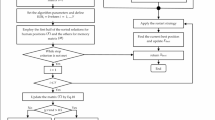
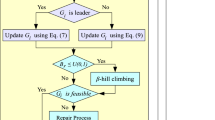
Abstract
Salp swarm algorithm (SSA) is a recent optimization technique inspired by behavior of the salp chains in deep oceans. However, the SSA is efficient, simple and easy to implement, it is susceptible to stagnation at local optima for some cases. The main contribution of this paper is proposing an improved salp swarm algorithm algorithm (ISSA) for enhancing the search capabilities of the original SSA to solve the optimal power flow (OPF) problem. In the proposed ISSA, both of exploration and the exploitation processes are enhanced. The exploration process is achieved by applying a random mutation to find new searching areas while an adaptive process is developed to enhance the exploitation process by focusing on the most promising search area. This strategy will balance the transformation between exploration and exploitation. The ISSA is employed to achieve OPF with non-smooth and non-convex generator fuel cost functions such as; minimizing quadratic fuel cost, piecewise quadratic cost, quadratic fuel cost considering the valve-point effect and prohibited zones. The main advantages of the ISSA are avoiding stagnation at local optima and can solve nonlinear and non-smooth optimization problems where its adaptive operators balance between the exploration and exploitation phases of this algorithm. However, the parameters of ISSA need to be carefully defined before application of algorithm. The proposed algorithm is validated using the standard IEEE 30-bus, IEEE 57-bus and IEEE 118-bus test systems. The performance of proposed algorithm is comprehensively compared with moth-flame optimization algorithm, improved harmony search algorithm, genetic algorithm and other reported optimization techniques. The results prove the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed algorithm compared with other optimization techniques.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Abbreviations
- \( x_{j}^{1} \) :
-
The position of the leader in the jth dimension
- \( x_{j}^{i} \) :
-
The position of ith follower salp in jth dimension
- \( F_{j} \) :
-
The position of the food source in the jth dimension
- \( L_{j} ,U_{j} \) :
-
The lower and upper bound of jth dimension
- C 2, C 3, C 4 :
-
Random numbers in the interval of [0,1]
- C 1 :
-
Time varying coefficient
- t :
-
The current iteration
- \( T_{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The maximum number of iterations
- \( v_{\text{final}} \) :
-
The final speed
- v 0 :
-
The initial speed
- \( V_{\text{L}} \) :
-
The voltage of load bus
- \( Q_{\text{G}} \) :
-
The reactive power output of generators
- \( S_{\text{TL}} \) :
-
The apparent power flow in transmission line
- NPQ:
-
Number of load buses
- NPV:
-
Number of generators PV buses
- NTL:
-
Number of transmission lines
- \( \lambda_{p} ,\lambda_{v} ,\lambda_{Q} ,\lambda_{s} \) :
-
Penalty factors
- \( \delta_{j} , \delta_{i} \) :
-
Voltage angles bus i and j
- A :
-
Time varying parameter
- \( V_{i}^{\hbox{min} } ,V_{i}^{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The minimum and the maximum voltage limits of load bus, respectively
- \( T_{i}^{\hbox{min} } ,T_{i}^{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The minimum and the maximum limits tap setting of transformers, respectively
- \( P_{\text{Gi}}^{\hbox{min} } ,P_{\text{Gi}}^{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The minimum and the maximum generated active limits ith generator, respectively
- \( S_{{{\text{TL}},i}}^{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The maximum apparent power flow limit of line i
- x 0 :
-
The initial position of salp
- E :
-
Time varying coefficient
- F :
-
The objective function
- x :
-
The state variables vector
- u :
-
The control variables vector
- \( g_{i} , h_{j} \) :
-
The equality and inequality constraints,
- m, n :
-
Number of equality and inequality constraints
- POZs:
-
Prohibited operating zones
- \( P_{G1} \) :
-
The generated power of slack bus
- \( P_{\text{G}} \) :
-
The output active power of generator
- \( V_{\text{G}} \) :
-
The voltage of generating bus
- \( Q_{\text{C}} \) :
-
The injected reactive power of shunt compensator
- T :
-
