Abstract
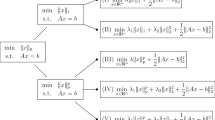
\(\ell _1\)-regularization-based sparse recovery has received a considerable attention over the last decade. In this paper, a solver called SQNSR is proposed to recover signals with high dynamic range. SQNSR utilizes linear search strategy and quasi-Newton step to the solve composite objective function for the sparse recovery problem. Since \(\ell _1\)-norm-regularized item is nonsmooth, smoothing technique is introduced to obtain an approximate smoothed function. The sufficient and necessary condition is also derived for the feasible smoothed objective function. By limiting the step length in each iteration, the convergence of SQNSR is guaranteed to obtain the sparsest solution. Numerical simulations are implemented to test the performance of the proposed approach and verify the theoretical analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Zahhad MM, Hussein AI, Mohamed AM (2015) Compressive sensing algorithms for signal processing applications: a survey. Int J Commun Netw Syst Sci 08(5):197–216
Andrei N (2006) An acceleration of gradient descent algorithm with backtracking for unconstrained optimization. Numer Algorithms 42(1):63–73
Armijo L (1966) Minimization of functions having lipschitz continuous first partial derivatives. Pac J Math 16(1):1–3
Asif MS, Romberg J (2013) Fast and accurate algorithms for re-weighted \(\ell _1\)-norm minimization. IEEE Trans Signal Process 61(23):5905–5916
Asif MS, Romberg J (2014) Sparse recovery of streaming signals using \(\ell _1\)-homotopy. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62(16):4209–4223
Babakmehr M, Simões MG, Wakin MB, Durra AA, Harirchi F (2016a) Smart-grid topology identification using sparse recovery. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 52(5):4375–4384
Babakmehr M, Simões MG, Wakin MB, Harirchi F (2016b) Compressive sensing-based topology identification for smart grids. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 12(2):532–543
Baraniuk R, Candès EJ, Elad M, Ma Y (2010) Applications of sparse representation and compressive sensing [scanning the issue]. Proc IEEE 98(6):906–909
Beck A, Teboulle M (2009a) Fast gradient-based algorithms for constrained total variation image denoising and deblurring problems. IEEE Trans Image Process 18(11):2419–2434
Beck A, Teboulle M (2009b) A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J Imaging Sci 2(1):183–202
Beck A, Teboulle M (2012) Smoothing and first order methods: a unified framework. SIAM J Optim 22(2):557–580
Becker S, Bobin J, Candès E (2011a) NESTA: A fast and accurate first-order method for sparse recovery. SIAM J Imaging Sci 4(1):1–39
Becker S, Fadili MJ, et al (2012) A quasi-Newton proximal splitting method. In: NIPS, pp 2627–2635
Becker SR, Candès EJ, Grant MC (2011b) Templates for convex cone problems with applications to sparse signal recovery. Math Program Comput 3(3):165–218
Bhotto MZA, Ahmad MO, Swamy MNS (2015) An improved fast iterative shrinkage thresholding algorithm for image deblurring. SIAM J Imaging Sci 8(3):1640–1657
Bioucas-Dias JM, Figueiredo MA (2007) A new twist: two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms for image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(12):2992–3004
Birgin EG, Martínez JM, Raydan M (2000) Nonmonotone spectral projected gradient methods on convex sets. SIAM J Optim 10(4):1196–1211
Bouchech HJ, Foufou S, Koschan A, Abidi M (2015) A kernelized sparsity-based approach for best spectral bands selection for face recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 74(19):8631–8654
Candès EJ, Romberg J, Tao T (2006a) Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52(2):489–509
Candès EJ, Romberg JK, Tao T (2006b) Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun Pure Appl Math 59(8):1207–1223
Candès EJ, Eldar YC, Needell D, Randall P (2011) Compressed sensing with coherent and redundant dictionaries. Appl Comput Harmonic Anal 31(1):59–73
Cetin M, Stojanovic I, Onhon O, Varshney K, Samadi S, Karl WC, Willsky AS (2014) Sparsity-driven synthetic aperture radar imaging: Reconstruction, autofocusing, moving targets, and compressed sensing. IEEE Signal Process Mag 31(4):27–40
