Abstract
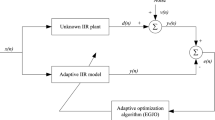
The design method of adaptive infinite impulse response (IIR) filter is a challenging problem. Its design principle is to determine the filter parameters by the iteration process of the adaptive algorithm, which is to obtain an optimal model for unknown plant based on minimizing mean square error (MSE). However, many adaptive algorithms cannot adjust the parameters of IIR filter to the minimum MSE. Therefore, a more efficient adaptive optimization algorithm is required to adjust the parameters of IIR filter. In this paper, we propose a selfish herd optimization algorithm based on chaotic strategy (CSHO) and apply it to solving IIR system identification problem. In CSHO, we add a chaotic search strategy, which is a better local optimization strategy. Its function is to search for better candidate solutions around the global optimal solution, which makes the local search of the algorithm more precise and finds out potential global optimal solutions. We use solving IIR system identification problem to verify the effectiveness of CSHO. Ten typical IIR filter models with the same order and reduced order are selected for experiments. The experimental results of CSHO compare with those of bat algorithm (BA), cellular particle swarm optimization and differential evolution (CPSO-DE), firefly algorithm (FFA), hybrid particle swarm optimization and gravitational search algorithm (HPSO-GSA), improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) and opposition-based harmony search algorithm (OHS), respectively. The experimental results show that CSHO has better optimization accuracy, convergence speed and stability in solving most of the IIR system identification problems. At the same time, it also obtains better optimization parameters and achieves smaller difference between actual output and expected output in test samples.






















































































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrom KJ et al (1995) Adaptive Control. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Cheng S, Li C-W (2011) Fuzzy PDFF-IIR controller for PMSM drive systems. Control Eng Pract 19:828–835
Dai C et al (2010) Seeker optimization algorithm for digital IIR filter design. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57:1710–1718
Derrac J, Gracie S, Molina D, Herrera F (2011) A practical tutorial on the use of nonparametric statistical tests as a methodology for comparing evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms. Swarm Evol Comput 1:3–18
Dimple K, Kotary DK et al (2017) An incremental RLS for distributed parameter estimation of IIR systems present in computing nodes of a wireless sensor network. Procedia Comput Sci 115:699–706
Fausto F, Cuevas E et al (2017) A global optimization algorithm inspired in the behavior of selfish herds. Biosystems 160:39–55
Gomez C (2018) Recursive identification of IIR systems with multilevel output quantization and lossy memoryless channels with transmission errors. IFAC-PapersOnLine 51:909–914
Griffiths EJ, Orponen P (2005) Optimization, block designs and No Free Lunch theorems. Inf Process Lett 94:55–61
Hamilton WD (1971) Geometry to the selfish herd. J Theory Biol 31:295–311
Huang C-Y, Lai C-H et al (2018) Inhibition of ERK-Drp1 signaling and mitochondria fragmentation alleviates IGF-IIR-induced mitochondria dysfunction during heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 122:58–68
Jiang C, Bompard E (2005) A hybrid method of chaotic particle swarm optimization and linear interior for reactive power optimization. Math Comput Simul 68:57–65
Jiang S et al (2015) A new design method for adaptive IIR system identification using hybrid particle swarm optimization and gravitational search algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn 9:2553–2576
Karaboga N et al (2011) A novel and efficient algorithm for adaptive filtering: artificial bee colony algorithm. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 19:175–190
Kumar M et al (2016) Bat algorithm: application to adaptive infinite impulse response system identification. Arab J Sci Eng 41:3587–3604
Lagos-Eulogio P et al (2017) A new design method for adaptive IIR system identification using hybrid CPSO and DE. Nonlinear Dyn 88:2371–2389
Liang W, Lu W, Fan J (2011) The signal detection in TWACS based on IIR filter. Procedia Eng 23:120–124
Liu B, Wang L et al (2005) Improved particle swarm optimization combined with chaos. Chaos Solitons Fract 25:1261–1271
Mandal S et al (2012) Differential evolution with wavelet mutation in digital FIR filter design. J Optim Theory Appl 155:315–324
Panda G et al (2011) IIR system identification using cat swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 38:12671–12683
Rashedi E et al (2011) Filter modeling using gravitational search algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24:117–122
Saha S, Mukherjee V (2018) A novel chaos-integrated symbiotic organisms search algorithm for global optimization. Soft Comput 22:3797–3816
Saha SK et al (2013) A new design method using opposition-based BAT algorithm for IIR system identification problem. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput 5:99–132
Sarangi A et al (2016) An approach to identification of unknown IIR systems using crossover cat swarm optimization. Perspect Sci 8:301–303
Scarpiniti M et al (2015) Nonlinear system identification using IIR spline adaptive filters. Sig Process 108:30–35
Shynk JJ (1989) Adaptive IIR filtering. IEEE ASSP Mag 6:4–21
Upadhyay P et al (2014) A novel design method for optimal IIR system identification using opposition based harmony search algorithm. J Frankl Inst 351:2454–2488
Upadhyay P et al (2016) A new design method based on firefly algorithm for IIR system identification problem. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 28:174–198
Wang Y, Ding F, Xu L (2018) Some new results of designing an IIR filter with colored noise for signal processing. Digit Signal Proc 72:44–58
Xiang T, Liao X, Wong K (2007) An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm combined with piecewise linear chaotic map. Appl Math Comput 190:1637–1645
Yan W, Zhang J, Zhang S, Wen P (2018) A novel pipelined neural IIR adaptive filter for speech prediction. Appl Acoust 141:64–70
Yao L, Sethares WA et al (1994) Nonlinear parameter estimation via the genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process 42:927–935
Zhang S, Zhou Y (2018) Grey wolf optimizer with ranking-based mutation operator for IIR model identification. Chin J Electron 27:1071–1079
Zou D-X, Deb S, Wang G-G (2018) Solving IIR system identification by a variant of particle swarm optimization. Neural Comput Appl 30:685–698
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. This paper has been awarded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61170035, 61272420, 81674099 and 61502233), the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities (30916011328, 30918015103 and 30918012204), Nanjing Science and Technology Development Plan Project (201805036) and “13th Five-Year” Equipment Field Fund (61403120501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Wang, Y., Liu, C. et al. Selfish herd optimization algorithm based on chaotic strategy for adaptive IIR system identification problem. Soft Comput 24, 7637–7684 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04390-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04390-9