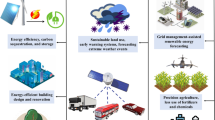
Abstract
Smart energy management improves the efficiency of the services and computing systems operated in a smart city environment. The heterogeneous environment makes use of artificial intelligence allied technologies for energy management. Depending upon the service data and its processing, energy management is proliferated for providing reliable service outcomes. In this paper, Enduring Data Analytics for Energy Management (EDA-EM) is proposed. The proposed method makes use of data distribution factors for optimal energy distribution. In this process, the cumulative and independent data streams require different energy requirements. This requirement is identified using principal component analysis for identifying other data streams. The data stream is a series of feature vectors describing one or more underlying patterns together. A stream framework demonstrates how the underlying patterns of different stream elements can be reconstructed. The stream classification helps to allocate desired energy without overloaded instances in the big data processing. The remaining and available renewable energy is distributed for the classified streams in handling big data. Big data streaming indicates that Big Data is processed rapidly to gain insight into it in virtual environments. The production data are in movement. The data are in trend. Ideally, big data streaming is a frequency solution that processes a prolonged data stream. In this allocation process, renewable energy available for the successive handling interval is predicted for improving the seamlessness in the data processing. The proposed method's performance is verified using energy distribution ratio, conservation rate, and data loses, processing rate, and processing delay. In EDA-EM, the achieved distribution ratio is 95.13% which is comparatively reasonable than other approaches.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 January 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07868-9
References
Ahmed W, Ansari H, Khan B, Ullah Z, Ali SM, Mehmood CAA et al (2020) Machine learning based energy management model for smart grid and renewable energy districts. IEEE Access 8:185059–185078
Ahrarinouri M, Rastegar M, Seifi AR (2020) Multi-agent reinforcement learning for energy management in residential buildings. IEEE Trans Indus Inform 17:659–666
Anbarasan M, Muthu B, Sivaparthipan CB, Sundarasekar R, Kadry S, Krishnamoorthy S, Dasel AA (2020) Detection of flood disaster system based on IoT, big data and convolutional deep neural network. Comput Commun 150:150–157
Anthony B, Petersen SA, Ahlers D, Krogstie J, Livik K (2019) Big data-oriented energy prosumption service in smart community districts: a multi-case study perspective. Energy Inform 2(1):36
Babar M, Rahman A, Arif F, Jeon G (2018) Energy-harvesting based on internet of things and big data analytics for smart health monitoring. Sustain Comput Inform Syst 20:155–164
Bibri SE (2020) The eco-city and its core environmental dimension of sustainability: green energy technologies and their integration with data-driven smart solutions. Energy Inform 3(1):1–26
Bibri SE, Krogstie J (2020) Environmentally data-driven smart sustainable cities: applied innovative solutions for energy efficiency, pollution reduction, and urban metabolism. Energy Inform 3(1):1–59
Cao X, Liu L, Cheng Y, Shen XS (2017) Towards energy-efficient wireless networking in the big data era: A survey. IEEE Commun Surveys Tutor 20(1):303–332
Celesti A, Fazio M (2019) A framework for real time end to end monitoring and big data oriented management of smart environments. J Parallel Distrib Comput 132:262–273
Chen L, Qiao S, Han N, Yuan C, Song X, Huang P, Xiao Y (2020) Friendship prediction model based on factor graphs integrating geographical location. CAAI Trans Intell Technol 5(3):193–199. https://doi.org/10.1049/trit.2020.0033
Cui S, Wang YW, Xiao JW (2019) Peer-to-peer energy sharing among smart energy buildings by distributed transaction. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 10(6):6491–6501
Easwaramoorthy S, Thamburasa S, Samy G, Bhushan SB, Aravind K (2016) Digital forensic evidence collection of cloud storage data for investigation. In: 2016 International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Technology (ICRTIT), 2016, pp 1–6. IEEE
Edalatpanah S (2020) Data envelopment analysis based on triangular neutrosophic numbers. CAAI Trans Intell Technol 5(2):94–98. https://doi.org/10.1049/trit.2020.0016
