Abstract
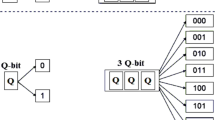
Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithms (QIEAs) combine the advantages of quantum-inspired bit (Q-bit), representation and operators with evolutionary algorithms for better performance. Using quantum-inspired representation the complete binary search space can be generated by collapsing a single Q-bit string repeatedly. Thus, even a population size of 1 can be taken in a QIEA implementation resulting in enormous saving in computation. Although this is correct in theory, QIEA implementations run into trouble in exploring large search spaces with this approach. The Q-bit string has to be initialized to produce each possible binary string with equal probability and then altered slowly to probabilistically favor generation of strings with better fitness values. This process is unacceptably slow when the search spaces are very large. Many ideas have been reported with EAs/QIEAs for speeding up convergence while ensuring that the algorithm does not get stuck in local optima. In this paper, the possible features are identified and systematically introduced and tested in the QIEA framework in various combinations. Some of these features increase the randomness in the search process for better exploration and the others compensate by local search for better exploitation together enabling a judicious combination tailored for particular problem being solved. This is referred to as “right-sizing the randomness” in the QIEA search. Benchmark instances of the well-known and well-studied Quadratic Knapsack Problem are used to demonstrate how effective these features are—individually and collectively. The new framework, dubbed QIEA-QKP, is shown to be much more effective than canonical QIEA. The framework can be utilized with profit on other problems and is being attempted.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Bäck T (1996) Evolutionary algorithms in theory and practice: evolution strategies, evolutionary programming, genetic algorithms. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Billionet A, Soutif E (2004) QKP instances. [Online] http://cedric.cnam.fr/soutif/QKP/QKP.html. Accessed 15 February 2013
Caprara A, Pisinger D, Toth P (1999) Exact solution of the quadratic knapsack problem. Inf J Comput 11(2):125–137
Dijkhuijen G, Faigle U (1993) A cutting-plane approach to he edge-weighted maximal clique problem. Eur J Oper Res 69:121–130
Engebretsen L, Holmerin J (2000) Clique is hard to approximate within n1-o(1). In: Proceedings of 27th international colloquium, ICALP 2000, vol 1853. Springer, Berlin, pp 2–12
Ferreira CE, Martin A, deSouza CC (1996) Formulations and valid inequalities for node capacitated graph partitioning. Math Program 74:247–266
Gallo G, Hammer P, Simeone B (1980) Quadratic knapsack problems. Math Program Study 12:132–149
Han K-H (2006) On the analysis of the quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm with a single individual. In: Proceedings of CEC’06, Vancouver, Canada, pp 2622–2629
Han K-H, Kim J-H (2002) Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for a class of combinatorial optimization. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 6(6):580–593
Han K-H, Kim J-H (2003) On setting the parameters of quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for practical application. In: Proceedings of CEC 2003, vol 1, pp 178–194
Han K-H, Kim J-H (2004) Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithms with a new termination criterion, h-epsilon gate, and two-phase scheme. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 8(2):156–169
Han K, Park K, Lee C, Kim J (2001) Parallel quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for combinatorial optimization problem. In: Proceedings of CEC 2001, vol 2, pp 1422–1429
Imabeppu T, Nakayama S, Ono S (2008) A study on a quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm based on pair swap. Artif Life Robot 12:148–152
Johnson E, Mehrotra A, Nemhauser G (1993) Min-cut clustering. Math Program 62:133–151
Julstorm BA (2005) Greedy, genetic and greedy genetic algorithms for the quadratic knapsack problem. In: Proceedings of GECCO 2005, Washingtom DC, USA, pp 607–614
Kellerer H, Pferschy U, Pisinger D (2004) Knapsack problems. Springer, Berlin
Kim Y, Kim JH, Han KH (2006) Quantum-inspired multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for multiobjective 0/1 knapsack problems. In: Proceedings of CEC 2006, pp 2601–2606
