Abstract
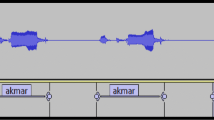
In this article, the authors have presented the design and development of automatic spontaneous speech recognition of the Punjabi language. To dimensions up to the natural speech recognizer, the very large vocabulary Punjabi text corpus has been taken from a Punjabi interview’s speech corpus, presentations, etc. Afterward, the Punjabi text corpus has been cleaned by using the proposed corpus optimization algorithm. The proposed automatic spontaneous speech model has been trained with 13,218 of Punjabi words and more than 200 min of recorded speech. The research work also confirmed that the 2,073,456 unique in-word Punjabi tri-phoneme combinations present in the dictionary comprise of 131 phonemes. The performance of the proposed model has grown increasingly to 87.10% sentence-level accuracy for 2381 Punjabi trained sentences and word-level accuracy of 94.19% for 13,218 Punjabi words. Simultaneously, the word error rate has been reduced to 5.8% for 13,218 Punjabi words. The performance of the proposed system has also been tested by using other parameters such as overall likelihood per frame and convergence ratio on various iterations for different Gaussian mixtures.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abushariah A, Gunawan TS, Khalifa O, Abushariah M (2010) English digits speech recognition system based on hidden markov models. In: Comput Commun Eng, pp 1423–1432
Akyildiz F, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, Cayirci E (2002) Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput Netw 38:393–422
Ali H, Jianwei A, Iqbal K (2015a) Automatic speech recognition of Urdu digits with optimal classification approach. Int J Comput Appl 5:118–125
Ali H, Jianwei A, Iqbal K (2015b) Automatic speech recognition of Urdu digits with optimal classification approach. Int J Comput Appl 118:1–5
Ankita Y, Kawahara T (2010) Statistical transformation of language and pronunciation models for spontaneous speech recognition. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 18:1539–1549
Beke A, Gosy M (2012) Characteristics and spectral features used in automatic prediction of vowel duration in spontaneous speech. In: 3rd IEEE international conference on cognitive info communications, CogInfoCom, pp 65–70
Braathen B, Bartlett MS, Littlewort G, Smith E, Movellan JR (2002) An approach to automatic recognition of spontaneous facial actions. In: Proceedings of 5th IEEE international conference on automatic face gesture recognition, pp 360–365
Choudhary A, Gupta G, Chauhan (2013) Automatic speech recognition system for isolated and connected words by using HTK toolkit. In: Association of computer electronic and electrical engineer, pp 847–853
Dahl GE, Yu D, Deng L (2012) Context-dependent pre-trained deep neural networks for large-vocabulary speech recognition. In: IEEE transactions on audio, speech, and language processing, pp 30–42
Digalakis V (2003a) Large vocabulary continuous speech recognition in greek: corpus and an automatic dictation system. Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering Technical University of Crete Language, pp 1–4
Digalakis V (2003b) Large vocabulary continuous speech recognition in Greek: corpus and an automatic dictation system, Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering Technical University of Crete, Geneva, vol 8, no 3, pp 1565–1568
Fohr D, Mella O, Illina I (2017) New paradigm in speech recognition: deep neural networks. IEEE Int Conf Inform Syst Econ Intell 7:870–879
Furui S (2003) Robust methods in automatic speech recognition and understanding. Proc EUROSPEECH. 3:1993–1998
Furui S (2007) The effect of spectral space reduction in spontaneous speech on recognition performances. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing—ICASSP, vol 4, pp 473–476
Ganesh A, Ravichandran C (2013) Grapheme Gaussian model and prosodic syllable based Tamil speech recognition system. Int Conf Signal Process Commun (ICSC) 29(3):56–61
Ghai W, Singh N (2012) Analysis of automatic speech recognition systems for Indo-Aryan Languages: Punjabi a case study. Int J Soft Comput Eng IJSCE 2:379–385
Ghai W, Singh N (2013) Continuous speech recognition for Punjabi Language. Int J Comput Appl 72:23–28
Hendy NA, Farag H (2013) Emotion recognition using neural network: a comparative study. Int J Comput Electr Autom Control Inf Eng 7:1149–1155
Hernandez-Mena CD, Meza-Ruiz IV, Herrera-Camacho JA (2017) Automatic speech recognizers for Mexican Spanish and its open resources. J Appl Res Technol 15:259–270
Hoesen D, Hardianto C, Lestari D, Khodra M (2016) Towards robust Indonesian speech recognition with spontaneous-speech adapted acoustic models. Procedia Comput Sci 81:167–173
Hofmann H, Sakti S, Isotani R, Kawai H (2010) Improving spontaneous English ASR using a joint-sequence pronunciation model. In: 4th International universal communication symposium, pp 58–61
