Abstract
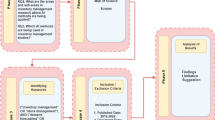
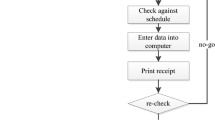
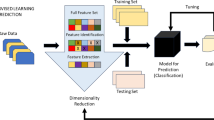
This paper focuses on the reliability of intelligent logistics for fresh food e-commerce. Based on the development of fresh food e-commerce, this paper analyses the factors that influence the reliability of fresh food logistics from the aspects of information technology, facilities and equipment, personnel operation and external environment. A Bayesian network is used to analyse the influence of each factor on system reliability, and the degree of importance of each factor is calculated. Based on the importance of each influential factor in fresh food e-commerce logistics systems, an intelligent logistics model for reliability control of fresh food is established. The purpose of this model is to improve the economic efficiency and the intelligent level of the fresh food e-commerce logistics system on the premise of meeting the system reliability requirements. Finally, simulation results show that the developed intelligent logistics reliability control model can significantly improve the reliability of fresh food e-commerce logistics systems, and provide practical suggestions for fresh food e-commerce enterprises.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameknassi L, Aït-Kadi D, Rezg N (2016) Integration of logistics outsourcing decisions in a green supply chain design: a stochastic multi-objective multi-period multi-product programming model. Int J Prod Econ 182:165–184
Chen C, Liu X, Chen HH (2018) A rear-end collision risk evaluation and control scheme using a Bayesian network model. IEEE Trans Intell Transp 99:264–284
Ersel D, İçen D (2016) Fuzzy probability calculation with confidence intervals in Bayesian networks. Soft Comput 20(2):819–829
Hackl J, Kohler J (2016) Reliability assessment of deteriorating reinforced concrete structures by representing the coupled effect of corrosion initiation and progression by Bayesian networks. Struct Saf 62:12–23
Kaipia R, Dukovska-Popovska I, Loikkanen L (2013) Creating sustainable fresh food supply chains through waste reduction. Int J Phys Distrib Logist 43(3):262–276
Kim H, Kim P (2017) Reliability redundancy allocation problem considering optimal redundancy strategy using parallel genetic algorithm. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 159:153–160
Lam CY, Ip WH (2012) An improved spanning tree approach for the reliability analysis of supply chain collaborative network. Enterp Inf Syst 6(4):405–418
Lessan J, Fu L, Wen C (2018) A hybrid Bayesian network model for predicting delays in train operations. Comput Ind Eng 127:1214–1222
Luque J, Straub D (2016) Reliability analysis and updating of deteriorating systems with dynamic Bayesian networks. Struct Saf 62:34–46
Manning L, Soon JM (2013) GAP framework for fresh produce supply. Br Food J 115(6):796–820
Mkrtchyan L, Podofillini L, Dang VN (2016) Methods for building conditional probability tables of Bayesian belief network from limited judgment: an evaluation for human reliability application. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 151:93–112
Mokhtar EHA, Chateauneuf A, Laggoune R (2016) Bayesian approach for the reliability assessment of corroded interdependent pipe networks. Int J Press Vessels Pip 148:46–58
Nahman J, Perić D (2017) Path-set based optimal planning of new urban distribution networks. Int J Electr Power 85:42–49
Nakandala D, Lau H, Zhang JJ (2016) Cost-optimization modelling for fresh food quality and transportation. Ind Manag Data Syst 116(3):564–583
Nakandala D, Samaranayake P, Lau H et al (2017) Modelling information flow and sharing matrix for fresh food supply chains. Bus Process Manag J 23(1):108–129
Okaro IA, Tao LB (2016) Reliability analysis and optimisation of subsea compression system facing operational covariate stresses. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 156:159–174
Oliveira SC, Cobre J, Ferreira TDP (2017) A Bayesian approach for the reliability of scientific co-authorship networks with emphasis on nodes. Soc Netw 48:110–115
Rijpkema WA, Rossi R, van der Vorst JGAJ (2014) Effective sourcing strategies for perishable product supply chains. Int J Phys Distrib Logist 44(6):494–510
Sharma S, Pai SS (2015) Analysis of operating effectiveness of a cold chain model using Bayesian networks. Bus Process Manag J 21(4):722–742
Sharma S, Routroy S (2016) Modeling information risk in supply chain using Bayesian networks. J Enterp Inf Manag 29(2):238–254
Srivastava SK, Chaudhuri A, Srivastava RK (2015) Propagation of risks and their impact on performance in fresh food retail. Int J Logist Manag 26(3):568–602
Walter G, Aslett LJM, Coolen FPA (2017) Bayesian nonparametric system reliability using sets of priors. Int J Approx Reason 80:67–88
Xu XF, Hao J, Deng Y, Wang Y (2017) Design optimization of resource combination for collaborative logistics network under uncertainty. Appl Soft Comput 560(7):684–691
Xu XF, Hao J, Yu L, Deng Y (2019) Fuzzy optimal allocation model for task-resource assignment problem in collaborative logistics network. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(5):1112–1125
Zhang H, Wang M, Tang M et al (2017) The reliability measures model of multilayer urban distribution network. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2900-4
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a Project of the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1600605), a Beijing Project of Philosophy and Social Science (17GLB013), a Project of the National Social Science Foundation of China (15BGL202), a Beijing's “High-grade, Precision and Advanced Discipline Construction (Municipal)-Business Administration” Project (No. 19005902053) and a project of Beijing Talents foundation of Organization Department of Beijing Municipal Committee of the CPC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not report any studies involving human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by X. Li.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Zhang, Q. et al. A Bayesian network model for the reliability control of fresh food e-commerce logistics systems. Soft Comput 24, 6499–6519 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04666-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04666-5