Tap setting of transformer
- NG:
-
Number of generators
- NC:
-
Number of shunt compensator
- NT:
-
Number of transformers
- \( X_{j}^{\text{new}} \) :
-
The new position of the salp swarm
- a i, b i, c i :
-
The cost coefficients of ith generator
- d i, e i :
-
The fuel cost coefficients of the ith generator unit with valve-point effects
- P D, Q D :
-
Active and reactive load demand
- G, B :
-
Conductance, substance of transmission line
- \( Q_{\text{ci}}^{\hbox{min} } ,Q_{\text{ci}}^{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The minimum and the maximum limits of compensator reactive power, respectively
- \( A_{\hbox{max} } ,A_{\hbox{min} } \) :
-
The minimum and the maximum A limit of the parameter, respectively
- \( Q_{\text{Gi}}^{\hbox{min} } ,Q_{\text{Gi}}^{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The minimum and the maximum generated reactive limits ith generator, respectively
- \( K_{\hbox{min} } ,K_{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
The minimum and the maximum K limiter respectively
- a :
-
The slap’s acceleration
References
Abbassi R, Abbassi A, Heidari AA, Mirjalili S (2019) An efficient salp swarm-inspired algorithm for parameters identification of photovoltaic cell models. Energy Convers Manag 179:362–372
Abdo M, Kamel S, Ebeed M, Yu J, Jurado F (2018) Solving non-smooth optimal power flow problems using a developed grey wolf optimizer. Energies 11(7):1692
Abido MA (2002a) Optimal power flow using tabu search algorithm. Electric Power Comp Syst 30(5):469–483
Abido MA (2002b) Optimal power flow using particle swarm optimization. Int J Electric Power Energy Syst 24(7):563–571
Abou El Ela AA, Abido MA, Spea SR (2010) Optimal power flow using differential evolution algorithm. Electric Power Syst Res 80(7):878–885
Adaryani MR, Karami A (2013) Artificial bee colony algorithm for solving multi-objective optimal power flow problem. Int J Electric Power Energy Syst 53:219–230
Alhejji A, Hussein ME, Kamel S, Alyami S (2020) Optimal power flow solution with an embedded center-node unified power flow controller using an adaptive grasshopper optimization algorithm. IEEE Access 8:119020–119037
Al-Muhawesh TA, Qamber IS (2008) The established mega watt linear programming-based optimal power flow model applied to the real power 56-bus system in eastern province of Saudi Arabia. Energy 33(1):12–21
Anter AM, Ali M (2020) Feature selection strategy based on hybrid crow search optimization algorithm integrated with chaos theory and fuzzy c-means algorithm for medical diagnosis problems. Soft Comput 24(3):1565–1584
Barik AK, Das DC (2018) Active power management of isolated renewable microgrid generating power from rooftop solar arrays, sewage waters and solid urban wastes of a smart city using salp swarm algorithm. In: Technologies for smart-city energy security and power (ICSESP). IEEE, pp 1–6
Baygi SMH, Karsaz A, Elahi A (2018) A hybrid optimal PID-fuzzy control design for seismic exited structural system against earthquake: a salp swarm algorithm. In: 6th Iranian joint congress on fuzzy and intelligent systems (CFIS). IEEE, pp 220–225
Bhattacharya A, Chattopadhyay PK (2011) Application of biogeography-based optimisation to solve different optimal power flow problems. IET Gen Transmission Distrib 5(1):70–80
Bouchekara HREH (2014) Optimal power flow using black-hole-based optimization approach. Appl Soft Comput 24:879–888
Bouchekara HREH, Abido MA (2014) Optimal power flow using differential search algorithm. Electric Power Comp Syst 42(15):1683–1699
Burchett RC, Happ HH, Vierath DR (1984) Quadratically convergent optimal power flow. IEEE Trans Power Apparat Syst 11:3267–3275
Chung TS, Li YZ (2001) A hybrid GA approach for OPF with consideration of FACTS devices. IEEE power Eng Rev 21(2):47–50
De Falco I, Della Cioppa A, Tarantino E (2002) Mutation-based genetic algorithm: performance evaluation. Appl Soft Comput 1(4):285–299
Dommel HW, Tinney WF (1968) Optimal power flow solutions. IEEE Trans Power Apparat Syst 10:1866–1876
Duman S (2017) Symbiotic organisms search algorithm for optimal power flow problem based on valve-point effect and prohibited zones. Neural Comput Appl 28(11):3571–3585
