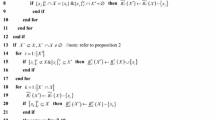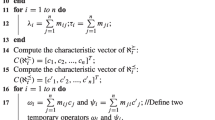Abstract
Dominance-based rough set approach (DRSA) is an effective knowledge acquisition tool for ordered data, and to meet the needs of practical applications, the DRSA-based extended models have been widely studied. Nevertheless, the collected data in practical applications are always polluted by noise and most of these extended models are very susceptible to noise. In addition, with the arrival of new attributes and the removal of obsolete attributes, the ordered data have the characteristic of attributes evolving over time (i.e., dynamic ordered data). How to efficiently mining knowledge from dynamic ordered data is a meaningful topic. Motivated by these two issues, we first propose a robust fuzzy dominance rough set model to combat noise interference and then develop incremental update approximation mechanisms based on the proposed model for dynamic ordered data. Firstly, the vaguely quantified fuzzy dominance rough set (VQFDRS) and its matrix representation are introduced. Subsequently, we develop the incremental mechanisms to update the approximations of VQFDRS when multiple attributes are added to or deleted from an ordered data, respectively. Then, on this basis, a static calculation approximations algorithm and two incremental calculation approximations algorithms are designed, respectively. Finally, a series of numerical comparative experiments are performed on six public datasets. Experimental results indicate that the VQFDRS has good robustness, and the incremental algorithms are highly efficient compared with static algorithm under the dynamic data environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Blaszczynski J, Filho A, Matuszyk A, Szelag M, Slowinski R (2021) Auto loan fraud detection using dominance-based rough set approach versus machine learning methods. Expert Syst Appl 163:113740
Cai M, Lang G, Fujita H, Li Z, Yang T (2019) Incremental approaches to updating reducts under dynamic covering granularity. Knowledge-Based Syst 172:130–140
Cano J-R, Aljohani N, Abbasi R, Alowidbi J, Garcia S (2017) Prototype selection to improve monotonic nearest neighbor. Eng Appl Artif Intell 60:128–135
Chen C-C, Li S-T (2014) Credit rating with a monotonicity-constrained support vector machine model. Expert Syst Appl 41(16):7235–7247
Chen H, Li T, Ruan D (2012) Maintenance of approximations in incomplete ordered decision systems while attribute values coarsening or refining. Knowledge-Based Syst 31:140–161
Chen H, Li T, Cai Y, Luo C, Fujita H (2016) Parallel attribute reduction in dominance-based neighborhood rough set. Inf Sci 373:351–368
Cornelis C, Cock M, Radzikowska A (2007) Vaguely quantified rough sets. In: RSFDGrC 2007, volume 4482 of Lecture notes in computer science, pages 87–94. Springer
Du W, Hu B (2016) Dominance-based rough set approach to incomplete ordered information systems. Inf Sci 346–347:106–129
Dubois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 17(2–3):191–209
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R, Stefanowski J (2000) Variable consistency model of dominance-based rough sets approach. In: Wojciech Ziarko and Y. Y. Yao, editors, Rough sets and current trends in computing, second international conference, RSCTC 2000 Banff, Canada, October 16-19, 2000, Revised Papers, volume 2005 of Lecture notes in computer science, pages 170–181. Springer
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R (1999) Rough approximation of a preference relation by dominance relations. Eur J Oper Res 117(1):63–83
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R (2001) Rough sets theory for multicriteria decision analysis. Eur J Oper Res 129(1):1–47
Guo Y, Tsang Eric CC, Hu M, Lin X, Chen D, Xu W, Sang B (2020) Incremental updating approximations for double-quantitative decision-theoretic rough sets with the variation of objects. Knowledge-Based Syst 189:105082
Hu C, Zhang L (2020) Incremental updating probabilistic neighborhood three-way regions with time-evolving attributes. Int J Approx Reason 120:1–23
Hu C, Liu S, Huang X (2017) Dynamic updating approximations in multigranulation rough sets while refining or coarsening attribute values. Knowledge-Based Syst 130:62–73
