Abstract
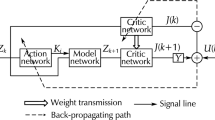
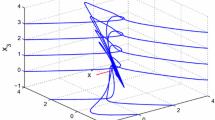
In this paper, a novel value iteration adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) algorithm, called “generalized value iteration ADP” algorithm, is developed to solve infinite horizon optimal tracking control problems for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. The developed generalized value iteration ADP algorithm permits an arbitrary positive semi-definite function to initialize it, which overcomes the disadvantage of traditional value iteration algorithms. Convergence property is developed to guarantee that the iterative performance index function will converge to the optimum. Neural networks are used to approximate the iterative performance index function and compute the iterative control policy, respectively, to implement the iterative ADP algorithm. Finally, a simulation example is given to illustrate the performance of the developed algorithm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Khalaf M, Lewis FL (2005) Nearly optimal control laws for nonlinear systems with saturating actuators using a neural network HJB approach. Automatica 41(5):779–791
Al-Tamimi A, Abu-Khalaf M, Lewis FL (2007) Adaptive critic designs for discrete-time zero-sum games with application to \(H_{\infty }\) control. IEEE Trans Syst Cybern Part B: Cybern 37(1):240–247
Al-Tamimi A, Lewis FL, Abu-Khalaf M (2008) Discrete-time nonlinear HJB solution using approximate dynamic programming: convergence proof. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B: Cybern 38(4):943–949
Bhasin S, Kamalapurkar R, Johnson M, Vamvoudakis KG, Lewis FL, Dixon WE (2013) A novel actor-critic-identifier architecture for approximate optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 49(1):82–92
Bellman RE (1957) Dynamic programming. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Bertsekas DP, Tsitsiklis JN (1996) Neuro-dynamic programming. Athena Scientific, Belmont
Bertsekas DP (2007) Dynamic programming and optimal control, 3rd edn. Athena Scientific, Belmont
Biswas S, Das S, Kundu S, Patra GR (2014) Utilizing time-linkage property in DOPs: an information sharing based artificial bee colony algorithm for tracking multiple optima in uncertain environments. Soft Comput 18(6):1199–1212
Chang HS (2013) On functional equations for \(K\)th best policies in Markov decision processes. Automatica 49(1):297–300
Enns R, Si J (2003) Helicopter trimming and tracking control using direct neural dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14(8):929–939
Fortier N, Sheppard J, Strasser S (2014) Abductive inference in Bayesian networks using distributed overlapping swarm intelligence. Soft Comput (in press). doi:10.1007/s00500-014-1310-0
Heydari A, Balakrishnan SN (2013) Finite-horizon control-constrained nonlinear optimal control using single network adaptive critics. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(1):145–157
Kouramas KI, Panos C, Faisca NP, Pistikopoulos EN (2013) An algorithm for robust explicit/multi-parametric model predictive control. Automatica 49(2):381–389
Kundu S, Das S, Vasilakos AV, Biswas S (2014) A modified differential evolution-based combined routing and sleep scheduling scheme for lifetime maximization of wireless sensor networks. Soft Comput (in press). doi:10.1007/s00500-014-1286-9
Lewis FL, Vrabie D, Vamvoudakis KG (2012) Reinforcement learning and feedback control: using natural decision methods to design optimal adaptive controllers. IEEE Control Syst 32(6):76–105
Lincoln B, Rantzer A (2006) Relaxing dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Autom Control 51(8):1249–1260
Liu D, Javaherian H, Kovalenko O, Huang T (2008) Adaptive critic learning techniques for engine torque and air-fuel ratio control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 38(4):988–993
Liu D, Wei Q (2013) Finite-approximation-error-based optimal control approach for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(2):779–789
Liu D, Wei Q (2014a) Multi-person zero-sum differential games for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. Int J Adaptive Control Signal Process 28(3–5):205–231
Liu D, Wei Q (2014b) Policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(3):621–634
Liu D, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2005) A self-learning call admission control scheme for CDMA cellular networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(5):1219–1228
Mohler RR, Kolodziej WJ (1981) Optimal control of a class of nonlinear stochastic systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 26(5):1048–1054
Murray JJ, Cox CJ, Lendaris GG, Saeks R (2002) Adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C Appl Rev 32(2):140–153
Ni Z, He H (2013) Heuristic dynamic programming with internal goal representation. Soft Comput 17(11):2101–2108
Powell WB (2007) Approximate dynamic programming. Wiley, Hoboken
Prokhorov DV, Wunsch DC (1997) Adaptive critic designs. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 8(5):997–1007
Rubio JDJ (2014) Adaptive least square control in discrete time of robotic arms. Soft Comput (in press). doi:10.1007/s00500-014-1300-2
Rugh WJ (1971) System equivalence in a class of nonlinear optimal control problems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 16(2):189–194
