Abstract
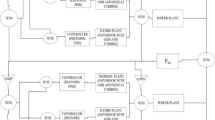
This paper, presents the particle swarm optimization-based fuzzy logic controller (PSO FLC) design for load frequency control in a two-area interconnected hydrothermal power system. Flexible alternating current transmission system devices and energy storage devices are being installed to improve the reliability and stability of the system under dynamic conditions. One such devices namely thyristor-controlled phase shifter (TCPS) is connected in series with the tie-line to damp out the power swings and frequency oscillations. Similarly at the terminal of one control area, a fast acting energy storage device of superconducting magnetic energy storage (SMES) is connected to meet the sudden changes in demand. The existing conventional controllers are unable to provide the satisfactory performance over a wide range of operating conditions due to system nonlinearity and plant parameter variations. To improve the dynamic performance of the system, this work proposes an intelligent tuning approach using a combination of particle swarm optimization (PSO) and fuzzy logic technique. In this work, PSO algorithm is employed for the optimal selection of membership function parameters of the proposed fuzzy PI, TCPS and SMES controllers by minimizing the time domain objective function. The simulation study is performed by the proposed PSO FLC in a two-area interconnected power system. To show the effective performance of the proposed controller, a comparative study has been made with the conventional, genetic algorithm and fuzzy logic-based optimized controller under varying load conditions.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Abbreviations
- \(T_{p1}\), \(T_{p2 }\) :
-
Generator time constants
- \(K_1, K_2\) :
-
Generator gains
- \(T_{gi}\) :
-
Thermal unit governor time constant
- \(T_{ri, }\)T\(_{ti }\) :
-
Thermal unit reheat time constant
- \(K_{ri }\) :
-
Reheater gain
- \(T_{w }\) :
-
Hydro unit water time constant
- \(T_{Ri}\), \(T_{Hi }\) :
-
Hydro turbine time constants
- \(T_{hi }\) :
-
Hydro unit governor time constant
- \(R_{i}\) :
-
Governor speed regulation of the units of two areas (\(i = 1, 2\))
- \(P_{r1}\), \(P_{r2 }\) :
-
Rated area capacities (\(a12 = P_{r1}/P_{r2})\)
- \(T_{12 }\) :
-
Synchronizing coefficient
- \(B_{i}\) :
-
Frequency bias coefficient (\(i =1, 2\))
- \(T_{s }\) :
-
Settling time
- \(T_{p }\) :
-
Peak time
- \(K_\mathrm{TCPS }\) :
-
Gain constant of TCPS
- \(T_\mathrm{TCPS }\) :
-
Time constant of TCPS
- \(K_\mathrm{SMES }\) :
-
Gain constant of SMES
- \(T_\mathrm{SMES }\) :
-
Time constant of SMES
- \(T_{1}\), \(T_{2}\), \(T_{3}\), \(T_{4 }\) :
-
Time constants of phase compensation block
- \(K_\mathrm{p}\), \(K_\mathrm{i}\) :
-
Proportional and integral gain of PI controller
References
Abraham RJ, Das D, Patra A (2009) AGC study of a hydrothermal system with SMES and TCPS. Eur Trans Electr Power 19:487–498. doi:10.1002/etep.235
Abraham RJ, Das D, Patra A (2007) Effect of TCPS on oscillations in tie-power and area frequencies in an interconnected thermal power system. IET Gener Transm Distrib 1:632–639. doi:10.1049/iet-td:20060361
Ali ES, Abd-Elazim SM (2011) Bacteria foraging optimization algorithm based load frequency controller for interconnected power system. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33:633–638. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2010.12.022
Allen WJ, Wollenberg BF (1994) Power generation, operation and control. Wiley, New York
Arivoli R, Chidambaram IA (2012) CPSO based LFC for a two-area power system with GDB and GRC nonlinearities interconnected through TCPS in series with the tie-line. Int J Comput Appl 38:1–10. doi:10.5120/4697-6846
Bevrani H et al (2012) Intelligent frequency control in an AC microgrid: online PSO-based fuzzy tuning approach. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 3:1935–1944. doi:10.1109/TSG.2012.2196806
Bevrani H, Daneshmand PR (2012) Fuzzy logic-based Load-frequency control concerning high penetration of wind turbines. IEEE Syst J 6:173–180. doi:10.1109/JSYST.2011.2163028
