Abstract
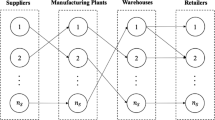
In this paper, a strategic level of a supply chain is studied. To deal with its objective, restructuring distribution and manufacturing centers under the parameter uncertainty and system disruption are formulated as a mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) model. Because of the complexity of such a hard model, it is converted to a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) model by conducting a simple linearization method. Capacity expansion and reduction, capacity consolidation, outsourcing, and transshipment strategies are used to reconfigure the considered supply chain. An inexact interval fixed-mix fuzzy approach is applied to deal with the parameter uncertainty, and an efficient two-stage model is conducted to analyze the system reliability. The developed model is solved by an efficient and effective Lagrangian relaxation procedure. Furthermore, a case study of dairy products is studied to present the model application and validation. Finally, several sensitivity analyses are carried out to identify the model behavior and solution algorithm validation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Arasteh A (2019) Supply chain management under uncertainty with the combination of fuzzy multi-objective planning and real options approaches Soft Comput 1–22
Ballou RH (1968) Dynamic warehouse location analysis. J Mark Res 5(3):271–276
Bai X, Liu Y (2016) Robust optimization of supply chain network design in fuzzy decision system. J Intell Manuf 27(6):1131–1149
Bhattacharya K, De SK (2021) A robust two layer green supply chain modelling under performance based fuzzy game theoretic approach. Comput Ind Eng 152:107005
Chouhan VK, Khan SH, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Subramanian S, (2020) Multi-facility-based improved closed-loop supply chain network for handling uncertain demands Soft Comput 1–23
Dias J, Captivo ME, Clímaco J (2006) Capacitated dynamic location problems with opening, closure and reopening of facilities. IMA J Manag Math 17(4):317–348
De SK, Sana SS (2018) Two-layer supply chain model for Cauchy-type stochastic demand under fuzzy environment Int J Intell Comput Cybern
DE, S. K., & Mahata, G. C. (2019) An EPQ model for three-layer supply chain with partial backordering and disruption: Triangular dense fuzzy lock set approach. Sādhanā 44(8):1–15
De SK, Mahata GC (2020) A production inventory supply chain model with partial backordering and disruption under triangular linguistic dense fuzzy lock set approach. Soft Comput 24(7):5053–5069
De SK, Mahata GC (2021) Solution of an imperfect-quality EOQ model with backorder under fuzzy lock leadership game approach. Int J Intell Syst 36(1):421–446
De SK (2021) Solving an EOQ model under fuzzy reasoning. Appl Soft Comput 99:106892
Fisher ML (1981) The Lagrangian relaxation method for solving integer programming problems. Manag Sci 27(1):1–18
Fisher ML (2004) The Lagrangian relaxation method for solving integer programming problems. Manag Sci 50(12):1861–1871
Ghasimi SA, Ramli R, Saibani N, Narooei KD (2018) An uncertain mathematical model to maximize profit of the defective goods supply chain by selecting appropriate suppliers. J Intell Manuf 29(6):1219–1234
Held M, Karp RM (1970) The traveling-salesman problem and minimum spanning trees. Oper Res 18(6):1138–1162
Held M, Karp RM (1971) The traveling-salesman problem and minimum spanning trees: Part II. Math Program 1(1):6–25
Huang G, Baetz BW, Patry GG (1992) A grey linear programming approach for municipal solid waste management planning under uncertainty. Civ Eng Syst 9(4):319–335
Jahani H, Abbasi B, Alavifard F, Talluri S (2018) Supply chain network redesign with demand and price uncertainty. Int J Prod Econ 205:287–312
Jafarian E, Razmi J, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2019) Forward and reverse flows pricing decisions for two competing supply chains with common collection centers in an intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Soft Comput 23(17):7865–7888
Kiya F, Davoudpour H (2012) Stochastic programming approach to re-designing a warehouse network under uncertainty. Transport Res Part e Logist Transport Rev 48(5):919–936
