heuristic search for optimizing diffusion of influence in a social network under the resource constraint. Soft Comput 15, 335–344 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-010-0601-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-010-0601-3