Duman S, Güvenç U, Sönmez Y, Yörükeren N (2012) Optimal power flow using gravitational search algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 59:86–95
Ekinci S, Hekimoglu B (2018) Parameter optimization of power system stabilizer via salp swarm algorithm. In: 5th International conference on electrical and electronic engineering (ICEEE). IEEE, pp 143–147
El Sehiemy RA, Selim F, Bentouati B, Abido MA (2020) A novel multi-objective hybrid particle swarm and salp optimization algorithm for technical-economical-environmental operation in power systems. Energy 193:116817
El-Fergany AA (2017) Electrical characterisation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells stack using grasshopper optimiser. IET Renew Power Gen 12(1):9–17
El-Fergany AA, Hasanien HM (2019) Salp swarm optimizer to solve optimal power flow comprising voltage stability analysis. Neural Comput Appl 32(9):1–17
Epitropakis MG, Tasoulis DK, Pavlidis NG, Plagianakos VP, Vrahatis MN (2011) Enhancing differential evolution utilizing proximity-based mutation operators. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 15(1):99–119
Fan L, Chen H, Gao Y (2019) An improved flower pollination algorithm to the urban transit routing problem. Soft Comput 24(7):5043–5052
Faris H, Mafarja MM, Heidari AA, Aljarah I, Ala’M AZ, Mirjalili S, Fujita H (2018) An efficient binary salp swarm algorithm with crossover scheme for feature selection problems. Knowl Based Syst 154:43–67
Faris H, Ala’M AZ, Heidari AA, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Hassonah MA, Fujita H (2019) An intelligent system for spam detection and identification of the most relevant features based on evolutionary random weight networks. Inf Fusion 48:67–83
Faris H, Mirjalili S, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Heidari AA (2020) Salp swarm algorithm: theory, literature review, and application in extreme learning machines. In: Mirjalili S, Song Dong J, Lewis A (eds) Nature-inspired optimizers, vol 811. Springer, pp 185–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12127-3_11
Ghasemi M, Ghavidel S, Gitizadeh M, Akbari E (2015) An improved teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm using Lévy mutation strategy for non-smooth optimal power flow. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 65:375–384
Goldberg DE, Holland JH (1988) Genetic algorithms and machine learning. Machine Learn 3:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022602019183
Habibollahzadeh H, Luo GX, Semlyen A (1989) Hydrothermal optimal power flow based on a combined linear and nonlinear programming methodology. IEEE Trans Power Syst 4(2):530–537
Hegazy AE, Makhlouf MA, El-Tawel GS (2020) Improved salp swarm algorithm for feature selection. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 32(3):335–344
Holland JH (1992) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: an introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence. MIT Press, Cambridge
Hussien AG, Hassanien AE, Houssein EH (2017) Swarming behaviour of salps algorithm for predicting chemical compound activities. In: Eighth international conference on intelligent computing and information systems (ICICIS). IEEE, pp 315–320
Ibrahim A, Ahmed A, Hussein S, Hassanien AE (2018) Fish image segmentation using salp swarm algorithm. In: International conference on advanced machine learning technologies and applications. Springer, pp 42–51
Ibrahim RA, Ewees AA, Oliva D, Abd Elaziz M, Lu S (2019) Improved salp swarm algorithm based on particle swarm optimization for feature selection. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 10(8):3155–3169
Islam MZ et al (2020) A Harris Hawks optimization based single-and multi-objective optimal power flow considering environmental emission. Sustainability 12(13):5248
Jadhav HT, Bamane PD (2016) Temperature dependent optimal power flow using g-best guided artificial bee colony algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 77:77–90
Jayabarathi T, Sadasivam G, Ramachandran V (1999) Evolutionary programming based economic dispatch of generators with prohibited operating zones. Electric Power Syst Res 52(3):261–266
Jayakumar N, Subramanian S, Ganesan S, Elanchezhian EB (2016) Grey wolf optimization for combined heat and power dispatch with cogeneration systems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 74:252–264