Bhatt P, Roy R, Ghoshal SP (2011) Comparative performance evaluation of SMES- SMES, TCPS-SMES and SSSC-SMES controllers in automatic generation control for a two area hydro- hydro system. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33:1585–1597. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2010.12.015
Bhatt P, Ranjit R, Ghosal SP (2010) GA/particle swarm intelligence based optimization of two specific varieties of controller devices applied to two-area multi-units automatic generation control. Int. Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 32: 299–310. doi.10.1016/j.ijpes.2009.09.004
Bouallegue S et al (2012) PID-type fuzzy logic controller tuning based on particle swarm optimization. Int J Eng Appl Artif Intell 25:484–493
Bouallegue S, Haggege J, Ayadi M, Benrejeb M (2012) PID-type fuzzy logic controller tuning based on particle swarm optimization. Eng Appl Artif Intell 25:484–493. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2011.09.018
Castillo O, Melin P (2012) A review on the design and optimization of interval type-2 fuzzy controllers. Appl Soft Comput 12:1267–1278. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2011.12.010
Cazarez-Castro NR, Aguilar L, Castillo O (2008) Hybrid genetic-fuzzy optimization of a type-2 fuzzy logic controller. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on hybrid intelligent systems, Barcelona, pp 216–221. doi:10.1109/HIS.2008.170
del Valle Y et al. (2008) Particle swarm optimization: basic concepts, variants and applications in power systems. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12:171–195. doi:10.1109/TEVC.2007.896686
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the 6\(^{th}\) int. symp. micro mach. hum. sci., Nagoya, pp 39–43. doi:10.1109/MHS.1995.494215
Elgerd Olle I (2006) Electric energy systems theory. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Farhangi R, Boroushaki M, Hosseini SH (2012) Load-frequency control of interconnected power system using emotional learning-based intelligent controller Int. J Electr Power Energy Syst 36:76–83. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2011.10.026
Fierro R, Castillo O, Valdez F (2013) Optimization of fuzzy control systems with different variants of particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference hybrid intelligent models and applications, Singapore, pp 51–56. doi:10.1109/HIMA.2013.6615022
IEEE Committee Report (1973) Dynamic models for steam and hydro turbines in power system studies. IEEE Trans Power Appar Syst PAS-92:1904–15. doi:10.1109/TPAS.1973.293570
Ise T, Mitani Y, Suji T (1986) Simultaneous active and reactive power control of superconducting magnetic energy storage using GTO converter. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 1:143–150. doi:10.1109/TPWRD.1986.4307900
Juang CF, Lu CF (2002) Power system load frequency control with fuzzy gain scheduling designed by new genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems, Honolulu, pp 64–68. doi:10.1109/FUZZ.2002.1004961
Juang CF, Lu CF (2006) Load-frequency control by hybrid evolutionary fuzzy controller. IEE Proc Gener Transm Distrib 153:196–204
Kocaarslan I, Cam K (2005) Fuzzy logic controller in interconnected electrical power systems for load-frequency control. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 27:542–549. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2005.06.003
Kundur P (1994) Power system stability and control. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Kunish HJ, Kramer KG, Domnik H (1986) Battery energy storage—another option for load frequency control and instantaneous reserve. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 1:41–46. doi:10.1109/TEC.1986.4765732
Lee J (1993) On methods for improving performance of PI-type fuzzy logic controllers. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 1:298–301. doi:10.1109/91.251930
Liang JJ, Ponnuthurai Nagaratnam Suganthan AK, Baskar S (2006) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizerfor global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10:281–295. doi:10.1109/TEVC.2005.857610