Chambolle A, Dossal C (2015) On the convergence of the iterates of the “fast iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithm”. J Optim Theory Appl 166(3):968–982
Chen L, Gu Y (2015) On the null space constant for \(\ell _p\) minimization. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(10):1600–1603
Costa F, Batatia H, Chaari L, Tourneret JY (2015) Sparse EEG source localization using Bernoulli laplacian priors. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 62(12):2888–2898
Craven D, McGinley B, Kilmartin L, Glavin M, Jones E (2015) Compressed sensing for bioelectric signals: a review. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 19(2):529–540
Daubechies I, Defrise M, De Mol C (2004) An iterative thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems with a sparsity constraint. Commun Pure Appl Math 57(11):1413–1457
Donoho DL (2006) For most large underdetermined systems of linear equations the minimal \(\ell _1\)-norm solution is also the sparsest solution. Commun Pure Appl Math 59(6):797–829
Elad M (2006) Why simple shrinkage is still relevant for redundant representations? IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52(12):5559–5569
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2013) Sparse subspace clustering: algorithm, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2765–2781
Figueiredo MAT, Nowak R, Wright S (2007) Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems. IEEE J Sel Topics Signal Process 1(4):586–597
Gasso G, Rakotomamonjy A, Canu S (2009) Recovering sparse signals with a certain family of nonconvex penalties and DC programming. IEEE Trans Signal Process 57(12):4686–4698
Gilbert A, Indyk P (2010) Sparse recovery using sparse matrices. Proc IEEE 98(6):937–947
Goswami G, Mittal P, Majumdar A, Vatsa M, Singh R (2016) Group sparse representation based classification for multi-feature multimodal biometrics. Inf Fusion 32, Part B: 3–12, sI Information Fusion in Biometrics
Gui J, Sun Z, Ji S, Tao D, Tan T (2016) Feature selection based on structured sparsity: a comprehensive study. In: IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, pp (99):1–18
Gutta S, Cheng Q (2016) Joint feature extraction and classifier design for ECG-based biometric recognition. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 20(2):460–468
Hale ET, Yin W, Zhang Y (2008) Fixed-point continuation for \(\ell _1\)-minimization: methodology and convergence. SIAM J Optim 19(3):1107–1130
Han X, Clemmensen L (2016) Regularized generalized Eigen-decomposition with applications to sparse supervised feature extraction and sparse discriminant analysis. Pattern Recognit 49:43–54
He B, Yuan X (2012) Convergence analysis of primal-dual algorithms for a saddle-point problem: From contraction perspective. SIAM J Imaging Sci 5(1):119–149
He C, Hu C, Li X, Yang X, Zhang W (2016a) A parallel alternating direction method with application to compound \(\ell _1\)-regularized imaging inverse problems. Inf Sci 348:179–197
He H, Cai X, Han D (2015a) A class of nonlinear proximal point algorithms for variational inequality problems. Int J Comput Math 92(7):1385–1401
He S, Chen H, Zhu Z, Ward DG, Cooper HJ, Viant MR, Heath JK, Yao X (2015b) Robust twin boosting for feature selection from high-dimensional omics data with label noise. Inf Sci 291:1–18
He S, Zhu Z, Jia G, Tennant D, Huang Q, Tang K, Heath J, Musolesi M, Yao X (2016b) Cooperative co-evolutionary module identification with application to cancer disease module discovery. In: IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation PP(99):1–1
He W, Zhang H, Zhang L, Philips W, Liao W (2016c) Weighted sparse graph based dimensionality reduction for hyperspectral images. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(5):686–690
Hu B, Dai Y, Su Y, Moore P, Zhang X, Mao C, Chen J, Xu L (2016) Feature selection for optimized high-dimensional biomedical data using the improved shuffled frog leaping algorithm. In: IEEE/ACM transactions on computational biology and bioinformatics, pp (99):1–1
Hyder MM, Mahata K (2016) A sparse recovery method for initial uplink synchronization in OFDMA systems. IEEE Trans Commun 64(1):377–386
