Abstract
This article presents a graphic simulation tool for the containership stowage problem at maritime ports using an agent-based approach to verify the effect of weight equilibrium stability on the containership. The container stowage problem is developed to guide the planning and procedures to allocate containers into a containership, based on the origin and destination ports previously schedule for each container. A methodological framework was developed to conduct the implementation of the graphic tool, using NetLogo® to setup and run the agent-based simulation. To test the graph simulation tool implemented, a total of 12 case studies were created based on combinations of the most influent input parameters with the weight equilibrium stability output variables. The computational results show that the assigned values for the input parameters allocation ordering sequence, number of containers, and stability limits have a direct influence on the weight equilibrium stability simulation during the allocation process.

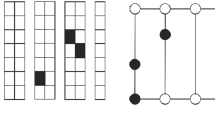
Source: Delgado et al. (2012)

Source: Delgado et al. (2012)





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Alderton P (2013) Port management and operations, 3rd edn. Taylor & Francis, New York
Ambrosino D, Sciomachen A (2004) Tanfani E (2004) Stowing a containership: the master bay plan problem. Transport Res Part a: Policy Practice 38(2):81–99
Ambrosino D, Sciomachen A (2021) A shipping line stowage-planning procedure in the presence of hazardous containers. Maritime Econ Logist 23(1):49–70
Ambrosino D, Sciomachen A, Tanfani E (2006) A decomposition heuristics for the container ship stowage problem. J Heurist 12(3):211–233
Ambrosino D, Anghinol D, Paolucci M, Sciomachen A (2010) An experimental comparison of different heuristics for the master bay plan problem. Experimental algorithms. Berlin, Springer
Ambrosino D, Paolucci M, Sciomachen A (2013) Experimental evaluation of mixed integer programming models for the multi-port master bay plan problem. Flex Serv Manuf J 27(2):263–284
Ambrosino D, Paolucci M, Sciomachen A (2017) Computational evaluation of a MIP model for multi-port stowage planning problems. Soft Comput 21(7):1753–1763
Avriel M, Penn M (1993) Exact and approximate solutions of the container ship stowage problem. Comput Ind Eng 25(1–4):271–274
Avriel M, Penn M, Shpirer N, Witteboon S (1998) Stowage planning for container ships to reduce the number of shifts. Ann Oper Res 76(1998):55–71
Avriel M, Penn M, Shpirer N (2000) Container ship stowage problem: complexity and connection to the coloring of circle graphs. Discret Appl Math 103(1):271–279
Bichou K (2014) Port operations, planning and logistics. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Bielli M, Boulmakoul A, Rida M (2006) Object oriented model for container terminal distributed simulation. Eur J Oper Res 175(3):1731–1751
Bortfeldt A, Wascher G (2013) Constraints in container loading - A state-of-the-art review. Eur J Oper Res 229(1):1–2013
Burns MG (2014) Port management and operations. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Chou CC, Fang PY (2021) Applying expert knowledge to containership stowage planning: an empirical study. Marit Econ Logist 23(1):4–27
Delgado A, Jensen RM, Janstrup K, Rose TH, Andersen KH (2012) A constraint programming model for fast optimal stowage of container vessel bays. Eur J Oper Res 220(1):251–261
Ding D, Chou MC (2015) Stowage planning for container ships: a heuristic algorithm to reduce the number of shifts. Eur J Oper Res 246(1):242–249
Dubrovsky O, Levitin G, Penn M (2002) A genetic algorithm with a compact solution encoding for the container ship stowage problem. J Heurist 8(6):585–599
Hu W, Hu Z, Shi L, Luo P, Song W (2012) Combinatorial optimization and strategy for ship stowage and loading schedule of container terminal. J Comput 7(8):2078–2092
Imai A, Sasaki K, Nishimura E, Papadimitriou S (2006) Multi-objective simultaneous stowage and load planning for a container ship with container rehandle in yard stacks. Eur J Oper Res 171(2):373–389
Ji M, Kong L, Guan Y (2021) Integrated optimization of feeder routing and stowage planning for containerships. Soft Comput 25(6):4465–4487
Júnior AN, Guimarães LR (2019) A greedy randomized adaptive search procedure application to solve the travelling salesman problem. Int J Ind Eng Manage 10(3):238–242
Kang J-G, Kim Y-D (2002) Stowage planning in maritime container transportation. J Operat Res Soc 53(4):415–426
Kim M, Jeong Y, Moon I (2021) Efficient stowage plan with loading and unloading operations for shipping liners using foldable containers and shift cost-sharing. Marit Policy Manag 48(6):877–894
LAC (2022) Latin American Cargo. https://www.latinamericancargo.com/20ft-vs-40ft-container-choosing-the-right-shipping-container-for-your-cargo
Lee E-S, Song D-W (2014) Maritime logistics value and knowledge management. Routledge, New York
Low MYH, Zeng M, Hsu WJ, Huang SY, Liu F, Win CA (2011) Improving safety and stability of large containerships in automated stowage planning. IEEE Syst J 5(1):5967–5974
Monaco MF, Sammarra M, Sorrentino G (2014) The terminal-oriented ship stowage planning problem. Eur J Oper Res 239(1):256–265
NetLogo (1999) NetLogo. http://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/. Center for Connected Learning and Computer-Based Modeling, Northwestern
Pacino D (2012) Fast generation of container vessel stowage plans using mixed integer programming for optimal master planning and constraint based local search for slot planning. Thesis, IT University of Copenhagen
Parola F, Sciomachen A (2005) Intermodal container flows in a port system network: analysis of possible growths via simulation models. Int J Prod Econ 97(1):75–88
Parreno F, Pacino D (2016) Alvarez-Valdes R (2016) A GRASP algorithm for the container stowage slot planning problem. Transp Res Part e: Logist Transport Rev 94:141–157
Parreño-Torres C, Alvarez-Valdes R, Parreño F (2019) Solution strategies for a multiport container ship stowage problem. Math Probl Eng 2019:1–12
Parreño-Torres C, Çalık H, Alvarez-Valdes R, Ruiz R (2021) Solving the generalized multi-port container stowage planning problem by a matheuristic algorithm. Comput Oper Res 133:105383
Rashed D, Eltawil A, Gheith M (2021) A fuzzy logic-based algorithm to solve the slot planning problem in container vessels. Logistics 5(4):67–79
Sciomachen A, Tanfani E (2007) A 3D-BPP approach for optimising stowage plans and terminal productivity. Eur J Oper Res 183(3):1433–1446
Villa JC, Boile M, Theofanis S (2020) International trade and transportation infrastructure development: experiences in North America and the European Union. Elsevier, New Jersey
Zeng M, Low MYH, Hsu WJ, Huang SY, Liu F, Win CA (2010) Improving ship stability in automated stowage planning for large containerships. In: Proceedings of the international multiconference of engineers and computer scientists
Zhu H, Ji M, Guo W (2020) Integer linear programming models for the containership stowage problem. Math Probl Eng 2020:1–14
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) [Grant No. 422095/2018–4, 105034/2020–7], by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) [Grant No. BEX200936/2014], and by BE MUNDUS project awarded by the European Commission Erasmus Mundus programme [Grant No. BM13DF0018/2014];
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuenfeldt-Júnior, A., de Oliveira, B. An agent-based approach to simulate the containership stowage problem. Soft Comput 26, 12583–12597 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07222-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07222-5