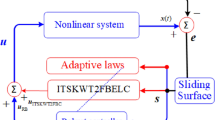
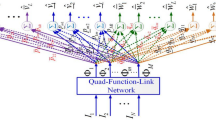
Abstract
Conventional control systems often suffer from the coexistence of nonlinearity and uncertainty. This paper proposes a novel brain emotional neural network to support addressing such challenges. The proposed network integrates a wavelet neural network into a conventional brain emotional learning network. This is further enhanced by the introduction of a recurrent structure to employ the two networks as the two channels of the brain emotional learning network. The proposed network therefore combines the advantages of the wavelet function, the recurrent mechanism, and the brain emotional learning system, for optimal performance on nonlinear problems under uncertain environments. The proposed network works with a bounding compensator to mimic an ideal controller, and the parameters are updated based on the laws derived from the Lyapunov stability analysis theory. The proposed system was applied to two uncertain nonlinear systems, including a Duffing-Homes chaotic system and a simulated 3-DOF spherical joint robot. The experiments demonstrated that the proposed system outperformed other popular neural-network-based control systems, indicating the superiority of the proposed system.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Al-Dunainawi Y, Abbod MF, Jizany A (2017) A new mimo anfis-pso based narma-l2 controller for nonlinear dynamic systems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 62:265–275
Baghbani F, Akbarzadeh-T MR, Naghibi-Sistani MB, Akbarzadeh A (2020) Emotional neural networks with universal approximation property for stable direct adaptive nonlinear control systems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 89:103447
Baghbani F, Akbarzadeh-T MR, Sistani M (2021) Cooperative adaptive emotional neuro-control for a class of higher-ordered heterogeneous uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems. Neurocomputing 447:196–212
Baghbani F, Akbarzadeh-T MR, Sistani MBN (2018) Stable robust adaptive radial basis emotional neurocontrol for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 309:11–26
Balkenius C, Morén J (2001) Emotional learning: a computational model of the amygdala. Cybernet Syst 32:611–636
Chao F, Zhou D, Lin C, Yang L, Zhou C, Shang C (2019) Type-2 fuzzy hybrid controller network for robotic systems. IEEE Trans Cybernet 50:1–15
Chao F, Zhou D, Lin CM, Zhou C, Shi M, Lin D (2018) Fuzzy cerebellar model articulation controller network optimization via self-adaptive global best harmony search algorithm. Soft Comput 22:3141–3153
Chen Z, Huang F, Chen W, Zhang J, Sun W, Chen J, Gu J, Zhu S (2019) RBFNN-based adaptive sliding mode control design for delayed nonlinear multilateral tele-robotic system with cooperative manipulation. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 16:1236–1247
Debnath B, Ms J (2020) Emotional learning based controller for quadruple tank system - an improved stimuli design for multiple set-point tracking. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 68:11296–11308
El-Garhy AM, El-Shimy ME (2015) Belbic for mras with highly non-linear process. Alex Eng J 54:7–16
Elhaki O, Shojaei K (2020) A robust neural network approximation-based prescribed performance output-feedback controller for autonomous underwater vehicles with actuators saturation. Eng Appl Artif Intell 88:103382
Fang W, Chao F, Lin C, Zhou D, Yang L, Chang X, Shen Q, Shang C (2020) Visual-guided robotic object grasping using dual neural network controllers. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 17:2282–2291
Fang W, Chao F, Lin CM, Yang L, Shang C, Zhou C (2019a) An improved fuzzy brain emotional learning model network controller for humanoid robots. Front Neurorobotics 13:2
Fang W, Chao F, Yang L, Lin CM, Shang C, Zhou C, Shen Q (2019b) A recurrent emotional cmac neural network controller for vision-based mobile robots. Neurocomputing 334:227–238
Fei J, Lu C (2018) Adaptive sliding mode control of dynamic systems using double loop recurrent neural network structure. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29:1275–1286
Hadjaissa A, Ameur K, Boutoubat M (2019) A wca-based optimization of a fuzzy sliding-mode controller for stand-alone hybrid renewable power system. Soft Comput 23:7831–7842
Huynh T, Lin C, Le T, Cho H, Pham TT, Le N, Chao F (2019) A new self-organizing fuzzy cerebellar model articulation controller for uncertain nonlinear systems using overlapped gaussian membership functions. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67:9671–9682
Huynh T, Lin C, Le T, Nguyen NP, Hong S, Chao F (2020) Wavelet interval type-2 fuzzy quad-function-link brain emotional control algorithm for the synchronization of 3d nonlinear chaotic systems. Int J Fuzzy Syst 22:2546–2564
