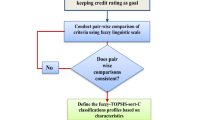
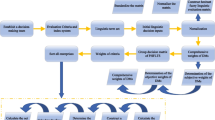
Abstract
With Chinese economic development in a new normal state, micro and small corporations have increasingly played an important role. The credit evaluation for micro and small corporations can contribute to efficient financial decisions. Traditional methods for the corporate credit evaluation rarely consider fuzzy features of micro and small entrepreneurs. Since the credit evaluation procedure for entrepreneurs consists of some alternatives and influential indicators, it can be recognized as a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problem. To better express uncertainty information, a four-branch fuzzy set (FBFS) is presented to deal with the issue, which is characterized by a truth-membership function, an unknown-membership function and a falsity-membership function. In the paper, to handle the MCDM problems under four-branch fuzzy environments, the evaluation based on distance from average solution (EDAS) method is extended and utilized. These obvious improvement places include integrating an interval weight vector, determining an average solution, transforming a decision matrix and analyzing a change trend of the coefficients. To demonstrate the applicability and rationality of the proposed method in practice, an illustrative example is implemented, concerning a credit evaluation for some micro and small entrepreneurs. Its feasibility and validity are further verified by a sensitivity analysis and a comparative analysis. The results show the FBFSs and extended EDAS method can well match the reality and appropriately handle the credit evaluation problems for micro and small entrepreneurs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:87–96
Atanassov KT (1989) More on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 33:37–46
Atanassov KT, Gargov G (1989) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 31:343–349
Bustince H, Burillo P (1996) Vague sets are intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 79:403–405
Cao YX, Zhou H, Wang JQ (2016) An approach to interval-valued intuitionistic stochastic multi-criteria decision-making using set pair analysis. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0589-9
Chen N, Xu ZS, Xia MM (2013) Correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy sets and their applications to clustering analysis. Appl Math Model 37:2197–2211
Chen ZC, Liu PH, Pei Z (2015) An approach to multiple attribute group decision making based on linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Int J Comput Intell Syst 8:747–760
Cuong BC (2014) Picture fuzzy sets. J Comput Sci Cybern 30:409–420
Farhadinia B (2014) Correlation for dual hesitant fuzzy sets and dual interval-valued hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 29:184–205
Gau WL, Buehrer DJ (1993) Vague sets. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23:610–614
Grzegorzewski P (2004) Intuitionistic fuzzy numbers-principles, metrics and ranking. In: Atanassov KT, Hryniewicz O, Kacprzyk J (eds) Soft computing foundations and theoretical aspects. Academic House Exit, Warszawa, pp 235–249
Hajek P, Michalak K (2013) Feature selection in corporate credit rating prediction. Knowl-Based Syst 51:72–84
He Y, Xu ZS, Gu J (2016) An approach to group decision making with hesitant information and its application in credit risk evaluation of enterprises. Appl Soft Comput 43:159–169
Ji Y, Huang GH, Sun W (2015) Risk assessment of hydropower stations through an integrated fuzzy entropy-weight multiple criteria decision making method: a case study of the Xiangxi River. Expert Syst Appl 42(12):5380–5389
Keshavarz-Ghorabaee M, Zavadskas EK, Amiri M, Turskis Z (2016) Extended EDAS method for fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making: an application to supplier selection. Int J Comput Commun Control 11:358–371
Keshavarz-Ghorabaee M, Zavadskas EK, Olfat L, Turskis Z (2015) Multicriteria inventory classification using a new method of evaluation based on distance from average solution (EDAS). Informatica 26:435–451
Khashman A (2010) Neural networks for credit risk evaluation: investigation of different neural models and learning schemes. Expert Syst Appl 37(9):6233–6239
Kim KJ, Ahn HC (2012) A corporate credit rating model using multi-class support vector machines with an ordinal pairwise partitioning approach. Comput Oper Res 39(8):1800–1811
Lee YC (2007) Application of support vector machines to corporate credit rating prediction. Expert Syst Appl 33(1):67–74
Li YY, Zhang HY, Wang JQ (2017) Linguistic neutrosophic sets and its application to multi-criteria decision-making problems. Int J Uncertain Quant. https://doi.org/10.1615/Int.J.UncertaintyQuantification.2017019627
Liang RX, Wang JQ, Zhang HY (2017) A multi-criteria decision-making method based on single-valued trapezoidal neutrosophic preference relations with complete weight information. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2925-8
Liu PD, Shi LL (2015) The generalized hybrid weighted average operator based on interval neutrosophic hesitant set and its application to multiple attribute decision making. Neural Comput Appl 26:457–471
Luo CC, Wu DS, Wu DX (2017) A deep learning approach for credit scoring using credit default swaps. Eng Appl Artif Intell 65:465–470
Lupiánez FG (2009) Interval neutrosophic sets and topology. Kybernetes 38:621–624
Meng FY, Chen XH, Zhang Q (2014) Multi-attribute decision analysis under a linguistic hesitant fuzzy environment. Inf Sci 267:287–305
Nikolic N, Zarkic-Joksimovic N, Stojanovski D, Joksimovic I (2013) The application of brute force logistic regression to corporate credit scoring models: evidence from Serbian financial statements. Expert Syst Appl 40(15):5932–5944
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Wang J, Chen XH (2014) Multicriteria decision-making approach with hesitant interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/868515
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Yang LJ, Qian J (2017a) A novel multi-criteria group decision-making approach using simplified neutrosophic information. Int J Uncertain Quant. https://doi.org/10.1615/Int.J.UncertaintyQuantification2017020126
