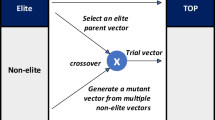
Abstract
A novel self-learning differential evolution (SLDE) algorithm for addressing large-scale internal tasks scheduling problems in cross-docking is proposed herein. The goal is to obtain an optimal schedule for working teams and transferring equipment for handling incoming containers at the inbound area and patient orders at the outbound area to minimise the total tardiness. The proposed SLDE aims to increase the search capability of its original differential evolution (DE). The key concept of SLDE is to allow a DE population to learn the capabilities of different search strategies and automatically adjust itself to potential search strategies. The performance of the proposed algorithms is evaluated on a set of generated data based on a real-case scenario of a medical product distribution centre; subsequently, the performance results are compared with results obtained from other metaheuristics. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed SLDE outperforms other algorithms in terms of solution quality and convergence behaviour by providing superior solutions using fewer function evaluations.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Afshar-Bakeshloo M, Jolai F, Mazinani M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2019) A satisfactory multi-agent single-machine considering a cross-docking terminal. Int J Syst Syst Eng 9:307–330. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSSE.2019.104164
Alvarez-Perez G, González-Velarde J, Fowler JW (2009) Crossdocking—just in time scheduling: an alternative solution approach. J Oper Res Soc 60:554–564. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601812
Arabani AB, Ghomi SF, Zandieh M (2010) A multi-criteria cross-docking scheduling with just-in-time approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49:741–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2429-5
Arabani AB, Ghomi SF, Zandieh M (2011) Meta-heuristics implementation for scheduling of trucks in a cross-docking system with temporary storage. Expert Syst Appl 38:1964–1979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.07.130
Assadi MT, Bagheri M (2016) Differential evolution and Population-based simulated annealing for truck scheduling problem in multiple door cross-docking systems. Comput Ind Eng 96:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2016.03.021
Beasley D, Bull DR, Martin RR (1993) An overview of genetic algorithms: Part 1, fundamentals. Univ Comput 15:56–69
Brest J, Maučec MS (2008) Population size reduction for the differential evolution algorithm. Appl Intell 29:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-007-0091-x
Brest J, Maučec MS (2011) Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm using population size reduction and three strategies. Soft Comput 15:2157–2174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-010-0644-5
Brest J, Greiner S, Boskovic B, Mernik M, Zumer V (2006) Self-adapting control parameters in differential evolution: a comparative study on numerical benchmark problems. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10:646–657. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2006.872133
Buakum D, Wisittipanich W (2019a) A literature review and further research direction in cross-docking. In: Proceedings of the international conference on industrial engineering and operations management, pp. 471–481
Buakum D, Wisittipanich W (2019b) A mathematical model for internal task scheduling in cross docking. In: 2019b IEEE international conference on industrial engineering and engineering management (IEEM) 2019b, pp. 14–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEM44572.2019.8978669
Buakum D, Wisittipanich W (2020) Stochastic internal task scheduling in cross docking using chance-constrained programming. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/17509653.2020.1764404
Do DT, Lee S, Lee J (2016) A modified differential evolution algorithm for tensegrity structures. Compos Struct 158:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.11.099
Fan Q, Yan X (2015a) Differential evolution algorithm with self-adaptive strategy and control parameters for P-xylene oxidation process optimization. Soft Comput 19:1363–1391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1349-y
Fan Q, Yan X (2015b) Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm with zoning evolution of control parameters and adaptive mutation strategies. IEEE Trans Cybern 46:219–232. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2015.2399478
Fan Q, Zhang Y (2016) Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm with crossover strategies adaptation and its application in parameter estimation. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 151:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2015.12.020
Gong W, Cai Z, Ling CX, Li H (2010) Enhanced differential evolution with adaptive strategies for numerical optimization. IEEE Transactions on Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybern) 41:397–413. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2010.2056367
Gong W, Fialho A, Cai Z, Li H (2011) Adaptive strategy selection in differential evolution for numerical optimization: an empirical study. Inf Sci 181:5364–5386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2011.07.049
Gou X, Huang T, Yang S, Su M, Zeng F (2018) Optimized differential evolution algorithm for software testing. Int J Comput Intell Syst 12:215–226. https://doi.org/10.2991/ijcis.d.190711.001
Hamdi I, Tekaya MF (2019) A genetic algorithm to minimize the Makespan in a two-machine cross-docking flow shop problem. J Oper Res Soc China. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40305-019-00277-6
Leon M, Xiong N, Molina D, Herrera F (2019) A novel memetic framework for enhancing differential evolution algorithms via combination with Alopex local search. Int J Comput Intell Syst 12:795–808. https://doi.org/10.2991/ijcis.d.190711.001
Leon M, Xiong N (2018) Enhancing adaptive differential evolution algorithms with rank-based mutation adaptation. In: 2018 IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation (CEC) 2018 https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2018.8477879
Leon M, Zenlander Y, Xiong N, Herrera F (2016) Designing optimal harmonic filters in power systems using greedy adaptive differential evolution. In: 2016 IEEE 21st International conference on emerging technologies and factory automation (ETFA) 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/ETFA.2016.7733571
Li Y, Lim A, Rodrigues B (2004) Crossdocking—JIT scheduling with time windows. J Oper Res Soc 55:1342–1351. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601812