Izzad M, Jamil N, Bakar ZA (2013) Speech/non-speech detection in malay language spontaneous speech. In: International conference on computing, management and telecommunications, ComManTel, pp 219–224
Kalaivani EC (2013) A study on speaker recognition system and pattern classification techniques 2, 963–967
Karpov A, Markov K, Kipyatkova I, Vazhenina D (2014) Large vocabulary Russian speech recognition using syntactico-statistical language modeling. Speech Commun 56:213–228
Kaur A, Gill J (2014) Punjabi speech recognition of isolated words using compound EEMD and neural network. Int J Soft Comput Eng IJSCE 1:150–154
Kumar Y, Singh N (2016) Automatic spontaneous speech recognition for Punjabi language interview speech corpus. Int J Educ Manag Eng 6:64–73
Kumar A, Dua M, Choudhary T (2014) Continuous Hindi speech recognition using monophone based acoustic modeling. Int J Comput Appl 2014:163–167
Lokesh S, Kumar PM, Devi MR, Parthasarathy P, Gokulnath C (2019) “An automatic Tamil speech recognition system by using bidirectional recurrent neural network with self-organizing map” neural network with self-organizing map. Neural Comput Appl 31:1521–1531
Maekawa K, Kita-ku N, Meguro-ku O (2000) Spontaneous speech corpus of Japanese. LREC 6:1–5
Martin W (2011) Localization of non-linguistic events in spontaneous speech by non-negative matrix factorization and long short-term memory, Felix Weninger, Bj Institute for Human-Machine Communication, pp 5840–5843
Menacer MA, Mella O, Fohr D, Jouvet D, Langlois D, Smaıli K (2017) Development of the Arabic Loria automatic speech recognition system (ALASR) and its evaluation for Algerian dialect. Procedia Comput Sci 117:81–88
Moneykumar M, Sherly E, Varghese WS (2015) Isolated word recognition system for Malayalam using machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on natural language processing, Trivandrum, India
Nimbargi S, Chandrashekara SN (2015) Isolated speaker independent Kannada ASR system using HTK. In: The international journal of combined research & development (IJCRD), vol 4, no 6
Patil UG, Shirbahadurkar SD, Paithane AN (2016) Automatic speech recognition of isolated words in Hindi language using MFCC. In: International conference on computing, analytics and security Trends (CAST), pp 433–438
Rahul A, Nandakishor S, Singh N, Dutta SK (2013) Design of Manipuri keywords spotting system using HMM. In: Fourth national conference on computer vision, pattern recognition, image processing and graphics (NCVPRIPG), vol 34, no 6, pp 1–3
Saini P, Kaur P (2013) Automatic speech recognition: a review. Int J Eng Trends Technol 4:132–136
Sajjan SC, Vijaya C (2016) Continuous speech recognition of Kannada language using triphone modeling. In: International conference on wireless communications, signal processing and networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, pp 451-455
Sarfraz H, Ali H, Ahmad N, Zhou X, Iqbal K, Ali S (2010) Large vocabulary continuous speech recognition for Urdu. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on frontiers of information technology—FIT10
Sarma H, Saharia N, Sharma U (2014) Development of Assamese speech corpus and automatic transcription using HTK. In: Thampi S, Gelbukh A, Mukhopadhyay J (eds) Advances in signal processing and intelligent recognition systems. Advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol 264, Springer, Cham
Sarma H, Saharia N, Sharma U (2017) Development and analysis of speech recognition systems for Assamese language using HTK. ACM Trans Asian Low Resour Lang Inf Process 17(1):7.1–7.14
Singh LG, Laitonjam L, Singh SR (2016) Automatic syllabification rules for Manipuri Language. Int J Adv Res Comput Sci 8(1):349–357
Stouten F, Duchateau J, Martens J, Wambacq P (2006) Coping with disfluencies spontaneous speech recognition: acoustic detection and linguistic context manipulation. Speech Commun 48:1590–1606
Tailor JH (2016) Speech Recognition System Architecture for Gujarati Language. International Journal of Computer Applications 138(12):28–31
Takaaki H, Chiori H, Yasuhiro M (2003) Speech summarization using weighted finite-state transducers. In: EUROSPEECH, pp 2817–2820
Vijayendra D, Thakar VK (2016) Neural network based Gujrati speech recognition for dataset collected by in-ear microphone. Procedia Comput Sci 93:668–675
Vimala C, Radha V (2012) Speaker independent isolated speech recognition system for Tamil language using HMM. Procedia Comput Sci 30:1097–1102
Yu C, Chen Y, Li Y, Kang M, Xu S, Liu X (2019) Cross-language end-to-end speech recognition research based on transfer learning for the low-resource Tujia language. Symmetry 11:1–14
Zarrouk E, Benayed Y, Uri FG (2015) Graphical models for multi-dialect Arabic isolated words recognition. Procedia Comput Sci 60(1):508–516
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, Y., Singh, N., Kumar, M. et al. AutoSSR: an efficient approach for automatic spontaneous speech recognition model for the Punjabi Language. Soft Comput 25, 1617–1630 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05248-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05248-1