Kaur M, Narang N (2020) An integrated optimization technique for optimal power flow solution. Soft Comput 24:10865–10882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04590-3
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (2010) Particle swarm optimization. Encycl Mach Learn 4:760–766
Kılıç U (2015) Backtracking search algorithm-based optimal power flow with valve point effect and prohibited zones. Electric Eng 97(2):101–110
Kumar AR, Premalatha L (2015) Optimal power flow for a deregulated power system using adaptive real coded biogeography-based optimization. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 73:393–399
Li Z, Cao Y, Dai LV, Yang X, Nguyen TT (2019) Optimal power flow for transmission power networks using a novel metaheuristic algorithm. Energies 12(22):4310
Li S, Gong W, Wang L, Yan X, Hu C (2020) Optimal power flow by means of improved adaptive differential evolution. Energy 198:117314
Mafarja M, Aljarah I, Heidari AA, Faris H, Fournier-Viger P, Li X, Mirjalili S (2018a) Binary dragonfly optimization for feature selection using time-varying transfer functions. Knowl Based Syst 161:185–204
Mafarja M, Aljarah I, Heidari AA, Hammouri AI, Faris H, Ala’M AZ, Mirjalili S (2018b) Evolutionary population dynamics and grasshopper optimization approaches for feature selection problems. Knowl Based Syst 145:25–45
Mahdad B (2019) Improvement optimal power flow solution under loading margin stability using new partitioning whale algorithm. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag 14(1):64–77
Mahdavi M, Fesanghary M, Damangir E (2007) An improved harmony search algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl Math Comput 188(2):1567–1579
Manoranjitham GE, Shunmugalatha A (2015) RETRACTED: application of firefly algorithm on optimal power flow control incorporating simplified impedance UPFC model. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mirjalili S (2015) Moth-flame optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl Based Syst 89:228–249
Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH, Mirjalili SZ, Saremi S, Faris H, Mirjalili SM (2017) Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw 114:163–191
Mohamed A-AA, Mohamed YS, El-Gaafary AA, Hemeida AM (2017) Optimal power flow using moth swarm algorithm. Electric Power Syst Res 142:190–206
Mota-Palomino R, Quintana VH (1986) Sparse reactive power scheduling by a penalty function-linear programming technique. IEEE Trans Power Syst 1(3):31–39
Niknam T, Narimani MR, Azizipanah-Abarghooee R (2012) A new hybrid algorithm for optimal power flow considering prohibited zones and valve point effect. Energy Convers Manag 58:197–206
Ongsakul W, Tantimaporn T (2006) Optimal power flow by improved evolutionary programming. Electric power Comp Syst 34(1):79–95
Osman MS, Abo-Sinna MA, Mousa AA (2004) A solution to the optimal power flow using genetic algorithm. Appl Math Comput 155(2):391–405
Pulluri H, Naresh R, Sharma V (2018) A solution network based on stud krill herd algorithm for optimal power flow problems. Soft Comput 22(1):159–176
Qais MH, Hasanien HM, Alghuwainem S (2019) Enhanced salp swarm algorithm: application to variable speed wind generators. Eng Appl Artif Intell 80:82–96
Rao RV, Saroj A (2019) An elitism-based self-adaptive multi-population Jaya algorithm and its applications. Soft Comput 23(12):4383–4406
Reddy SS (2019) Optimal power flow using hybrid differential evolution and harmony search algorithm. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10(5):1077–1091
Roy PK, Paul C (2015) Optimal power flow using krill herd algorithm. Int Trans Electric Energy Syst 25(8):1397–1419
Santos AJ, Da Costa GRM (1995) Optimal-power-flow solution by Newton’s method applied to an augmented Lagrangian function. IEE Proc Gen Transmission and Distrib 142(1):33–36
Savsani VJ, Tejani GG, Patel VK, Savsani P (2017) Modified meta-heuristics using random mutation for truss topology optimization with static and dynamic constraints. J Comput Des Eng 4(2):106–130
Sayah S, Zehar K (2008) Modified differential evolution algorithm for optimal power flow with non-smooth cost functions. Energy Convers Manag 49(11):3036–3042
