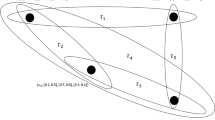
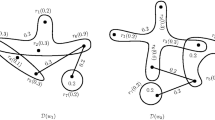
Abstract
Fuzzy hypergraphs are useful tools for representing granular structures when describing the relations between objects and set of hyperedges, at minute detail, in a specific granularity. Their merit over classical hypergraphs lies in their ability to model uncertainty that may arise with objects and/or granules incident to each other. Many previous studies on fuzzy hypergraphs seek to exploit their strong descriptive potential to analyze n-ary relations in several contexts. However, due to the very detailed numeric membership grades of their objects, fuzzy hypergraphs are sensitive to noise, which may be overwhelming in their general interpretation. To address this issue, a principle of least commitment to certain membership grades is sort by embracing a framework of shadowed sets. The specific concern of this paper is to study a noise-tolerable framework, viz. shadowed hypergraph. Our goal is to capture and quantify noisy objects in clearly marked out zones. We discuss some characteristic properties of shadowed hypergraph and describe an algorithm for transforming a given fuzzy hypergraph into its resulting shadowed hypergraph. Finally, some illustrative examples are provided to demonstrate the essence of shadowed hypergraphs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram M, Alshehri NO (2015) Tempered interval—valued fuzzy hypergraphs. UPB Sci Bull Ser A 77:39–48
Akram M, Dudek WA (2013) Intuitionistic fuzzy hypergraphs with applications. Inf Sci 218:182–193
Berge C (1970) Graphes et hypergraphes. Dunod, Paris
Chen SM (1997) Interval-valued fuzzy hypergraph and fuzzy partition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 27:725–733
Chen G, Zhong N, Yiyu Y (2008) A hypergraph model of granular computing. In: IEEE international conference on granular computing, pp 26–28
Deng XF, Yao YY (2014) Decision-theoretic three-way approximations of fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 279:702–715
Dubois D, Prade H (1980) Fuzzy sets and systems: theory and applications. Academic Press, New York
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Siddiqui N (2017) Aggregation operators on triangular cubic fuzzy numbers and its application to multi-criteria decision making problems. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-162007
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Sajjad MA, Khan WA (2018a) Trapezoidal cubic fuzzy number Einstein hybrid weighted averaging operators and its application to decision making. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3242-6
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Ali A, Khan WA (2018b) Some geometric operators with triangular cubic linguistic hesitant fuzzy number and their application in group decision-making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-18125
Fahmi A, Amin F, Abdullah S, Ali A (2018c) Cubic fuzzy einstein aggregation operators and its application to decision making. Int J Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207721.2018.1503356
Ibrahim AM, William-West TO (2019) Induction of shadowed sets from fuzzy sets. Granul Comput 4(1):27–38
Kaufmann A (1977) introduction a la thiorie des sous-ensemble flous, vol 4. Masson, Paris
Lee-Kwang H, Lee KM (1995) An application of intuitionistic fuzzy sets in medical diagnosis, Fuzzy hypergraphs and fuzzy partitions. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 25(1):196–201
Lee-Kwang H, Lee K (2011) Fuzzy hypergraph and fuzzy partition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 25:196–201
Motro A (1988) VAGUE: a user interface to relational databases that permits vague queries. ACM Trans Inf Syst 6(3):187–214
Parvathi R, Thilagavathi S, Karunambigai MG (2009) Intuitionistic fuzzy hypergraphs. Cybern Inf Technol 9:46–53
Pedrycz W (1998) Shadowed sets: representing and processing fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 28:103–109
Pedrycz W (2005) Interpretation of clusters in the framework of shadowed sets. Pattern Recogn Lett 26:2439–2449
Pedrycz W, Vukovich G (2002) Granular computing with shadowed sets. Int J Intell Syst 17(2):173–197
Stell G (2010) Relational granularity for hypergraphs. LNAI 6086:267–276
Tahayori H, Sadeghian A, Pedrycz W (2013) Induction of shadowed sets based on the gradual grade of fuzziness. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 21(5):937–949
Wald A (1945) Sequential tests of statistical hypotheses. Ann Math Stat 16:117–186
Wang Q, Gong Z (2018) An application of fuzzy hypergraphs and hypergraphs in granular computing. Inf Sci 42:296–314
William-West TO, Singh D (2018) Information granulation for rough fuzzy hypergraphs. Granul Comput 3:75–92
William-West TO, Ibrahim AM, Kana AFD (2019) Shadowed set approximation of fuzzy sets based on nearest quota of fuzziness. Ann Fuzzy Math Inform 4(1):27–38
Wong MH, Leung KS (1990) A fuzzy database-query language. Inf Syst 15(5):583–590
Yager R (1977) Multi-objective decision using fuzzy sets, decision sciences. Int J Man-Mach Stud 9:375–382
Yang T, Wu X (2014) Dimensionality reduction of hypergraph information system. In: IEEE international conference on granular computing (GrC), pp 346–351
Yao YY, Deng XF (2011) Sequential three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. In: Wang Y et al (eds) ICCI-CC 2011, pp 120–125
Yao Y, Wang S, Deng X (2017) Constructing shadowed sets and three-way approximations of fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 413(1):132–153
Zhang Y, Yao JT (2018) Game theoretic approach to shadowed sets: a three-way tradeoff perspective. Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.07.058
Acknowledgements
The author sincerely wishes to thank the Editor-in-Chief Professor Antonio Di Nola, and the anonymous reviewers for their technical comments and other valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
William-West, T.O. On shadowed hypergraphs. Soft Comput 24, 1213–1224 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03955-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03955-y