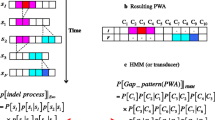
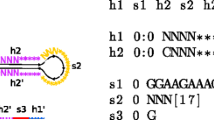
Abstract
Transposable elements (TEs) are DNA sequences that can either move or copy themselves to new positions within a genome. They constitute approximately 45 % of the human genome. Knowing the evolution of TEs is helpful in understanding the activities of these elements and their impacts on genomes. In this paper, we devise a formal model providing notations/definitions that are compatible with biological nomenclature, while still providing a suitable formal foundation for computational analysis. We define sequential interruptions between TEs that occur in a genomic sequence to estimate how often TEs interrupt other TEs, useful in predicting their ages. We also describe the problem in terms of a matrix problem—the linear ordering problem. We then define the recursive interruption context-free grammar to capture the recursive nature in which TEs nest themselves into other TEs, and associate probabilities to convert the context-free grammar into a stochastic context-free grammar, as well as discuss how to use the CYK algorithm to find a most likely parse tree predicting TE nesting. We also discuss improvements on the theoretical model and adjust the parse trees to capture both sequential and recursive interruptional activities between TEs and obtain more standard evolutionary trees.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
hg19, the February 2009 assembly of the human genome.
We calculate the amount that separates them or the amount they overlap using the abs() function to get the absolute value.
References
Bastiani Medina SS, Castilla Valdez G (2012) Iterated local search for the linear ordering problem. Int J Comb Optim Probl Inform 3(1):12–20
Batzer M, Deininger P, Hellmann-Blumberg U, Jurka J, Labuda D, Rubin C, Schmid C, Zietkiewicz E, Zuckerkandl E (1996) Standardized nomenclature for alu repeats. J Mol Evolut 42(1):3–6
Belancio V, Roy-Engel A, Deininger P (2010) All y’all need to know ’bout retroelements in cancer. In: Seminars in Cancer Biology, vol 20. Elsevier, pp 200–210
Bergman CM, Quesneville H (2007) Discovering and detecting transposable elements in genome sequences. Brief Bioinform 8(6):382–392
Caspi A, Pachter L (2006) Identification of transposable elements using multiple alignments of related genomes. Genome Res 16(2):260–270
Charon I, Hudry O (2006) A branch-and-bound algorithm to solve the linear ordering problem for weighted tournaments. Discrete Appl Mathematics 154(15):2097–2116
Decani JS (1972) A branch and bound algorithm for maximum likelihood paired comparison ranking. Biometrika 59(1):131–135
de Koning AJ, Gu W, Castoe TA, Batzer MA, Pollock DD (2011) Repetitive elements may comprise over two-thirds of the human genome. PLoS Genetics 7(12):e1002,384
Durbin R, Eddy S, Krogh A, Mitchison G (1998) Biological sequence analysis: probabilistic models of proteins and nucleic acids. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Feo TA, Resende MG (1995) Greedy randomized adaptive search procedures. J Global Optim 6(2):109–133
Finnegan DJ (1989) Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genetics 5:103–107
Garey M, Johnson D (1979) Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP completeness, vol 174. Freeman, San Francisco
Giordano J, Ge Y, Gelfand Y, Abrusán G, Benson G, Warburton P (2007) Evolutionary history of mammalian transposons determined by genome-wide defragmentation. PLoS Comput Biol 3(7):e137
Glover F, Laguna M (2013) Tabu search. Springer, New York
Gregory T (2005) The evolution of the genome. Academic Press, New York
Hansen P, Mladenović N (2003) Variable neighborhood search. Springer, New York
Hopcroft JE (2008) Introduction to automata theory, languages, and computation. Pearson Education India, India
Jones NC, Pevzner P (2004) An introduction to bioinformatics algorithms. MIT press, Cambridge
Jurka J, Kapitonov V, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, Walichiewicz J (2005) Repbase update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet Genome Res 110(1–4):462–467
Kapitonov V, Jurkal J (1996) The age of alu subfamilies. J Mol Evolut 42(1):59–65
Kirkpatrick S, Vecchi M et al (1983) Optimization by simmulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680
Korte B, Oberhofer W (1968) Zwei algorithmen zur lösung eines komplexen reihenfolgeproblems. Unternehmensforschung Oper Res Recherche Opérationnelle 12:217–231
Korte B, Oberhofer W (1970) Triangularizing input-output matrices and the structure of production. Eur Econ Rev 1(4):482–511
Kronmiller BA, Wise RP (2008) TEnest: automated chronological annotation and visualization of nested plant transposable elements. Plant Physiol 146(1):45–59
Laguna M, Marti R, Martí RC (2003) Scatter search: methodology and implementations in C, vol 24. Springer, New York
Lander E, Linton L, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody M, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W et al (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409(6822):860–921
Lerat E (2009) Identifying repeats and transposable elements in sequenced genomes: how to find your way through the dense forest of programs. Heredity 104(6):520–533
Loureiro T, Camacho R, Vieira J, Fonseca NA (2013) Improving the performance of transposable elements detection tools. J Integr Bioinform 10(3):231
Martí R, Reinelt G (2011) The linear ordering problem: exact and heuristic methods in combinatorial optimization, vol 175. Springer, New York
Martí R, Reinelt G, Duarte A (2012) A benchmark library and a comparison of heuristic methods for the linear ordering problem. Comput Optim Appl 51(3):1297–1317
McClintock B (1951) Chromosome organization and genic expression. In: Cold spring harbor symposia on quantitative biology, vol 16. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, pp 13–47
Schiavinotto T, Stützle T (2004) The linear ordering problem: instances, search space analysis and algorithms. J Mathematical Model Algorithms 3(4):367–402
Smit A, Toth G, Riggs A, Jurka J (1995) Ancestral, mammalian-wide subfamilies of LINE-1 repetitive sequences. J Mole Biol 246(3):401–417
Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P (2013–2015) RepeatMasker Open-4.0. http://www.repeatmasker.org
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O et al (2007) A unified classification system for Eukaryotic transposable elements. Nature Rev Genetics 8(12):973–982
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C.M. Vide.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, L., McQuillan, I. Computational modelling of interruptional activities between transposable elements using grammars and the linear ordering problem. Soft Comput 20, 19–35 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1725-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1725-2