Sayed GI, Khoriba G, Haggag MH (2018) A novel chaotic salp swarm algorithm for global optimization and feature selection. Appl Intell 48(10):3462–3481
Selvakumar AI, Thanushkodi K (2007) A new particle swarm optimization solution to nonconvex economic dispatch problems. IEEE Trans Power Syst 22(1):42–51
Shaheen AM, El-Sehiemy RA, Farrag SM (2016) Solving multi-objective optimal power flow problem via forced initialised differential evolution algorithm. IET Gen Transmission Distrib 10(7):1634–1647
Shaheen MA, Mekhamer SF, Hasanien HM, Talaat HE (2019) Optimal power flow of power systems using hybrid firefly and particle swarm optimization technique. In 2019 21st international middle east power systems conference (MEPCON). IEEE, pp 232–237
Shilaja C, Arunprasath T (2019) Optimal power flow using moth swarm algorithm with gravitational search algorithm considering wind power. Future Gen Comput Syst 98:708–715
Sun DI, Ashley B, Brewer B, Hughes A, Tinney WF (1984) Optimal power flow by Newton approach. IEEE Trans Power Apparat Syst 10:2864–2880
Taher MA, Kamel S, Jurado F, Ebeed M (2019) Modified grasshopper optimization framework for optimal power flow solution. Electric Eng 101(1):121–148
Tolba M, Rezk H, Diab AAZ, Al-Dhaifallah M (2018) A novel robust methodology based salp swarm algorithm for allocation and capacity of renewable distributed generators on distribution grids. Energies 11(10):2556
Vaisakh K, Srinivas LR (2011) Evolving ant direction differential evolution for OPF with non-smooth cost functions. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24(3):426–436
Walters DC, Sheble GB (1993) Genetic algorithm solution of economic dispatch with valve point loading. IEEE Trans Power Syst 8(3):1325–1332
Wang L, Zou F, Hei X, Yang D, Chen D, Jiang Q (2014) An improved teaching–learning-based optimization with neighborhood search for applications of ANN. Neurocomputing 143:231–247
Wang M, Yang M, Han X (2020) Optimal power flow considering transient thermal behavior of overhead transmission lines. Int J Electric Power Energy Syst 114:105396
Xing H, Song F, Yan L, Pan W (2019) A modified artificial bee colony algorithm for load balancing in network-coding-based multicast. Soft Comput 23(15):6287–6305
The IEEE power Systems test cases. Available: https://labs.ece.uw.edu/pstca/
Yan X, Quintana VH (1999) Improving an interior-point-based OPF by dynamic adjustments of step sizes and tolerances. IEEE Trans Power Syst 14(2):709–717
Yang XS (2012) Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. In: International conference on unconventional computing and natural computation. Springer, pp 240–249
Yi W, Gao L, Li X, Zhou Y (2015) A new differential evolution algorithm with a hybrid mutation operator and self-adapting control parameters for global optimization problems. Appl Intell 42(4):642–660
Younes M, Khodja F, Kherfane RL (2014) Multi-objective economic emission dispatch solution using hybrid FFA (firefly algorithm) and considering wind power penetration. Energy 67:595–606
Zhang X, Yuen SY (2015) A directional mutation operator for differential evolution algorithms. Appl Soft Comput 30:529–548
Zhang Y, Cui G, Wu J, Pan WT, He Q (2016) A novel multi-scale cooperative mutation fruit fly optimization algorithm. Knowl Based Syst 114:24–35
Zhang J, Wang Z, Luo X (2018) Parameter estimation for soil water retention curve using the salp swarm algorithm. Water 10(6):815
Zhang Z, Mao L, Guan C, Zhu L, Wang Y (2020) An improved scatter search algorithm for the corridor allocation problem considering corridor width. Soft Comput 24(1):461–481
Zimmerman RD, Murillo-Sánchez CE, Thomas RJ (2010) MATPOWER: steady-state operations, planning, and analysis tools for power systems research and education. IEEE Trans Power Syst 26(1):12–19
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the support of the National Research and Development Agency of Chile (ANID), ANID/Fondap/15110019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd el-sattar, S., Kamel, S., Ebeed, M. et al. An improved version of salp swarm algorithm for solving optimal power flow problem. Soft Comput 25, 4027–4052 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05431-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05431-4