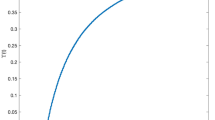
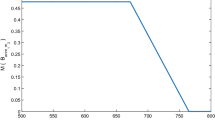
Abstract
In this paper, we study a modified risk model in which both the claim amount and premium are assumed to be random fuzzy variables. In this risk model, some new theorems concerning the mean chance of ultimate ruin time are proved in two cases where the initial surplus is zero and nonzero. Finally, a numerical example is mentioned to illustrate the method.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ammeter H (1948) A generalization of the collective theory of risk in regard to fluctuating basic probabilities. Skand Aktuarietidskr 34:171–198
Andersen E (1957) On the collective theory of risk in case of contagion betten claims. Bull Inst Math Appl 12:275–279
Boutsikas MV, Rakitzis AC, Antzoulakos DL (2016) On the number of claims until ruin in a two-barrier renewal risk model with Erlang mixtures. J Comput Appl Math 294:124–137
Dickson D (1998) On a class of renewal risk process. N Am Actuar J 2:60–68
Dickson D, Hipp C (1998) Ruin probabilities for Erlang (2) risk process. Insur Math Econ 22:251–262
Dong H, Liu Z (2013) The ruin problem in a renewal risk model with two-sided jumps. Math Comput Model 57:800–811
Gerber H (1979) An introduction to mathematical risk theory. Philadelphia: S. S. Heubner Foundation monograph series 8
Huang T, Zhao R, Tang W (2009) Risk model with fuzzy random individual claim amount. Eur J Oper Res 192:879–890
Huang T, Diao J (2010) Risk model in fuzzy random environments. In: Intelligent computing and intelligent systems (ICIS), 2010 IEEE international conference
Huang T, Diao J, Wei Zh (2011) Inequality for mean chance of ultimate ruin in risk model with random fuzzy theory. In: Emergency management and management sciences (ICEMMS), 2nd IEEE international conference
Huang T, Wei Z, Diao J (2011) Risk model with random fuzzy theory. In: The 13th IEEE joint international computer science and information technology conference
Li J, Dickson D, Li S (2015) Some ruin problems for the MAP risk model. Insur Math Econ 65:1–8
Li S, Garrido J (2004) On ruin for the Erlang(n) risk process. Insur Math Econ 34:391–408
Liu B (2002) Theory and practice of uncertain programming. Physica, Heidelberg
Liu B (2004) Uncertainty theory. Springer, Berlin
Liu B (2007) Uncertainty theory, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Liu B, Liu Y (2002) Expected value of fuzzy variable and fuzzy expected value models. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10:445–450
Liu YK, Liu BD (2003) Expected value operator of random fuzzy variable and random fuzzy expected value models. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 11:195–215
Liu Y, Liu B (2003) Fuzzy random variables: a scalar expected value operator. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 2:143–160
Shen Q, Zhao R, Tang W (2008) Modeling random fuzzy renewal reward processes. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 16:1379–1385
Yao K, Qin Z (2015) A modified insurance risk process with uncertainty. Insur Math Econ 62:227–233
Zhao R, Tang W, Yun H (2006) Random fuzzy renewal process. Eur J Oper Res 169:189–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemalipour, S., Fathi-Vajargah, B. The mean chance of ultimate ruin time in random fuzzy insurance risk model. Soft Comput 22, 4123–4131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2629-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2629-0