Liao TW, Egbelu PJ, Chang P-C (2012) Two hybrid differential evolution algorithms for optimal inbound and outbound truck sequencing in cross docking operations. Appl Soft Comput 12:3683–3697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2012.05.023
Liao T, Egbelu P, Chang P-C (2013) Simultaneous dock assignment and sequencing of inbound trucks under a fixed outbound truck schedule in multi-door cross docking operations. Int J Prod Econ 141:212–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.03.037
Liu J, Lampinen J (2005) A fuzzy adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Soft Comput 9:448–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-004-0363-x
Mallipeddi R, Suganthan PN (2010) Differential evolution algorithm with ensemble of parameters and mutation and crossover strategies. International conference on swarm, evolutionary, and memetic computing 2010. Springer, Berlin, pp 71–78
Montgomery DC (2009) Introduction to statistical quality control. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Moussa TM, Awotunde AA (2018) Self-adaptive differential evolution with a novel adaptation technique and its application to optimize ES-SAGD recovery process. Comput Chem Eng 118:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2018.07.018
Pan Q-K, Suganthan PN, Wang L, Gao L, Mallipeddi R (2011) A differential evolution algorithm with self-adapting strategy and control parameters. Comput Oper Res 38:394–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2010.06.007
Plagianakos V, Tasoulis D, Vrahatis MN (2008) A review of major application areas of differential evolution. Advances in differential evolution. Springer, Berlin, pp 197–238
Price K, Storn R, Lampinen J (2005) Differential evolution—a practical approach to global optimization, vol 141. Springer, Berlin
Qin AK, Suganthan PN (2005) Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm for numerical optimization. In: 2005 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation 2005: 1785–1791. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2005.1554904
Sallam KM, Elsayed SM, Sarker RA, Essam DL (2017) Landscape-based adaptive operator selection mechanism for differential evolution. Inf Sci 418:383–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.08.028
Sallam KM, Elsayed SM, Chakrabortty RK, Ryan MJ (2020) Improved multi-operator differential evolution algorithm for solving unconstrained problems. In: 2020 IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation (CEC) 2020, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC48606.2020.9185577
Sharma N, Anpalagan A (2014) Composite differential evolution aided channel allocation in OFDMA systems with proportional rate constraints. J Commun Netw 16:523–533. https://doi.org/10.1109/JCN.2014.000091
Song E, Li H (2021) Differential evolution using novel individual evaluation and constraint handling techniques for constrained optimization. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05831-0
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution–a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Global Optim 11:341–359. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008202821328
Tanabe R, Fukunaga A (2013) Success-history based parameter adaptation for differential evolution. In: 2013 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation 2013: 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2013.6557555
Tanabes R, Fukunaga AS (2014) Improving the search performance of SHADE using linear population size reduction. In: 2014 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC) 2014: 1658–1665. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2014.6900380
Wang Y, Cai Z, Zhang Q (2011) Differential evolution with composite trial vector generation strategies and control parameters. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 15:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2010.2087271
Weihmann L, Martins D, dos Santos Coelho L (2012) Modified differential evolution approach for optimization of planar parallel manipulators force capabilities. Exp Syst Appl 39(6):6150–6156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.11.099
Wisittipanich W, Hengmeechai P (2015) A multi-objective differential evolution for Just-In-Time door assignment and truck scheduling in multi-door Cross docking problems. Ind Eng Manag Syst 14:299–311. https://doi.org/10.7232/iems.2015.14.3.299
Wisittipanich W, Hengmeechai P (2016) Particle swarm optimization for just-in-time trucks scheduling in cross docking terminals. Proc Int Conf Ind Eng Oper Manag 2016:3357–3368
Wisittipanich W, Irohara T, Hengmeechai P (2019) Truck scheduling problems in the cross docking network. Int J Logist Syst Manag 33:420–439. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLSM.2019.101164
Wu G, Mallipeddi R, Suganthan PN, Wang R, Chen H (2016) Differential evolution with multi-population based ensemble of mutation strategies. Inf Sci 329:329–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2015.09.009
Yang WP, Tarng YS (1998) Design optimization of cutting parameters for turning operations based on the Taguchi method. J Mater Process Technol 84:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(98)00079-X
Zhang J, Sanderson AC (2009) JADE: adaptive differential evolution with optional external archive. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 13:945–958. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2009.2014613
Zhang Y, Gong D-W, Gao X-Z, Tian T, Sun X-Y (2020) Binary differential evolution with self-learning for multi-objective feature selection. Inf Sci 507:67–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.08.040
Zhao Z, Yang J, Hu Z, Che H (2016) A differential evolution algorithm with self-adaptive strategy and control parameters based on symmetric Latin hypercube design for unconstrained optimization problems. Eur J Oper Res 250:30–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2015.10.043
Funding
This study was supported by Chiang Mai University (CMU), Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A novel SLDE algorithm that increases the search capability of its original DE is proposed for addressing large-scale internal tasks scheduling problems in cross-docking.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buakum, D., Wisittipanich, W. Self-learning differential evolution algorithm for scheduling of internal tasks in cross-docking. Soft Comput 26, 11809–11826 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06959-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06959-3