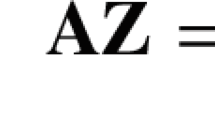Abstract
Robust principal component analysis (RPCA) is one of the most useful tools to recover a low-rank data component from the superposition of a sparse component. The augmented Lagrange multiplier (ALM) method enjoys the highest accuracy among all the approaches to the RPCA. However, it still suffers from two problems, namely, a brutal force initialization phase resulting in low convergence speed and ignorance of other types of noise resulting in low accuracy. To this end, this paper proposes a double-noise, dual-problem approach to the augmented Lagrange multiplier method, referred to as DNDP-ALM, for robust principal component analysis. Firstly, the original ALM method considers sparse noise only, ignoring Gaussian noise, which generally exists in real-world data. In our proposed DNDP-ALM, the data consist of low-rank component, sparse component and Gaussian noise component, with RPCA problem converted to convex optimization. Secondly, the original ALM uses a rough initialization of multipliers, leading to more work of iterative calculation and lower calculation accuracy. In our proposed DNDP-ALM, the initialization is carried out by solving a dual problem to obtain the optimal multiplier. The experimental results show that the proposed approach super-performs in solving robust principal component analysis problems in terms of speed and accuracy, compared to the state-of-the-art techniques.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Bao BK, Liu G, Xu C, Yan S (2012) Inductive robust principal component analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(8):3794–3800
Beck A, Teboulle M (2009) A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J Imag Sci 2(1):183–202
Bishop CM et al (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning, vol 1. Springer, New York
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2009) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Candès EJ, Li X, Ma Y, Wright J (2011) Robust principal component analysis? J ACM (JACM) 58(3):11
Ding X, He L, Carin L (2011) Bayesian robust principal component analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(12):3419–3430
Duong TD, Nguyen HV (2012) Some extension of sparse principal component analysis. Int J Mach Learn Comput 2:701–705
Eckart C, Young G (1936) The approximation of one matrix by another of lower rank. Psychometrika 1(3):211–218
Gao J (2008) Robust l1 principal component analysis and its bayesian variational inference. Neural Comput. 20(2):555–572
He R, Hu B-G, Zheng W-S, Kong X-W (2011) Robust principal component analysis based on maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(6):1485–1494
He R, Tan T, Wang L (2013) Robust recovery of corrupted low-rank matrix by implicit regularizers. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, p 1
Jolliffe I (2005) Principal Component Analysis. Wiley Online Library, New York
Lin Z, Ganesh A, Wright J, Wu L, Chen M, Ma Y (2009) Fast convex optimization algorithms for exact recovery of a corrupted low-rank matrix. In: International workshop on computational advances in multi-sensor adaptive processing. Aruba, Dutch Antilles, pp 1–18
Lin Z, Chen M, Ma Y (2010) The augmented lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. arXiv:1009.5055
Luttinen J, Ilin A, Karhunen J (2012) Bayesian robust PCA of incomplete data. Neural Process Lett 36(2):189–202
Moore B (1981) Principal component analysis in linear systems: controllability, observability, and model reduction. IEEE Trans Autom Control 26(1):17–32
Salakhutdinov R, Mnih A (2008) Bayesian probabilistic matrix factorization using markov chain monte carlo. In: Proceedings of the 25th international conference on machine learning. ACM, New York, pp 880–887
Tenenbaum JB, De Silva V, Langford JC (2000) A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290(5500):2319–2323
Tipping ME, Bishop CM (1999) Probabilistic principal component analysis. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 61(3):611–622
Toh KC, Yun S (2010) An accelerated proximal gradient algorithm for nuclear norm regularized linear least squares problems. Pac J Optim 6(615–640):15
Verbeek J (2006) Learning nonlinear image manifolds by global alignment of local linear models. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell 28(8):1236–1250
Wright J, Ganesh A, Rao S, Peng Y, Ma Y (2009) Robust principal component analysis: exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices via convex optimization. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2009:2080–2088
Zhang T, Lerman G (2014) A novel M-estimator for robust PCA. J Mach Learn Res 15(1):749–808
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) of this publication has research support from Harbin Institute of Technology. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the university in accordance with its policy on objectivity in research.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, D., Yang, J., Wang, J. et al. Double-noise-dual-problem approach to the augmented Lagrange multiplier method for robust principal component analysis. Soft Comput 21, 2723–2732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1976-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1976-y