Abstract
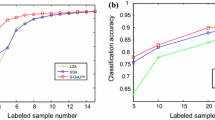
Dimensionality reduction plays an important role in many machine learning tasks. This paper studies semi-supervised dimensionality reduction using pairwise constraints. In this setting, domain knowledge is given in the form of pairwise constraint, which specifies whether a pair of instances belongs to the same class (must-link constraint) or different classes (cannot-link constraint). In this paper, a novel semi-supervised dimensionality reduction method called LGS3DR is proposed, which can integrate both local and global topological structures of the data as well as pairwise constraints. The LGS3DR method is effective and has a closed form solution. Experiments on data visualization and face recognition show that LGS3DR is superior to many existing dimensionality reduction methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An S, Liu W, Venkatesh S (2008) Exploiting side information in locality preserving projection. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE conference on computer vision and, pattern recognition, pp 1–8
Baghshah MS, Shouraki SB (2009) Semi-supervised metric learning using pairwise constraints. In: Proceedings of the 21st international joint conference on, artificial intelligence, pp 1217–1222
Bar-Hillel A, Hertz T, Shental N, Weinshall D (2005) Learning a mahalanobis metric from equivalence constraints. J Mach Learn Res 6:937–965
Belkin M, Niyogi P (2003) Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation. Neural Comput 15(6):1373–1396
Cevikalp H, Verbeek J, Jurie F, Klaser A (2008) Semi-supervised dimensionality reduction using pairwise equivalence constraints. In: Proceedings of the 2008 international conference on computer vision theory and applications, pp 489–496
Chapelle O, Schölkopf B, Zien A (eds) (2006) Semi-supervised learning. MIT Press, Cambridge
Chatpatanasiri R, Kijsirikul B (2010) A unified semi-supervised dimensionality reduction framework for manifold learning. Neurocomputing 73(10–12):1631–1640
Chen J, Ye J, Li Q (2007) Integrating global and local structures: a least squares framework for dimensionality reduction. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE conference on computer vision and, pattern recognition, pp 1–8
Chen S, Zhang D (2011) Semisupervised dimensionality reduction with pairwise constraints for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 8(2):369–373
Cox TF, Cox MAA (eds) (1994) Multidimensional scaling. Chapman & Hall, London
Davidson I (2009) Knowledge driven dimension reduction for clustering. In: Proceedings of the 21st international joint conference on, artificial intelligence, pp 1034–1039
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2001) Pattern classification, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Georghiades AS, Belhumeur PN, Kriegman DJ (2001) From few to many: illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(6):643–660
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2009) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
He X, Niyogi P (2004) Locality preserving projections. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 16:153–160
He X, Cai D, Yan S, Zhang H (2005) Neighborhood preserving embedding. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1208–1213
Jolliffe IT (2002) Principal component analysis, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Klein D, Kamvar SD, Manning CD (2002) From instance-level constraints to space-level constraints: making the most of prior knowledge in data clustering. In: Proceedings of the 19th international conference on, machine learning, pp 307–314
Loia V, Pedrycz W, Senatore S (2003) P-FCM: a proximity-based fuzzy clustering for user-centered web applications. Int J Approx Reason 24(2–3):121–144
Loia V, Pedrycz W, Senatore S (2007) Semantic web content analysis: a study in proximity-based collaborative clustering. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(6):1294–1312
Lu J, Plataniotis KN, Venetsanopoulos AN (2003) Face recognition using LDA-based algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14(1):195–200
van der Maaten LJP, Postma EO, van den Herik HJ (2009) Dimensionality reduction: a comparative review. Technical report TiCC-TR 2009–005, Tilburg University, Tilburg
Pedrycz W (1985) Algorithms of fuzzy clustering with partial supervision. Pattern Recognit Lett 3(1):13–20
Pedrycz W (2002) Collaborative fuzzy clustering. Pattern Recognit Lett 23(14):1675–1686
Pedrycz W (2005) Knowledge-based clustering: from data to information granules. Wiley, New York
Pedrycz W, Waletzky J (1997) Fuzzy clustering with partial supervision. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 27(5):787–795
Pedrycz W, Loia V, Senatore S (2004) P-FCM: a proximity-based fuzzy clustering. Fuzzy Sets Syst 148(1):21–41
Roweis ST, Saul LK (2000) Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290(5500):2323–2327
Samaria F, Harter A (1994) Parameterisation of a stochastic model for human face identification. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE workshop on applications of computer vision, pp 138–142
Sim T, Barker S, Bsat M (2003) The CMU pose, illumination, and expression database. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(12):1615–1618
Song Y, Nie F, Zhang C, Xiang S (2008) A unified framework for semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. Pattern Recognit 41(9):2789–2799
Sun M, Liu C, Yang J, Jin Z, Yang J (2010) A two-step framework for highly nonlinear data unfolding. Neurocomputing 73(10–12):1801–1807
Tang W, Zhong S (2006) Pairwise constraints-guided dimensionality reduction. In: Proceedings of the SDM06 workshop on feature selection for data mining, pp 59–66
Turk M, Pentland A (1991) Face recognition using eigenfaces. In: Proceedings of the 1991 IEEE conference on computer vision and, pattern recognition, pp 586–591
Wagstaff K, Cardie C (2000) Clustering with instance-level constraints. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on, machine learning, pp 1003–1110
Wang XZ, Dong LC, Yan JH (2012) Maximum ambiguity-based sample selection in fuzzy decision tree induction. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(8):1491–1505
Wei J, Peng H (2008) Neighborhood preserving based semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. Electron Lett 44(20):1190–1191
Wu M, Yu K, Yu S, Schölkopf B (2007) Local learning projections. In: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on, machine learning, pp 1039–1046
Xing EP, Ng AY, Jordan MI, Russell S (2003) Distance metric learning, with application to clustering with side-information. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 15:505–512
Yan S, Bouaziz S, Lee D, Barlow J (2012) Semi-supervised dimensionality reduction for analyzing high-dimensional data with constraints. Neurocomputing 76(1):114–124
Yang J, Zhang D, Yang J, Niu B (2007) Globally maximizing, locally minimizing: unsupervised discriminant projection with application to face and palm biometrics. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(4):650–664
Yeung DY, Chang H (2006) Extending the relevant component analysis algorithm for metric learning using both positive and negative equivalence constraints. Pattern Recognit 39(5):1007–1010
Zhai JH (2011) Fuzzy decision tree based on fuzzy-rough technique. Soft Comput 15(6):1087–1096
Zhai JH, Xu HY, Wang XZ (2012) Dynamic ensemble extreme learning machine based on sample entropy. Soft Comput 16(9):1493–1502
Zhai JH, Zhai MY, Bai CY (2013) An improved algorithm for calculating fuzzy attribute reducts. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 25(2):303–313
Zhang D, Zhou Z, Chen S (2007a) Semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. In: Proceedings of the 7th SIAM international conference on data mining, pp 629–634
Zhang T, Yang J, Zhao D, Ge X (2007b) Linear local tangent space alignment and application to face recognition. Neurocomputing 70(7–9):1547–1553
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (S2012040008022) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61273363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. Pedrycz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Zeng, Qf., Wang, X. et al. Integrating local and global topological structures for semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. Soft Comput 18, 1189–1198 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-013-1137-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-013-1137-0