Laghhunn DL (1970) Quadratic binary programming with applications to capital budgetting problems. Oper Res 18:454–461
Li Z, Rudolph G, Li K (2009) Convergence performance comparison of quantum-inspired multi-objective evolutionary algorithms. Comput Math Appl 57:1843–1854
Lu TC, Yu GR (2013) An adaptive population multi-objective quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for multi-objective 0/1 knapsack problems. Inf Sci 243:39–56
Mahdabi P, Jalili S, Abadi M (2008) A multi-start quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for solving combinatorial optimization problems. In: Proceedings of GECCO ’08, pp 613–614
Nowotniak R, Kucharski J (2012) GPU-based tuning of quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for a combinatorial optimization problem. Bull Pol Acad Sci Tech Sci 60(2):323–330
Park K, Lee K, Park S (1996) An extended formulation approach to the edge weighted maximal cliqur problem. Eur J Oper Res 95:671–682
Patvardhan C, Narayan A, Srivastav A (2007) Enhanced quantum evolutionary algorithms for difficult knapsack problems. In: Proceedings of PReMI’07. Springer, Berlin, pp 252–260
Patvardhan C, Prakash P, Srivastav A (2012) A novel quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for the quadratic knapsack problem. Int J Math Oper Res 4(2):114–127
Patvardhan C, Bansal S, Srivastav A (2014a) Solution of “Hard” knapsack instances using quantum inspired evolutionary algorithm. Int J Appl Evolut Comput 5(1):52–68
Patvardhan C, Bansal S, Srivastav A (2014b) Balanced quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for multiple knapsack problem. Int J Intell Syst Appl 11:1–11
Pisinger D (2007) The quadratic knapsack problem—a survey. Discrete Appl Math 155:623–648
Platel M D, Schliebs S, Kasabov N (2007) A versatile quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm. In: Proceedings of CEC’07, pp 423–430
Platel MD, Schliebs S, Kasabov N (2009) Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm: a multimodel EDA. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 13(6):1218–1232
Qin Y, Zhang G, Li Y, Zhang H (2012) A comprehensive learning quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm. In: Qu X, Yang Y (eds) LNCS, IBI 2011, Part-II, CCIS 268, pp 151–157
Rhys J (1970) A selection problem of shared fixed costs and network flows. Manag Sci 17:200–207
Tayarani-N M-H, Akbarzadeh-T M-R (2008) A sinusoid size ring structure quantum evolutionary algorithm. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference on cybernetics and intelligent systems, pp 1165–1170
Witzall C (1975) Mathematical methods of site selection for electronic message system (EMS). In: Technical report, NBS internal report Washington, DC. Operational Research Section
Xie X, Liu J (2007) A mini-swarm for the quadratic knapsack problem. In: Proceedings of IEEE swarm intelligence symposium, Honolulu, USA, pp 190–197
Zhang G, Gheorghe M, Wu CZ (2008) A quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm based on p systems for knapsack problem. Fund Inf 87(1):93–116
Zhang G (2011) Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithms: a survey and empirical study. J Heurist 17(3):303–351
Zhang G, Gheorghe M, Li Y (2012) A membrane algorithm with quantum-inspired subalgorithms and its application to image processing. Nat Comput 11:701–707
Zhao Z, Peng X, Peng Y, Yu, E (2006) An effective repair procedure based on quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for 0/1 knapsack problems. In: Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS int. conf. on instrumentation, measurement, circuits and systems, Hangzho, pp 203–206
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Department of Science and Technology, India (DST) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Germany (DFG) for the support under Project No. INT/FRG/DFG/P-38/2012 titled “Algorithm Engineering of Quantum Evolutionary Algorithms for Hard Optimization Problems”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patvardhan, C., Bansal, S. & Srivastav, A. Towards the right amount of randomness in quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithms. Soft Comput 21, 1765–1784 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1880-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1880-5