Abstract
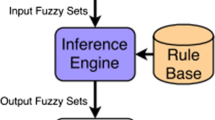
Artificial intelligence methods resemble human thinking structure that are used in hydrological modeling. In this work, water consumption estimation modeling is done using Mamdani fuzzy inference system. Different combinations of the models were developed by changing structures scenario such as: membership function, rules criteria, fuzzy set and defuzzification method. Mapping of input and output function are done using climatic variables and water consumption data. Rainfall, maximum temperature, minimum temperature and relative humidity were used as input factors and water consumption as output function. The reasoning mechanism of the fuzzy inference system calculates the recommended value of water consumption. Obtained value is compared with the actual recommended values to determine the usefulness of the system. The performances of the models were evaluated using performance indices such as correlation coefficient, mean square error and mean relative error. Results highlight that Mamdani fuzzy inference system is effective in actual application.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Bastian A (2000) Identifying fuzzy models utilizing genetic programming. Fuzzy Set Syst 113:333–350
Chang L-C, Chu H-J, Chen Y-W (2013) A fuzzy inference system for the conjunctive use of surface and subsurface water. Fuzzy Funct Relat Fuzzy Transforms,. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/128393
Chu H, Chang L (2009) Optimal control algorithm and neural network for dynamic groundwater management. Hydrol Process 23(19):2765–2773
Dai B, Chen R-C, Zhu S-Z, Huang C-Y (2016) Fuzzy recommendations system for daily water intake. Adv Mech Eng 8(5):1–8
Kazeminezhad MH, Etemad-Shahidi A, Mousavi SJ (2005) Application of fuzzy inference system in the prediction of wave parameters. Ocean Eng 32:1709–1725
McKinney DC, Lin MD (1994) Genetic algorithm solution of groundwater management models. Water Resour Res 30(6):1897–1906
Minns AW, Hall MJ (1996) Artificial neural networks as rainfall-runoff models. Hydrol Sci J 41(3):399–417
Moorthi PVP, Singh AP, Agnivesh P (2018) Regulation of water resources systems using fuzzy logic: a case study of Amaravathi dam. Appl Water Sci 8:132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0777-8
Raman BV, Bouwmeester R, Mohan S (2020) Fuzzy logic water quality index and importance of water quality parameters. Air, Soil Water Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/ASWR.S2156
Şen Z, Altunkaynak A (2009) Fuzzy system modeling of drinking water consumption prediction. Expert Syst Appl 36:11745–11752
Shimakawa M, Murakami S (2003) Fuzzy prediction model for water demand prediction using an interpolative fuzzy reasoning method. Int J Syst Sci 14–15:775–785. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207720310001640250
Skowronska KT et al (2006) Application of a fuzzy neural network for river water quality prediction. Chem Anal (warsaw) 51(3):365–375
Sylaios G, Bouchette F, Tsihrintzis VA, Denamiel C (2009) A fuzzy inference system for wind-wave modelling. Ocean Eng 36:1358–1365
Zubaidi SL, Abdulkareem IH, Hashim K, Al-Bugharbee H, Ridha HM, Gharghan SK, Al-Qaim FF, Muradov M, Kot P, Al-Khaddar R (2020a) Hybridised artificial neural network model with slime mould algorithm: a novel methodology for prediction of urban stochastic water demand. Water 12(10):1–18
Zubaidi SL, Hashim K, Ethaib S, Al-Bdairi NSS, Al-Bugharbee H, Gharghan SK (2020b) A novel methodology to predict monthly municipal water demand based on weather variables scenario. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2020.09.011
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Director, Executive Engineer (civil) and Assistant Engineers (civil) of New Mangalore Port, for their valuable support and access to data for the research work.
Funding
Not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surendra, H.J., Deka, P.C. & Rajakumara, H.N. Application of Mamdani model-based fuzzy inference system in water consumption estimation using time series. Soft Comput 26, 11839–11847 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06966-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06966-4