Jamali S, Bahmanyar A (2016) A new fault location method for distribution networks using sparse measurements. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 81:459–468
Jia X, Lu H, Yang MH (2016) Visual tracking via coarse and fine structural local sparse appearance models. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(10):4555–4564
Jin ZF, Wan Z, Jiao Y, Lu X (2016) An alternating direction method with continuation for nonconvex low rank minimization. J Sci Comput 66(2):849–869
Kim SJ, Koh K, Lustig M, Boyd S, Gorinevsky D (2007) An interior-point method for large-scale \(\ell _1\)-regularized least squares. IEEE J Sel Topics Signal Process 1(4):606–617
Kong H, Lai Z, Wang X, Liu F (2016) Breast cancer discriminant feature analysis for diagnosis via jointly sparse learning. Neurocomputing 177:198–205
Kuppinger P, Durisi G, Bolcskei H (2012) Uncertainty relations and sparse signal recovery for pairs of general signal sets. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 58(1):263–277
Lai Z, Wong WK, Jin Z, Yang J, Xu Y (2012) Sparse approximation to the eigensubspace for discrimination. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(12):1948–1960
Lai Z, Li Y, Wan M, Jin Z (2013a) Local sparse representation projections for face recognition. Neural Comput Appl 23(7–8):2231–2239
Lai Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Tang J, Zhang D (2013b) Sparse tensor discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(10):3904–3915
Lai Z, Wong WK, Xu Y, Zhao C, Sun M (2014a) Sparse alignment for robust tensor learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(10):1779–1792
Lai Z, Xu Y, Chen Q, Yang J, Zhang D (2014b) Multilinear sparse principal component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(10):1942–1950
Lai Z, Xu Y, Jin Z, Zhang D (2014c) Human gait recognition via sparse discriminant projection learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 24(10):1651–1662
Lai Z, Wong WK, Xu Y, Yang J, Zhang D (2016) Approximate orthogonal sparse embedding for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(4):723–735
Li Y, Yu Z, Bi N, Xu Y, Gu Z, Si Amari (2014a) Sparse representation for brain signal processing: a tutorial on methods and applications. IEEE Signal Process Mag 31(3):96–106
Li Y, Yu ZL, Bi N, Xu Y, Gu Z, Amari SI (2014b) Sparse representation for brain signal processing: a tutorial on methods and applications. IEEE Signal Process Mag 31(3):96–106
Liavas AP, Sidiropoulos ND (2015) Parallel algorithms for constrained tensor factorization via alternating direction method of multipliers. IEEE Trans Signal Process 63(20):5450–5463
Liu Y, Tennant DA, Zhu Z, Heath JK, Yao X, He S (2014) DiME: a scalable disease module identification algorithm with application to glioma progression. PLoS ONE 9(2):e86,693
Liu Y, Vos MD, Huffel SV (2015) Compressed sensing of multichannel EEG signals: the simultaneous cosparsity and low-rank optimization. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 62(8):2055–2061
Lu X, Han L, Yu J, Chen X (2015) L1 norm constrained migration of blended data with the fista algorithm. J Geophys Eng 12(4):620
Majidi M, Arabali A, Etezadi-Amoli M (2015a) Fault location in distribution networks by compressive sensing. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 30(4):1761–1769
Majidi M, Etezadi-Amoli M, Fadali MS (2015b) A novel method for single and simultaneous fault location in distribution networks. IEEE Trans Power Syst 30(6):3368–3376
Mei X, Ling H (2011) Robust visual tracking and vehicle classification via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(11):2259–2272
Nesterov Y (2005) Smooth minimization of non-smooth functions. Math Progr 103(1):127–152
Nguyen LH, Tran T, Do T (2014) Sparse models and sparse recovery for ultra-wideband SAR applications. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 50(2):940–958
Olsen PA, öztoprak F, Nocedal J, Rennie SJ (2012) Newton-like methods for sparse inverse covariance estimation. In: NIPS, pp 764–772
Pan H, Jing Z, Lei M, Liu R, Jin B, Zhang C (2013) A sparse proximal Newton splitting method for constrained image deblurring. Neurocomputing 122:245–257