Si J, Wang YT (2001) On-line learning control by association and reinforcement. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(2):264–276
Song R, Xiao W, Wei Q (2013) Multi-objective optimal control for a class of nonlinear time-delay systems via adaptive dynamic programming. Soft Comput 17(11):2109–2115
Song R, Xiao W, Wei Q, Sun C (2014) Neural-network-based approach to finite-time optimal control for a class of unknown nonlinear systems. Soft Comput 18(8):1645–1653
Sutton RS, Barto AG (1998) Reinforcement learning: an introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge
Wang F, Zhang H, Liu D (2009) Adaptive dynamic programming: an introduction. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 4(2):39–47
Wang F, Jin N, Liu D, Wei Q (2011) Adaptive dynamic programming for finite-horizon optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems with \(\epsilon \)-error bound. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(1):24–36
Wei Q, Liu D (2012) An iterative \(\epsilon \)-optimal control scheme for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems with unfixed initial state. Neural Netw 32:236–244
Wei Q, Liu D (2013) Numerical adaptive learning control scheme for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IET Control Theory Appl 7(11):1472–1486
Wei Q, Wang D, Zhang D (2013) Dual iterative adaptive dynamic programming for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems with time-delays. Neural Comput Appl 23(7–8):1851–1863
Wei Q, Liu D (2014a) Adaptive dynamic programming for optimal tracking control of unknown nonlinear systems with application to coal gasification. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 11(4):1020–1036
Wei Q, Liu D (2014b) A novel iterative \(\theta \)-adaptive dynamic programming for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 11(4):1176–1190
Wei Q, Liu D (2014c) Data-driven neuro-optimal temperature control of water gas shift reaction using stable iterative adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(11):6399–6408
Wei Q, Liu D (2014d) Stable iterative adaptive dynamic programming algorithm with approximation errors for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Neural Comput Appl 24(6):1355–1367
Wei Q, Liu D, Shi G (2014) A novel dual iterative Q-learning method for optimal battery management in smart residential environments. IEEE Trans Ind Electron (in press). doi:10.1109/TIE.2014.2361485
Wei Q, Wang F, Liu D, Yang X (2014) Finite-approximation-error based discrete-time iterative adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Cybern (in press). doi:10.1109/TCYB.2014.2354377
Wei Q, Zhang H, Dai J (2009) Model-free multiobjective approximate dynamic programming for discrete-time nonlinear systems with general performance index functions. Neurocomputing 72(7–9):1839–1848
Werbos PJ (1977) Advanced forecasting methods for global crisis warning and models of intelligence. General Syst Yearb 22:25–38
Werbos PJ (1991) A menu of designs for reinforcement learning over time. In: Miller WT, Sutton RS, Werbos PJ (eds) Neural Netw Control. MIT Press, Cambridge
Werbos PJ (1992) Approximate dynamic programming for real-time control and neural modeling. In: White DA, Sofge DA (eds) Handbook of intelligent control: neural, fuzzy, and adaptive approaches. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Xu H, Jagannathan S (2013) Stochastic optimal controller design for uncertain nonlinear networked control system via neuro dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(3):471–484
Zhang H, Cui L, Luo Y (2013) Near-optimal control for nonzero-sum differential games of continuous-time nonlinear systems using single-network ADP. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(1):206–216
Zhang D, Liu D, Wang D (2014) Approximate optimal solution of the DTHJB equation for a class of nonlinear affine systems with unknown dead-zone constraints. Soft Comput 18(2):349–357
Zhang H, Luo Y, Liu D (2009) The RBF neural network-based near-optimal control for a class of discrete-time affine nonlinear systems with control constraint. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(9):1490–1503
Zhang H, Wei Q, Luo Y (2008) A novel infinite-time optimal tracking control scheme for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems via the greedy HDP iteration algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 38(4):937–942
Zhang H, Wei Q, Liu D (2011) An iterative adaptive dynamic programming method for solving a class of nonlinear zero-sum differential games. Automatica 47(1):207–214
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61034002, 61374105, 61233001, and 61273140, in part by Beijing Natural Science Foundation under Grant 4132078, in part by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant FRF-TP-14-119A2, and in part by the Open Research Project from SKLMCCS under Grant 20120106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Q., Liu, D. & Xu, Y. Neuro-optimal tracking control for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems via generalized value iteration adaptive dynamic programming approach. Soft Comput 20, 697–706 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1533-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1533-0