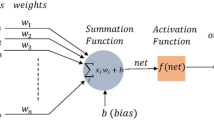
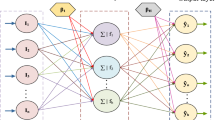
Abstract
Designing an ANN is a complex task as its performance is highly dependent on the network architecture as well as the training algorithm used to select proper synaptic weights and biases. Choosing an optimal design leads to greater accuracy when the ANN is used for classification. In this paper, we propose an approach multilayer perceptron-lion optimization algorithm (MLP-LOA) that uses lion optimization algorithm to find an optimum multilayer perceptron (MLP) architecture for a given classification problem. MLP-LOA uses back-propagation (BP) for training during the optimization process. MLP-LOA also optimizes learning rate and momentum as they have a significant role while training MLP using BP. LOA is a population-based metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the lifestyle of lions and their cooperative behavior. LOA, unlike other metaheuristics, uses different strategies to search for optimal solution, performs strong local search and helps to escape from worst solutions. A new fitness function is proposed to evaluate MLP based on its generalization ability as well as the network’s complexity. This is done to avoid dense architectures as they increase chances of overfitting. The proposed approach is tested on different classification problems selected from University of California Irvine repository and compared with the existing state-of-the-art techniques in terms of accuracy achieved during testing phase. Experimental results show that MLP-LOA performs better as compared to the existing state-of-the-art techniques.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Aljarah I, Faris H, Mirjalili S (2016) Optimizing connection weights in neural networks using the whale optimization algorithm. In: Proceedings soft computing, pp 1–15
Amato F, López A, Peña-Méndez EM, Vaňhara P, Hampl A, Havel J (2013) Artificial neural networks in medical diagnosis. J Appl Biomed 11:47–58
Bishop C (1995) Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Carvalho M, Ludermir T (2007) Particle swarm optimization of neural network architectures and weights. In: 7th International conference on hybrid intelligent systems, pp 336–339
Carvalho AR, Ramos FM, Chaves AA (2011) Metaheuristics for the feedforward artificial neural network (ann) architecture optimization problem. Neural Comput Appl 20(8):1273–1284
Chen L, Zhang X (2009) Application of artificial neural networks to classify water quality of the yellow river. In: Cao B, Zhang C, Li T (eds) Fuzzy information and engineering. Advances in soft computing, vol 54, pp 15–23. . Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Conforth M, Meng Y (2008) Toward evolving neural networks using bio-inspired algorithms. In: Proceedings of the international conference on artificial intelligence, pp 413–419
Ettaouil M, Ghanou Y (2009) Neural architectures optimization and genetic algorithms. WSEAS Trans Comput 8(3):526–537
Frank A, Asuncion A (2010) UCI machine learning repository http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml. University of California, School of Information and Computer Science, Irvine, CA
Garro BA, Vázquez RA (2015) Designing artificial neural networks using particle swarm optimization algorithms. Comput Intell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/369298
Garro BA, Sossa H, Vazquez RA (2011) Artificial neural network synthesis by means of artificial bee colony (abc) algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC’11), pp 331–338
Islam MM, Sattar MA, Amin MF, Yao X, Murase K (2009a) A new constructive algorithm for architectural and functional adaptation of artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 39(6):1590–1605
Islam MM, Sattar MA, Amin MF, Yao X, Murase K (2009b) A new adaptive merging and growing algorithm for designing artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 39(3):705–722
Jaddi NS, Abdullah S, Hamdan AR (2015) Optimization of neural network model using modified bat-inspired algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 37:71–86
Lauret P, Fock E, Mara TA (2006) A node pruning algorithm based on a Fourier amplitude sensitivity test method. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(2):273–293
Lu C, Shi B, Chen L (2000) Hybrid BP-GA for multilayer feedforward neural networks. In: Proceedings 7th IEEE international conference electronics, circuits and systems (ICECS), pp 958–961
Ma X, Gan X (2009) Condition monitoring and faults recognizing of dish centrifugal separator by artificial neural network combined with expert system. In: Proceedings 5th international conference on natural computing, pp 203–207
Ma L, Khorasani K (2005) Constructive feedforward neural networks using hermite polynomial activation functions. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(4):821–833
Sheng W, Shan P, Mao J, Zheng Y, Chen S, Wang Z (2017) An adaptive memetic algorithm with rank-based mutation for artificial neural network architecture optimization. IEEE Access 5:8895–18908
Silalahi DD, Reano CE, Lansigan FP, Panopio RG, Bantayan NC (2016) Using genetic algorithm neural network on near infrared spectral data for ripeness grading of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) fresh fruit. Inf Process Agric 3(4):252–261
Tizhoosh HR (2005) Opposition-based learning: a new scheme for machine intelligence. In: Proceedings of international conference on computational intelligence for modeling control and automation, pp 695–701
Tsai JT, Chou JH, Liu TK (2006) Tuning the structure and parameters of a neural network by using hybrid Taguchi-genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(1):69–80
Wdaa ASI (2008) Differential evolution for neural networks learning enhancement. Ph.D. thesis, University Teknologi, Malaysia
Wilson DR, Martinez TR (2001) The need for small learning rates on large problems. In: Proceedings of international joint conference on neural networks, pp 115–119
Wolpert DH, Macready WG (1997) No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1(1):67–82
Yang S-H, Chen Y-P (2012) An evolutionary constructive and pruning algorithm for artificial neural networks and its prediction applications. Neurocomputing 86(4):140–149
Yao X (1999) Evolving artificial neural networks. Proc IEEE 87(9):1423–1447
Yazdani M, Jolai F (2015) Lion optimization algorithm (LOA): a nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm. J Comput Des Eng 1:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcde.2015.06.003
Zanchettin C, Ludermir TB, Almeida LM (2011) Hybrid training method for MLP: optimization of architecture and training. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 41(4):1097–1109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Priti Bansal, Shakshi Gupta, Sumit Kumar, Shubham Sharma and Shreshth Sharma declare that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, P., Gupta, S., Kumar, S. et al. MLP-LOA: a metaheuristic approach to design an optimal multilayer perceptron. Soft Comput 23, 12331–12345 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03773-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03773-2