Hu C, Zhang L, Wang B, Zhang Z, Li F (2019) Incremental updating knowledge in neighborhood multigranulation rough sets under dynamic granular structures. Knowledge-Based Syst 163:811–829
Hu Q, Yu D, Liu J, Wu C (2008) Neighborhood rough set based heterogeneous feature subset selection. Inform Sci 178(18):3577–3594
Hu Q, Yu D, Guo M (2010) Fuzzy preference based rough sets. Inf Sci 180(10):2003–2022
Hu Q, Yu D, Pedrycz W, Chen D (2011) Kernelized fuzzy rough sets and their applications. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 23(11):1649–1667
Hu Q, Chakhar S, Siraj S, Labib A (2017) Spare parts classification in industrial manufacturing using the dominance-based rough set approach. Eur J Oper Res 262(3):1136–1163
Huang Q, Li T, Huang Y, Yang X (2020) Incremental three-way neighborhood approach for dynamic incomplete hybrid data. Inf Sci 541:98–122
Huang Q, Li T, Huang Y, Yang X, Fujita H (2020) Dynamic dominance rough set approach for processing composite ordered data. Knowledge-Based Syst 187:104829
Kim M-J, Han I (2003) The discovery of experts’ decision rules from qualitative bankruptcy data using genetic algorithms. Expert Syst Appl 25(4):637–646
Kotlowski W, Dembczyński K, Greco S, Slowiński R (2008) Stochastic dominance-based rough set model for ordinal classification. Inf Sci 178(21):4019–4037
Lang G, Miao D, Cai M, Zhang Z (2017) Incremental approaches for updating reducts in dynamic covering information systems. Knowledge-Based Syst 134:85–104
Li S, Li T (2015) Incremental update of approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach under the variation of attribute values. Inf Sci 294:348–361
Li T, Ruan D, Wets G, Song J, Xu Y (2007) A rough sets based characteristic relation approach for dynamic attribute generalization in data mining. Knowledge-Based Systems 20(5):485–494
Li S, Li T, Liu D (2013) Incremental updating approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach under the variation of the attribute set. Knowledge-Based Syst 40:17–26
Li W, Xue X, Xu W, Zhan T, Fan B (2020) Double-quantitative variable consistency dominance-based rough set approach. Int J Approx Reason 124:1–26
Liang J, Wang F, Dang C, Qian Y (2014) A group incremental approach to feature selection applying rough set technique. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26:294–308
Liou James JH, Tzeng G-H (2010) A dominance-based rough set approach to customer behavior in the airline market. Inform Sci 180(11):2230–2238
Luo C, Li T, Yi Z, Fujita H (2016) Matrix approach to decision-theoretic rough sets for evolving data. Knowledge-Based Syst 99:123–134
Luo C, Li T, Chen H, Fujita H, Yi Z (2018) Incremental rough set approach for hierarchical multicriteria classification. Inf Sci 429:72–87
Luo C, Li T, Huang Y, Fujita H (2019) Updating three-way decisions in incomplete multi-scale information systems. Inf Sci 476:274–289
Nettleton DF, Orriols-Puig A, Fornells A (2010) A study of the effect of different types of noise on the precision of supervised learning techniques. Artif Intell Rev 33(4):275–306
Palangetic M, Cornelis C, Greco S, Slowinski R (2021) Fuzzy extensions of the dominance-based rough set approach. Int J Approx Reason 129:1–19
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Parallel Program 11(5):341–356
Qian Y, Liang J, Dang C (2008) Interval ordered information systems. Comput Math Appl 56(8):1994–2009
Qian Y, Dang C, Liang J, Tang D (2009) Set-valued ordered information systems. Inf Sci 179(16):2809–2832
Qian Y, Liang J, Yao Y, Dang C (2010) Mgrs: a multi-granulation rough set. Inform Sci 180(6):949–970
Qian Y, Liang X, Wang Q, Liang J, Liu B, Skowron A, Yao Y, Ma J, Dang C (2018) Local rough set: a solution to rough data analysis in big data. Intern J Approx Reason 97:38–63
Roy S, Shivakumara P, Jain N, Khare V, Dutta A, Pal U, Lu T (2018) Rough-fuzzy based scene categorization for text detection and recognition in video. Pattern Recognit 80:64–82
Sang B, Chen H, Wan J, Yang L, Li T, Weihua X, Luo C (2022) Self-adaptive weighted interaction feature selection based on robust fuzzy dominance rough sets for monotonic classification. Knowledge-Based Syst 253:109523