Hafeez G, Alimgeer KS, Wadud Z, Khan I, Usman M, Qazi AB, Khan FA (2020) An innovative optimization strategy for efficient energy management with day-ahead demand response signal and energy consumption forecasting in smart grid using artificial neural network. IEEE Access 8:84415–84433
Hopf K, Sodenkamp M, Staake T (2018) Enhancing energy efficiency in the residential sector with smart meter data analytics. Electron Mark 28(4):453–473
Kim S, Mowakeaa R, Kim SJ, Lim H (2020) Building energy management for demand response using kernel lifelong learning. IEEE Access 8:82131–82141
Manogaran G, Lopez D (2018) Spatial cumulative sum algorithm with big data analytics for climate change detection. Comput Electr Eng 1(65):207–221
Manogaran G, Lopez D (2018) A Gaussian process based big data processing framework in cluster computing environment. Clust Comput 21(1):189–204
Manogaran G, Vijayakumar V, Varatharajan R, Kumar PM, Sundarasekar R, Hsu CH (2018) Machine learning based big data processing framework for cancer diagnosis using hidden Markov model and GM clustering. Wireless Pers Commun 102(3):2099–2116
Manogaran G, Varatharajan R, Lopez D, Kumar PM, Sundarasekar R, Thota C (2018) A new architecture of Internet of Things and big data ecosystem for secured smart healthcare monitoring and alerting system. Futur Gener Comput Syst 1(82):375–387
Marinakis V, Doukas H, Tsapelas J, Mouzakitis S, Sicilia Á, Madrazo L, Sgouridis S (2018) From big data to smart energy services: An application for intelligent energy management. Fut Gener Comput Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.04.062
Marino CA, Marufuzzaman M (2020) A microgrid energy management system based on chance-constrained stochastic optimization and big data analytics. Comput Ind Eng 143:106392
Nie X, Fan T, Wang B, Li Z, Shankar A, Manickam A (2020) Big data analytics and IoT in operation safety management in under water management. Comput Commun 154:188–196
Raspopov D, Belousov P (2020) Development of methods and algorithms for identification of a type of electric energy consumers using artificial intelligence and machine learning models for Smart Grid Systems. Proc Comput Sci 169:597–605
Saravanan V, Anpalagan A, Kothari DP, Woungang I, Obaidat MS (2014) A comparative simulation study on the power–performance of multi-core architecture. J Supercomput 70(1):465–487
Silva BN, Khan M, Han K (2020) Integration of big data analytics embedded smart city architecture with RESTful web of things for efficient service provision and energy management. Futur Gener Comput Syst 107:975–987
Sivaparthipan CB, Muthu BA, Manogaran G, Maram B, Sundarasekar R, Krishnamoorthy S, Hsu CH, Chandran K (2019) Innovative and efficient method of robotics for helping the Parkinson’s disease patient using IoT in big data analytics. Trans Emerg Telecommun Technol 11:e3838
Varatharajan R, Manogaran G, Priyan MK (2018) A big data classification approach using LDA with an enhanced SVM method for ECG signals in cloud computing. Multimed Tools Appl 77(8):10195–10215
Wang S, Liang YC, Li WD, Cai XT (2018) Big data enabled intelligent immune system for energy efficient manufacturing management. J Clean Prod 195:507–520
Wu W, Lin W, Hsu CH, He L (2018) Energy-efficient hadoop for big data analytics and computing: a systematic review and research insights. Futur Gener Comput Syst 86:1351–1367
Yin H, Zhao C, Ma C (2018) Decentralized real-time energy management for a reconfigurable multiple-source energy system. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 14(9):4128–4137
Zhang Y, Ma S, Yang H, Lv J, Liu Y (2018) A big data driven analytical framework for energy-intensive manufacturing industries. J Clean Prod 197:57–72
Zhang W, Zhang Z, Zeadally S, Chao HC, Leung VC (2019) MASM: A multiple-algorithm service model for energy-delay optimization in edge artificial intelligence. IEEE Trans Indus Inf 15(7):4216–4224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Vincente Garcia Diaz.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07868-9
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalra, D., Pradhan, M.R. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Enduring data analytics for reliable data management in handling smart city services. Soft Comput 25, 12213–12225 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05892-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05892-1