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Yang WE (2017b) A multi-valued neutrosophic qualitative flexible approach based on likelihood for multi-criteria decision-making problems. Int J Syst Sci 48:425–435
Petropoulos A, Chatzis SP, Xanthopoulos S (2016) A novel corporate credit rating system based on Student’s-t hidden Markov models. Expert Syst Appl 53:87–105
Siddiqi N (2005) Credit risk scorecards: developing and implementing intelligent credit scoring. Wiley, London
Singh P (2015) Correlation coefficients for picture fuzzy sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28:591–604
Smarandache F (2003) A unifying field in logics: neutrosophic logic, neutrosophy, neutrosophic set, neutrosophic probability. American Research Press, Rehoboth, Mass, USA
Smarandache F (2004) Neutrosophic set-a generalization of the intuitionistic fuzzy set. J Def Resour Manag 24:38–42
Smarandache F, Kandasamy WBV (1999) Analysis of social aspects of migrant labourers living with hiv/aids using fuzzy theory and neutrosophic cognitive maps. IEEE Softw 16:115–117
Son LH (2015) DPFCM: a novel distributed picture fuzzy clustering method on picture fuzzy sets. Expert Syst Appl 42:51–66
Stević Ž, Tanackov I, Vasiljević M, Vesković S (2016) Evaluation in logistics using combined AHP and EDAS method. International Symposium on Operational Research SYM-OP-IS. Tara, Serbia, pp 309–313
Tian ZP, Wang J, Zhang HY, Wang JQ (2016) Multi-criteria decision-making based on generalized prioritized aggregation operators under simplified neutrosophic uncertain linguistic environment. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0552-9
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25:529–539
Torra V, Narukawa Y (2009) On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. The 18th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Jeju Island, South Korea, pp 1378–1382
Wan SP, Dong JY (2014) A possibility degree method for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making. J Comput Syst Sci 80:237–256
Wang CH, Wang JQ (2016) A multi-criteria decision-making method based on triangular intuitionistic fuzzy preference information. Intell Autom Soft Comput 22:473–482
Wang HB, Smarandache F,Zhang YQ,Sunderraman R (2005) Interval neutrosophic sets and logic: theory and applications in computing. Neutrosophic Book Series: No. 5. Hexis, Phoenix, Ariz, USA
Wang HB, Smarandache F, Zhang YQ, Sunderraman R (2010) Single valued neutrosophic sets. Multispace Multistruct 4:410–413
Wang JQ, Wu JT, Wang J, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2014) Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic sets and their applications in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Inf Sci 288:55–72
Wang JQ, Yang Y, Li L (2016) Multi-criteria decision-making method based on single valued neutrosophic linguistic Maclaurin symmetric mean operators. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2747-0
Wu TC, Hsu MF (2012) Credit risk assessment and decision making by a fusion approach. Knowl-Based Syst 35:102–110
Wu XH, Wang JQ (2017) Cross-entropy measures of multi-valued neutrosophic sets and its application in selecting middle-level manager. Int J Uncertain Quant 7(2):155–176
Wu ZB, Xu JP (2016) Possibility distribution-based approach for MAGDM with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(3):694–705
Xia YF, Liu CZ, Li YY, Liu NN (2017) A boosted decision tree approach using Bayesian hyper-parameter optimization for credit scoring. Expert Syst Appl 78:225–241
Yager RR (2013) Pythagorean fuzzy subsets. in: IFSA World Congress and NAFIPS Annual Meeting (IFSA/NAFIPS), Edmonton, AB, Canada, pp 57–61
Yager RR (2014) Pythagorean membership grades in multi-criteria decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22:958–965
Ye J (2014a) A multicriteria decision-making method using aggregation operators for simplified neutrosophic sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst Appl Eng Technol 26:2459–2466
Ye J (2014b) Correlation coefficient of dual hesitant fuzzy sets and its application to multiple attribute decision making. Appl Math Model 38:659–666
Ye J (2014c) Multiple-attribute decision-making method under a single-valued neutrosophic hesitant fuzzy environment. J Intell Syst 24:23–36
Yu LA, Wang SY, Lai KK (2009) An intelligent-agent-based fuzzy group decision making model for financial multicriteria decision support: The case of credit scoring. Eur J Oper Res 195(3):942–959
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–356
Zadeh LA (1973) Outline of a new approach to the analysis of complex systems and decision processes interval-valued fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 3:28–44
Zhang HY, Peng HG, Wang J, Wang JQ (2017) An extended outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Appl Soft Comput 59:462–474
Zhang XL (2016) Multicriteria Pythagorean fuzzy decision analysis: a hierarchical QUALIFLEX approach with the closeness index-based ranking methods. Inf Sci 330:104–124
Zhao XF, Lin R, Wei GW (2014) Hesitant triangular fuzzy information aggregation based on Einstein operations and their application to multiple attribute decision making. Expert Syst Appl 41:1086–1094
Zhong HM, Miao CY, Shen ZQ, Feng YH (2014) Comparing the learning effectiveness of BP, ELM, I-ELM, and SVM for corporate credit ratings. Neurocomputing 128:285–295
Zhu XQ, Li JP, Wu DS, Wang HY, Liang CZ (2013) Balancing accuracy, complexity and interpretability in consumer credit decision making: a C-TOPSIS classification approach. Knowl-Based Syst 52:258–267
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 15BJY163), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2018JJ2198), and Key Scientific Research Projects of Hunan Education Department (Grant No. 19A276).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors Ren, Hu, Yu, and Cheng declare they have no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Hu, Ch., Yu, Sq. et al. An extended EDAS method under four-branch fuzzy environments and its application in credit evaluation for micro and small entrepreneurs. Soft Comput 25, 2777–2792 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05337-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05337-1