Pant JK, Krishnan S (2014) Compressive sensing of electrocardiogram signals by promoting sparsity on the second-order difference and by using dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 8(2):293–302
Patel VM, Nguyen HV, Vidal R (2015) Latent space sparse and low-rank subspace clustering. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 9(4):691–701
Poian GD, Bernardini R, Rinaldo R (2016) Separation and analysis of fetal-ECG signals from compressed sensed abdominal ECG recordings. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(6):1269–1279
Qu X, Hou Y, Lam F, Guo D, Zhong J, Chen Z (2014) Magnetic resonance image reconstruction from undersampled measurements using a patch-based nonlocal operator. Medical Image Analysis 18(6):843–856, sparse Methods for Signal Reconstruction and Medical Image Analysis
Rosa MJ, Portugal L, Hahn T, Fallgatter AJ, Garrido MI, Shawe-Taylor J, Mourao-Miranda J (2015) Sparse network-based models for patient classification using fMRI. NeuroImage 105:493–506
Shi J, Jiang Q, Zhang Q, Huang Q, Li X (2015) Sparse kernel entropy component analysis for dimensionality reduction of biomedical data. Neurocomputing 168:930–940
Song H, Yang W, Zhong N, Xu X (2016) Unsupervised classification of PolSAR imagery via kernel sparse subspace clustering. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(10):1487–1491
Stanković L, Daković M, Vujović S (2014) Adaptive variable step algorithm for missing samples recovery in sparse signals. IET Signal Process 8(3):246–256
Strohmeier D, Bekhti Y, Haueisen J, Gramfort A (2016) The iterative reweighted mixed-norm estimate for spatio-temporal meg/eeg source reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(10):2218–2228
Sun T, Cheng L (2016) Reweighted fast iterative shrinkage thresholding algorithm with restarts for \(\ell _1\)-\(\ell _1\) minimisation. IET Signal Process 10(1):28–36
Tan Z, Eldar Y, Beck A, Nehorai A (2014) Smoothing and decomposition for analysis sparse recovery. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62(7):1762–1774
Vrahatis M, Androulakis G, Lambrinos J, Magoulas G (2000) A class of gradient unconstrained minimization algorithms with adaptive stepsize. J Comput Appl Math 114(2):367–386
Wang H, Li X (2016) Regularized filters for l1-norm-based common spatial patterns. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 24(2):201–211
Wang K, Chai Y, Su C (2013) Sparsely corrupted stimulated scattering signals recovery by iterative reweighted continuous basis pursuit. Rev Sci Instrum 84(8):083103
Wei L, Balz T, Zhang L, Liao M (2015) A novel fast approach for sar tomography: two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(6):1377–1381
Wolfe P (1969) Convergence conditions for ascent methods. SIAM Rev 11(2):226–235
Wolfe P (1971) Convergence conditions for ascent methods. II: some corrections. SIAM Rev 13(2):185–188
Wright S, Nowak R, Figueiredo MAT (2009) Sparse reconstruction by separable approximation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 57(7):2479–2493
Wu J, Yu G (2014) On the convergence and o(1/n) complexity of a class of nonlinear proximal point algorithms for monotonic variational inequalities. Stat Optim Inf Comput 2(2):105–113
Xiao Y, Zhu H, Wu SY (2013) Primal and dual alternating direction algorithms for \(\ell _1\)-\(\ell _1\)-norm minimization problems in compressive sensing. Comput Optim Appl 54(2):441–459
Xie Y, Zhang W, Li C, Lin S, Qu Y, Zhang Y (2014) Discriminative object tracking via sparse representation and online dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(4):539–553
Xu J, Xu K, Chen K, Ruan J (2015a) Reweighted sparse subspace clustering. Comput Vis Image Underst 138:25–37
Xu Q, Yang D, Tan J, Sawatzky A, Anastasio MA (2016) Accelerated fast iterative shrinkage thresholding algorithms for sparsity-regularized cone-beam ct image reconstruction. Med Phys 43(4):1849–1872
Xu Y, Yu L, Xu H, Zhang H, Nguyen T (2015b) Vector sparse representation of color image using quaternion matrix analysis. IEEE Trans Image Proces 24(4):1315–1329
Yan H, Yang J (2015) Sparse discriminative feature selection. Pattern Recognit 48(5):1827–1835