Liu X, Zhan X, Qian D (2010) Load frequency control considering generation rate constraints. In: Proceedings of the 8th world congress on intelligent control and automation, Jinan, 1398–1401. doi:10.1109/WCICA.2010.55548
Maldonado Y, Castillo O, Melin P (2013) Particle swarm optimization of interval type-2 fuzzy systems for FPGA applications. Appl Soft Comput 13:496–508. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2012.08.032
Mathur HD (2006) A comprehensive analysis of intelligent controllers for load frequency control. Power India Conf. doi:10.1109/POWERI.2006.1632619
Melin P, Olivas F, Castillo O et al (2013) Optimal design of fuzzy classification systems using PSO with dynamic parameter adaptation through fuzzy logic. Expert Syst Appl 40:3196–3206. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2012.12.033
Oh SK, Jang HJ, Pedrycz W (2011) A comparative experimental study of type-1/type-2 fuzzy cascade controller based on genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 38:11217–11229. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2011.02.169
Rasolomampionona D, Anwar S (2011) Interaction between phase shifting transformers installed in the tie-lines of interconnected power systems and automatic frequency controllers. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33:1351–1360. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2011.06.001
Siano P, Citro C (2014) Designing fuzzy logic controllers for DC–DC converters using multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Electr Power Syst Res 112:74–83. doi:10.1016/j.epsr.2014.03.010
Thiruppathi U, Prakash Ayyappan B, Balaganapath G (2013) Load frequency control of an interconnected power system using thyristor controlled phase shifter. Int J Eng Res Technol 2:2971–2977
Timothy J, Rose NR (2010) Fuzzy logic with engineering applications. Wiley, UK
Tripathy SC, Juengst KP (1997) Sampled data generation control with superconducting magnetic energy storage in power systems. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 12:187–192. doi:10.1109/60.629702
Wagner C, Hagras H (2007) A genetic algorithm based architecture for evolving type-2 fuzzy logic controllers for real world autonomous mobile robots. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems, London. doi:10.1109/FUZZY.2007.4295364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Appendix
Appendix
Power system data
\(B_{1} = B_{2} = 0.545\) Hz/pu MW; \(T_{12} = 0.545\) pu;
\(R_{1} = R_{2} = 2.4\) Hz/pu MW; \(P_{r1} = P_{r2} = 1500\) MW;
Nominal load = 1250 MW (each area)
Generator data
\(T_{p1 }= T_{p2 }= 20 \mathrm{s}; K1=K2=120\) Hz/pu MW.
Thermal unit data
\(T_{g1 }= T_{g2 =} 0.08\,\mathrm{s}; T_{r1 }= T_{r2 }= 10.2 \)s;
\(T_{t1 }= T_{t2 }= 0.3\,\mathrm{s}; K_{r1 }=K_{r2 }= 3\) Hz/pu MW.
Hydro unit data
\(T_{R1 }= T_{R2 }= 4.9 \mathrm{s}; T_{h1 }= T_{h2 }= 0.2\) s
\(T_{H1 }= T_{H2 }= 28.75\,\mathrm{s}; T_{w }= 1\) s
TCPS data
Rating = 2 MVA; \(\Phi _\mathrm{min} = -10^{\circ }; \Phi _\mathrm{max} = 10^{\circ }\);
\(K_\mathrm{TCPSmin} = -2; K_\mathrm{TCPSmax} = 2; T_{TCPS} = 1.5\) s;
SMES data
Rating = 1.25 MVA; \(K_\mathrm{SMESmin} = 0.2\);
\(K_\mathrm{SMESmax} = 4; T_\mathrm{SMES }= 0.01\) s;
\(T_{1 }= 0.3\,\mathrm{s}; T_{2 }= 0.02\,\mathrm{s}; T_{3} = 0.8\,\mathrm{s}; T_{4} = 0.4\) s.
PI controller data
\(K_\mathrm{pmin} = -10; K_\mathrm{pmax} = 10; K_\mathrm{imin} = -2; K_\mathrm{imax} = 2\).
PSO parameters
No of particles = 50; \(c_{1} = c_{2} = 2; W_\mathrm{max} = 0.9\);
\(W_\mathrm{min }= 0.2; \mathrm{Iter}_\mathrm{max }= 50; V_\mathrm{max} = 0.2; V_\mathrm{min }= -0.2\)
GA parameters
No of generation = 100; population size = 50;
Cross over probability = 0.6;
Mutation probability = 0.03.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeyalakshmi, V., Subburaj, P. PSO-scaled fuzzy logic to load frequency control in hydrothermal power system. Soft Comput 20, 2577–2594 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1659-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1659-8