Shaheen T, Mian B, Shabir M, Feng F (2019) A novel approach to decision analysis using dominance-based soft rough sets. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(3):954–962
Shao M, Zhang W (2005) Dominance relation and rules in an incomplete ordered information system. Int J Intell Syst 20(1):13–27
Shu W, Qian W, Xie Y (2019) Incremental approaches for feature selection from dynamic data with the variation of multiple objects. Knowledge-Based Syst 163:320–331
Shu W, Qian W, Xie Y (2020) Incremental feature selection for dynamic hybrid data using neighborhood rough set. Knowledge-Based Syst 194:1–15
Tan A, Wu W, Qian Y, Liang J, Chen J, Li J (2019) Intuitionistic fuzzy rough set-based granular structures and attribute subset selection. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(3):527–539
Wang S, Li T, Luo C, Fujita H (2016) Efficient updating rough approximations with multi-dimensional variation of ordered data. Inf Sci 372:690–708
Wang S, Li T, Luo C, Chen H, Fujita H (2019) Domain-wise approaches for updating approximations with multi-dimensional variation of ordered information systems. Inf Sci 478:100–124
Wang S, Li T, Luo C, Hu J, Fujita H, Huang T (2020) A novel approach for efficient updating approximations in dynamic ordered information systems. Inf Sci 507:197–219
Wei W, Liang J (2019) Information fusion in rough set theory : an overview. Inform Fus 48:107–118
Wei W, Wu X, Liang J, Cui J, Sun Y (2018) Discernibility matrix based incremental attribute reduction for dynamic data. Knowledge-Based Syst 140:142–157
Wu X, Zhu X (2008) Mining with noise knowledge: error-aware data mining. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A-Syst Hum 38(4):917–932
Yang X, Yang J, Wu C, Yu D (2008) Dominance-based rough set approach and knowledge reductions in incomplete ordered information system. Inf Sci 178(4):1219–1234
Yang X, Qi Y, Yu D, Yu H, Yang J (2015) \(\alpha \)-dominance relation and rough sets in interval-valued information systems. Inf Sci 294:334–347
Yang Y, Chen D, Hui W (2017) Active sample selection based incremental algorithm for attribute reduction with rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(4):825–838
Yang Y, Chen D, Hui W, Wang X (2018) Incremental perspective for feature selection based on fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26(3):1257–1273
Yang X, Liu D, Yang X, Liu K, Li T (2021) Incremental fuzzy probability decision-theoretic approaches to dynamic three-way approximations. Inf Sci 550:71–90
Yao Y, Zhao Y (2008) Attribute reduction in decision-theoretic rough set models. Inform Sci 178(17):3356–3373
Yu J, Chen H, Xu W (2017) Dynamic computing rough approximations approach to time-evolving information granule interval-valued ordered information system. Appl Soft Comput 60:18–29
Zadeh LA (1997) Toward a theory of fuzzy information granulation and its centrality in human reasoning and fuzzy logic. Fuzzy Sets Syst 90(2):111–127
Zeng A, Li T, Hu J, Chen H, Luo C (2017) Dynamical updating fuzzy rough approximations for hybrid data under the variation of attribute values. Inf Sci 378:363–388
Zhang X, Mei C, Chen D, Yang Y, Li J (2020) Active incremental feature selection using a fuzzy rough set-based information entropy. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(5):901–915
Zhu X, Wu X (2004) Class noise vs. attribute noise: a quantitative study. Artif Intell Rev 22:177–210
Ziarko W (1993) Variable precision rough set model. J Comput Syst Sci 46(1):39–59
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61976130 provided by Keyun Qin, No. 61976245 provided by Weihua Xu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LY helped in conceptualization, writing—original draft, read, and contributed to the manuscript. KQ contributed to supervision; project administration; and funding acquisition. BS was involved in conceptualization, read, and contributed to the manuscript. WX helped in resources; funding acquisition. HY read and contributed to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Qin, K., Sang, B. et al. Vaguely quantified fuzzy dominance rough set and its incremental maintenance approximation approaches. Soft Comput 27, 867–886 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07598-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07598-4