Yang H, Huang D, Wang Y, Wang H, Tang Y (2016) Face aging effect simulation using hidden factor analysis joint sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(6):2493–2507
Yang J, Zhang Y (2011) Alternating direction algorithms for \(\ell _1\)-problems in compressive sensing. SIAM J Sci Comput 33(1):250–278
Yang J, Gan Z, Wu Z, Hou C (2015) Estimation of signal-dependent noise level function in transform domain via a sparse recovery model. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(5):1561–1572
Yin W, Osher S, Goldfarb D, Darbon J (2008) Bregman iterative algorithms for \(\ell _1\)-minimization with applications to compressed sensing. SIAM J Imaging Sci 1(1):143–168
Zhang C, Zhang T, Li M, Peng C, Liu Z, Zheng J (2016a) Low-dose ct reconstruction via L1 dictionary learning regularization using iteratively reweighted least-squares. Biomed Eng Online 15(1):66
Zhang D, He J, Zhao Y, Du M (2015a) MR image super-resolution reconstruction using sparse representation, nonlocal similarity and sparse derivative prior. Comput Biol Med 58:130–145
Zhang H, Chen X, Du Z, Yan R (2016b) Kurtosis based weighted sparse model with convex optimization technique for bearing fault diagnosis. Mech Syst Signal Process 80:349–376
Zhang H, Zhai H, Zhang L, Li P (2016c) Spectralcspatial sparse subspace clustering for hyperspectral remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(6):3672–3684
Zhang J, Gu Z, Yu ZL, Li Y (2015b) Energy-efficient ECG compression on wireless biosensors via minimal coherence sensing and weighted \(ell_1\) minimization reconstruction. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 19(2):520–528
Zhang J, Shi J, Guang H, Zuo S, Liu F, Bai J, Luo J (2016d) Iterative correction scheme based on discrete cosine transform and L1 regularization for fluorescence molecular tomography with background fluorescence. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(6):1107–1115
Zhang L, Zhou WD, Chen GR, Lu YP, Li FZ (2013) Sparse signal reconstruction using decomposition algorithm. Knowl Based Syst 54:172–179
Zhang Y, Zhou G, Jin J, Zhao Q, Wang X, Cichocki A (2015c) Sparse Bayesian classification of EEG for brain-computer interface. In: IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, pp (99):1–1
Zhao ZQ, Cheung Y, Hu H, Wu X (2016) Corrupted and occluded face recognition via cooperative sparse representation. Pattern Recognit 56:77–87
Zhou G, Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Adalı T, Xie S, Cichocki A (2016) Linked component analysis from matrices to high-order tensors: applications to biomedical data. Proc IEEE 104(2):310–331
Zhu H, Xiao Y, Wu SY (2013a) Large sparse signal recovery by conjugate gradient algorithm based on smoothing technique. Comput Math Appl 66(1):24–32
Zhu Y, Wu J, Yu G (2015) A fast proximal point algorithm for \(\ell _1\)-minimization problem in compressed sensing. Appl Math Comput 270:777–784
Zhu Z, Zhang Y, Ji Z, He S, Yang X (2013b) High-throughput DNA sequence data compression. Brief Bioinform 16(1):1–15
Zonoobi D, Kassim AA (2014) A computationally efficient method for reconstructing sequences of MR images from undersampled k-space data. Med Image Anal 18(6):857–865, sparse Methods for Signal Reconstruction and Medical Image Analysis
Zou C, Kou KI, Wang Y (2016) Quaternion collaborative and sparse representation with application to color face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(7):3287–3302
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61374135 and 61633005. The authors would like to thank Prof. Hong Zhu for his helpful suggestions in improving the performance of the proposed method. The code for FISTA, NESTA and \(\ell _1\_ls\) has helped the authors greatly to implement SQNSR which is presented by Prof. Stephen Becker, Kwangmoo Koh, etc. We are are grateful to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful and constructive comments on this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Chai, Y., Chen, T. et al. Smoothed \(\ell _1\)-regularization-based line search for sparse signal recovery. Soft Comput 21, 4813–4828 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2423-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2423-4