Abstract
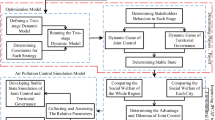
The pollution and its governing problem have drawn the world’s extremely attention. To study the sensitivities of different governing methods, we formulate a dynamic system which is analyzed through two cases of noncooperation and with-cooperation among the enterprises and the government. The dynamic system describes the influences caused by the pollution control investment, the time delay of the abatement investment and the degree of the cooperation between the government and the enterprise. At last, we solve the optimal control problem based on turnpike theorem. It is shown that the economic output in a country could affect the steady state of the pollutant emissions. Moreover, the threshold value of time delay that the society can accept on the pollution control investment is non-integer. Furthermore, the environmental policies’ implementation could remedy the polluting weakness of the countries with higher economic outputs. Finally, we solve the optimal control problem in the G–P model through education promoting.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Aitziber I (2017) Optimal control of the Lotka–Volterra system: turnpike property and numerical simulations. J Biol Dyn 11(1):25–41
Bao XD, Roossinck MJ (2013) A life history view of mutualistic viral symbioses: quantity or quality for cooperation. J Curr Opin Microbiol 16(4):514–518
Bulirsch R (1994) The maximum principle, Bellman’s equation, and Carathéodory’s work. J Optim Theory Appl 80(2):199–225
Cai XQ, Li L, Wuc MQ, Yu LH (2016) Does environmental regulation drive away inbound foreign direct investment? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J Dev Econ 123:73–85
Chiang SY (2012) An application of Lotka–Volterra model to Taiwan’s transition from 200 mm to 300 mm silicon wafers. J Technol Forecast Soc Change 79:383–392
Cobb CW, Douglas PH (1928) A theory of production. J Am Econ Rev 18(Supplement):139–165
Dorfman R, Samuclson PA, Solow RM (1958) Linear programming and economic analysis. McGraw Hill, New York
Gani A, Scrimgeour F (2014) Modeling governance and water pollution using the institutional ecological economic framework. J Econ Model 42:363–372
Horne Y, Strengers A Strempel (2016) Policing and polluting: the role of practices in contemporary urban environmental pollution governance. J Environ Sci Policy 66:112–118
Huang CS, Yu HX (2016) Study on the cooperation effect of energy enterprises under the participation of internet enterprises-based on Lotka–Volterra model. J Chin Int Energy 21:14–21
Jie MH (2010) Empirical environmental investment efficiency of and policy recommendations. Chin J Popul Resour Environ 20(4):100–105
Kanada MTF, Fujii M, Ohnishi S (2013) The long-term impacts of air pollution control policy: historical links between municipal actions and industrial energy efficiency in Kawasaki City, Japan. J Clean Prod 58:92–101
Lopez JMR, Sakhel A, Busch T (2017) Corporate investments and environmental regulation: The role of regulatory uncertainty, regulation-induced uncertainty, and investment history. J Eur Manag 35(1):91–101
Lotka AJ (1910) Contribution to the theory of periodic reaction. J Phys Chem C 14(3):271–274
Lotka AJ (1925) Elements of physical biology. Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
Morris SA, Pratt D (2003) Analysis of the Lotka–Volterra competition equations as a technological substitution model. J Technol Forecast Soc Change 70:103–133
Neumann V (1937) A model of general economic equilibrium. Rev Econ Stud 13:1–9
Nonhebel G (1981) Industrial air pollution: British progress—a review. Atmos Environ 15(3):213–219
Peng Y, Zhou T, Xu YA (2013) Effects of environmental investment on emissions reduction of industrial waste gas under environmental regulation—GMM method based on Chinese provincial panel data. J Ind Technol Econ 8(8):123–131
Searf AP (2015) Development economics. Renmin University of China Press, Beijing
Söderberg C (2016) Complex governance structures and incoherent policies: implementing the EU water framework directive in Sweden. J Environ Manage 183(1):90–97
Song R, Xiao W, Wei Q (2013) Multi-objective optimal control for a class of nonlinear time-delay systems via adaptive dynamic programming. J Soft Comput 17(11):2109–2115
Sueyoshi T, Gotob M (2014) Investment strategy for sustainable society by development of regional economies and prevention of industrial pollutions in Japanese manufacturing sectors. J Energy Econ 42:299–312
Sussmann HJ, Willems JC (1997) 300 years of optimal control: from the brachystochrone to the maximum principle. IEEE Control Syst 17(3):32–44
Trélat E, Zuazua E (2015) The turnpike property in finite-dimensional nonlinear optimal control. J Differ Equ 258:81–114
Volterra V (1926) Variazioni e fluttuazioni del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi. Mem Acad Lincei Roma 2:31–113
Wang D, Li SL (2014) DEA environmental assessment on U.S. Industrial sectors: investment for improvement in operational and environmental performance to attain corporate sustainability. J Energy Econ 45:254–267
Wang D, Liu D, Li H, Ma H, Li C (2016) A neural-network-based online optimal control approach for nonlinear robust decentralized stabilization. J Soft Comput 20(2):707–716
Xiong X, Zhang W, Li S, Wang F (2009) Analysis of stock index futures market competition based on Lotka–Volterra model. Chin J Syst Eng 24(5):581–588
Yin XG (2015) Evaluation and empirical study on the efficiency of environmental investment. Mod Financ Econ J Tianjin 7:89–92
Zhang SH, Worrell ZE, Wina CG (2015) Cutting air pollution by improving energy efficiency of China’s cement industry. J Energy Proc 83:10–20
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors Jiaorui Li and Siqi Yu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Number [Grant Numbers: 11572231] and “Yan Ta” Scholars Project of Xi’an University of Finance and Economics.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by X. Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yu, S. Dynamic analysis for Governance–Pollution model with education promoting control. Soft Comput 22, 5311–5321 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3019-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3019-y