Abstract
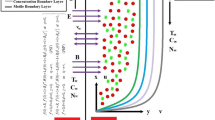
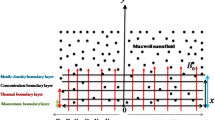
In the current era of nanotechnology, the design of biological devices requires efficient transmission of energy among the components. Computational studies are always prerequisite for general models. In view of this importance, this paper investigated the characterizations regarding the steady flow of 2D Oldroyd-B nanofluid in the presence of thermal radiation (nonlinear) over a radially stretched sheet. Buongiorno revised nanofluid relation of the nanomaterial is instigated in precise modeling. For the mechanism of mass transmission, we utilized features of constructive–destructive prescription. As a result of modeling, the raised PDEs are converted into ODEs by appropriate transformations. The numeric scheme BVP4C is utilized for the solutions. The physical variables of the assumed flow pattern are shown graphically with the significance of the involved parameter. Besides, the prescribed investigation explored the significant impact by involved physical parameters along with the declining conduct influenced by chemical reaction parameters on the considered model. Moreover, the numerical outcomes of surface drag force and the transfer rate of heat–mass are tabulated for numerous sets of physical parameters. The improvement of these results is guaranteed by comparing it with existing techniques.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbar NS, Raza M, Ellahi R (2015) Influence of induced magnetic field and heat flux with the suspension of carbon nanotubes for the peristaltic flow in a permeable channel. J Magn Magn Mater 381:405–415
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME, FED, New York, p 231
Hayat T, Khan MI, Farooq M, Alsaedi A, Waqas M, Yasmeen T (2016a) Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model in the flow of variable thermal conductivity fluid over a variable thicked surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 99:702–710
Hayat T, Khan MI, Farooq M, Yasmeen T, Alsaedi A (2016b) Stagnation point flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux and homogeneous reactions. J Mol Liq 220:49–55
Hayat T, Rashid M, Imtiaz M, Alsaedi A (2017a) Nanofluid flow due to rotating disk with variable thickness and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. Int J Heat Mass Transf 113:96–105
Hayat T, Javed M, Imtiaz M, Alsaedi A (2017b) Double stratification in the MHD flow of a nanofluid due to a rotating disk with variable thickness. Eur Phys J Plus 17:132–146
Huimin Z, Zheng J, Xu J, Deng W (2019) Fault diagnosis method based on principal component analysis and broad learning system. IEEE Access 7:99263–99272
Khan WA, Khan M, Malik R (2014) Three-dimensional flow of an Oldroyd-B nanofluid towards stretching surface with heat generation/absorption. PLoS ONE 9(8):e10510
Khan WA, Alshomrani AS, Khan M (2016) Assessment on characteristics of heterogeneous–homogeneous processes in three-dimensional flow of Burgers fluid. Results Phys 6:772–779
Khan WA, Irfan M, Khan M, Alshomrani AS, Alzahrani AK, Alghamdi MS (2017) Impact of chemical processes on magneto nanoparticle for the generalized Burgers fluid. J Mol Liq 234:201–208
Mustafa M, Khan JA, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017) Buoyancy effects on the MHD nanofluid flow past a vertical surface with chemical reaction and activation energy. Int J Heat Mass Transf 108:1340–1346
Oztop HF, Abu-Nada E (2008) Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 29:1326–1336
Rahman SU, Ellahi R, Nadeem S, Zaigham Zia QM (2016) Simultaneous effects of nanoparticles and slip on Jeffrey fluid through tapered artery with mild stenosis. J Mol Liq 218:484–493
Ramzan M, Bilal M, Chung JD (2016) Radiative flow of Powell–Eyring magneto-nanofluid over a stretching cylinder with chemical reaction and double stratification near a stagnation point. PLoS ONE 12(1):e0170790
Ramzan M, Ullah N, Chung JD, Lu D, Farooq U (2017) Buoyancy effects on the radiative magneto micropolar nanofluid flow with double stratification, activation energy and binary chemical reaction. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13140-6
Rehman S, ul Haq R, Khan ZH, Lee C (2016) Entropy generation analysis for non-Newtonian nanofluid with zero normal flux of nanoparticles at the stretching surface. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 63:226–235
Sandeep N (2017) Effect of aligned magnetic field on liquid thin film flow of magnetic-nanofluids embedded with graphene nanoparticles. Adv Powder Technol 28:865–875
Sandeep N, Kumar BR, Kumar MSJ (2015) A comparative study of convective heat and mass transfer in non-Newtonian nanofluid flow past a permeable stretching sheet. J Mol Liq 212:585–591
Shafique Z, Mustafa M, Mushtaq A (2016) Boundary layer flow of Maxwell fluid in rotating frame with binary chemical reaction and activation energy. Results Phys 6:627–633
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R (2015) Three dimensional mesoscopic simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 89:799–808
ul Haq R, Khan ZH, Hussain ST, Hammouch Z (2016) Flow and heat transfer analysis of water and ethylene glycol based Cu nanoparticles between two parallel disks with suction/injection effects. J Mol Liq 221:298–304
Wu D, Zhao H, Zou L, Li G, Yang X, Wu D (2017) A novel collaborative optimization algorithm in solving complex optimization problems. Soft Comput 21(15):4387–4398
Wu D, Xu J, Zhao H (2019) An improved ant colony optimization algorithm based on hybrid strategies for scheduling problem. IEEE Access 7:20281–20292
Acknowledgements
The authors extended their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Majmaah University for funding this work under Project No. (RGP-2019-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by A. Di Nola.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, W., Mahmood, S., Chammam, W. et al. Mathematical modeling and chemical conduct considering non-Newtonian nanofluid by utilizing heat flux features. Soft Comput 24, 11829–11839 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05072-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05072-7