Huynh TT, Le TL, Lin CM (2018) A topsis multi-criteria decision method-based intelligent recurrent wavelet cmac control system design for mimo uncertain nonlinear systems. Neural Comput Appl 32:4025–4043
Le TL, Lin CM, Huynh TT (2018) Self-evolving type-2 fuzzy brain emotional learning control design for chaotic systems using pso. Appl Soft Comput 73:418–433
Lin C, Boldbaatar E (2017) Fault accommodation control for a biped robot using a recurrent wavelet Elman neural network. IEEE Syst J 11:2882–2893
Lin C, Nguyen H, Huynh T (2021) A new self-organizing double function-link brain emotional learning controller for MIMO nonlinear systems using sliding surface. IEEE Access 9:73826–73842
Lin CM, Chung CC (2015) Fuzzy brain emotional learning control system design for nonlinear systems. Int J Fuzzy Syst 17:117–128
Lin CM, Huynh TT, Le TL (2019) Adaptive topsis fuzzy cmac back-stepping control system design for nonlinear systems. Soft Comput 23:6947–6966
Lin Q, Chen S, Lin C (2019) Parametric fault diagnosis based on fuzzy cerebellar model neural networks. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66:8104–8115
Liu ZT, Xie Q, Wu M, Cao WH, Mei Y, Mao JW (2018) Speech emotion recognition based on an improved brain emotion learning model. Neurocomputing 309:145–156
Lotfi E, Rezaee AA (2019) Generalized BELBIC. Neural Comput Appl 31:4367–4383
Lucas C, Shahmirzadi D, Sheikholeslami N (2004) Introducing belbic: Brain emotional learning based intelligent controller. Intell Autom Soft Comput 10:11–21
Mehrabian AR, Lucas C, Roshanian J (2006) Aerospace launch vehicle control: an intelligent adaptive approach. Aerosp Sci Technol 10:149–155
Mishra RN, Mohanty KB (2020) Development and implementation of induction motor drive using sliding-mode based simplified neuro-fuzzy control. Eng Appl Artif Intell 91:103593
Mj A, Hao XB, Lrgc C (2020) A biologically-inspired reinforcement learning based intelligent distributed flocking control for multi-agent systems in presence of uncertain system and dynamic environment. IFAC J Syst Control 13:100096
Oveisi A, Jeronimo MB, Nestorović T (2018) Nonlinear observer-based recurrent wavelet neuro-controller in disturbance rejection control of flexible structures. Eng Appl Artif Intell 69:50–64
Parsa P, Akbarzadeh-T MR, Baghbani F (2021) Command-filtered backstepping robust adaptive emotional control of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with mismatched uncertainties. Inf Sci 579:434–453
Qutubuddin M, Yadaiah N (2017) Modeling and implementation of brain emotional controller for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. Eng Appl Artif Intell 60:193–203
Rouhani H, Jalili M, Araabi BN, Eppler W, Lucas C (2007) Brain emotional learning based intelligent controller applied to neurofuzzy model of micro-heat exchanger. Ex Syst Appl 32:911–918
Uçak K, Günel GÖ (2020) An adaptive sliding mode controller based on online support vector regression for nonlinear systems. Soft Comput 24:4623–4643
Wu Q, Lin C, Fang W, Chao F, Yang L, Shang C, Zhou C (2018) Self-organizing brain emotional learning controller network for intelligent control system of mobile robots. IEEE Access 6:59096–59108
Zhao J, Lin C (2019) Wavelet-tsk-type fuzzy cerebellar model neural network for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27:549–558
Zhao J, Lin CM, Chao F (2019) Wavelet fuzzy brain emotional learning control system design for mimo uncertain nonlinear systems. Front Neurosci 12:918
Zhou D, Shi M, Chao F, Lin CM, Yang L, Shang C, Zhou C (2018) Use of human gestures for controlling a mobile robot via adaptive cmac network and fuzzy logic controller. Neurocomputing 282:218–231
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments which have helped significantly in revising this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ involved in methodology, software, writing–original draft preparation; FC involved in conceptualization of this study, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing–original draft preparation; C-ML involved in conceptualization of this study; Longzhi Yang involved in writing–Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61673322, 61673326, and 91746103), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 20720190142), and the Key Project of National Key R & D Project (No. 2017YFC1703303).
Integrating a wavelet neural network to a brain emotional network to accelerate the learning rate. Sensitive sequential input detection by recurrent loop mechanisms leading to improved dynamic characteristics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Chao, F., Zeng, H. et al. A recurrent wavelet-based brain emotional learning network controller for nonlinear systems. Soft Comput 26, 3013–3028 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06422-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06422-9