Li W, Bao Z, Huang GH Xie YL (2018) An inexact credibility chance-constrained integer programming for greenhouse gas mitigation management in regional electric power system under uncertainty J Environ Inform 31(2)
Lu HW, Cao MF, Li J, Huang GH, He L (2015) An inexact programming approach for urban electric power systems management under random-interval-parameter uncertainty. Appl Math Model 39(7):1757–1768
Ma H, Li X, Liu Y (2020) Multi-period multi-scenario optimal design for closed-loop supply chain network of hazardous products with consideration of facility expansion. Soft Comput 24(4):2769–2780
Melachrinoudis E, Messac A, Min H (2005) Consolidating a warehouse network: a physical programming approach. Int J Prod Econ 97(1):1–17
Melachrinoudis E, Min H (2000) The dynamic relocation and phase-out of a hybrid, two-echelon plant/warehousing facility: a multiple objective approach. Eur J Oper Res 123(1):1–15
Melachrinoudis E, Min H (2007) Redesigning a warehouse network. Eur J Oper Res 176(1):210–229
Melo MT, Nickel S, Da Gama FS (2006) Dynamic multi-commodity capacitated facility location: a mathematical modeling framework for strategic supply chain planning. Comput Oper Res 33(1):181–208
Min H, Melachrinoudis E (1999) The relocation of a hybrid manufacturing/distribution facility from supply chain perspectives: a case study. Omega 27(1):75–85
Paul SK, Sarker R, Essam D (2018) A reactive mitigation approach for managing supply disruption in a three-tier supply chain. J Intell Manuf 29(7):1581–1597
Peng P, Snyder LV, Lim A, Liu Z (2011) Reliable logistics networks design with facility disruptions. Transport Res Part b Methodol 45(8):1190–1211
Razmi J, Zahedi-Anaraki A, Zakerinia M (2013) A bi-objective stochastic optimization model for reliable warehouse network redesign. Math Comput Model 58(11–12):1804–1813
Sauvey C, Melo T, Correia I (2020) Heuristics for a multi-period facility location problem with delayed demand satisfaction. Comput Ind Eng 139:106171
Shi J, Chen W, Zhou Z, Zhang G (2019) A bi-objective multi-period facility location problem for household e-waste collection Int J Prod Res 1–20
Shishebori D, Yousefi-Babadi A, Noormohammadzadeh Z (2018) A Lagrangian relaxation approach to fuzzy robust multi-objective facility location network design problem. Scientia Iranica. Transaction E, Indust Eng 25(3):1750–1767
Shishebori D, Yousefi-Babadi A (2015) Robust and reliable medical services network design under uncertain environment and system disruptions. Transport Res Part e Logist Transport Rev 77:268–288
Wang Q, Batta R, Bhadury J, Rump CM (2003) Budget constrained location problem with opening and closing of facilities. Comput Oper Res 30(13):2047–2069
Wesolowsky GO (1973) Dynamic facility location. Manag Sci 19(11):1241–1248
Wesolowsky GO, Truscott WG (1975) The multiperiod location-allocation problem with relocation of facilities. Manag Sci 22(1):57–65
Wu CB, Huang GH, Li W, Zhen JL, Ji L (2016) An inexact fixed-mix fuzzy-stochastic programming model for heat supply management in wind power heating system under uncertainty. J Clean Prod 112:1717–1728
Yousefi-Babadi A, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Bozorgi-Amiri A, Seifi S (2017) Designing a reliable multi-objective queuing model of a petrochemical supply chain network under uncertainty: a case study. Comput Chem Eng 100:177–197
Zhang C, Fan LW, Tian YX (2020) Optimal operational strategies of capital-constrained supply chain with logistics service and price dependent demand under 3PL financing service. Soft Comput 24(4):2793–2806
Zimmermann HJ (2010) Fuzzy set theory. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Statistics 2(3):317–332
Zimmermann HJ (1978) Fuzzy programming and linear programming with several objective functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1(1):45–55
Funding
This study was funded by the Iranian National Science Foundation (INSF) [grant number 96001557].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
This paper does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefi-Babadi, A., Bozorgi-Amiri, A. & Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. Redesigning a supply chain network with system disruption using Lagrangian relaxation: a real case study. Soft Comput 26, 10275–10299 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07340-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07340-0