Abstract
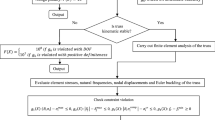
In this paper, an enhanced, memory-assisted version of the multi-verse optimizer (MVO) is proposed for the shape and size optimization of various types of truss structures. The cosmology-based MVO processes the interaction of the multiple universes through white, black, and wormholes to solve the target optimization problem. However, the MVO has drawbacks such as slow convergence speed, easy to fall into local optimum, and low efficiency in the case of continuous and discrete variables existing in structural optimization. This paper aims to modify the Multi-verse Optimizer and propose an enhanced version, named as memory-assisted adaptive multi-verse optimizer (MAMVO). The enhanced algorithm seeks to reinforce the performance of the standard algorithm using two mechanisms: (I) Using an adaptive pseudorandom transfer strategy in cases with both continuous and discrete variables to strike a better balance between the diversification and the intensification tasks (II) using a multi-elite memory, by which several best so far solutions are saved and exchanged with several worst ones for better convergence. The performance of the proposed MAMVO is compared with those of the standard MVO and some other optimization methods through various types of truss benchmarks (beams, towers, and bridges) under different constraints such as displacement, stress, buckling, or frequency. Results confirm that MAMVO significantly outperforms the standard MVO and has comparable or superior performance to the other methods.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable. Authors can confirm that all relevant data are included in the article and/or its supplementary information files.
References
Abualigah L (2020) Multi-verse optimizer algorithm: a comprehensive survey of its results, variants, and applications. Neural Comput Applic 32:12381–12401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04839-1
Amézquita L, Castillo O, Soria J, Cortés-Antonio P (2022) Fuzzy logic augmentation of the multiverse optimizer applied to fuzzy controllers design. J Multiple Valued Log Soft Comput 39(5–6):591–613
Amézquita L, Castillo O, Soria J, Cortes-Antonio P (2021) Optimal design of fuzzy controllers using the multiverse optimizer. In: Abraham A, Hanne T, Castillo O, Gandhi N, Nogueira Rios T, Hong TP (eds) Hybrid intelligent systems. HIS 2020. Advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol 1375. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-73050-5_29
Ashtari P, Karami R, Farahmand‐Tabar S (2021) Optimum geometrical pattern and design of real-size diagrid structures using accelerated fuzzy-genetic algorithm with bilinear membership function. Appl Soft Comput 110:107646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107646
Babaei M, Mollayi M (2016) Multi-objective optimization of reinforced concrete frames using NSGA-II algorithm. Eng Struct Technol 8(4):157–164. https://doi.org/10.3846/2029882X.2016.1250230
Babaei M, Mollayi M (2019) An improved constrained differential evolution for optimal design of steel frames with discrete variables. Mech Based Des Struct Mach 48(6):697–723. https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2019.1657890
Babaei M, Sanaei E (2016) Multi-objective optimal design of braced frames using hybrid genetic and ant colony optimization. Front Struct Civ Eng 10(4):472–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-016-0368-4
Baykasoğlu A, Baykasoğlu C (2021) Weighted superposition attraction-repulsion (WSAR) algorithm for truss optimization with multiple frequency constraints. Structures 30(30):253–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2021.01.017
Cao H, Qian X, Chen Z, Zhu H (2017) Enhanced particle swarm optimization for size and shape optimization of truss structures. Eng Optim 49(11):1939–1956. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2016.1273912
Cuevas F, Castillo O, Cortés-Antonio P (2022) Generalized type-2 fuzzy parameter adaptation in the marine predator algorithm for fuzzy controller parameterization in mobile robots. Symmetry 14(5):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14050859
Dede T, Ayvaz Y (2015) Combined size and shape optimization of structures with a new meta-heuristic algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 28:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.12.007
Degertekin SO, Lamberti L, Ugur IB (2017) Sizing, layout and topology design optimization of truss structures using the Jaya algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 70:903–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.10.001
Esfandiari M, Urgessa G (2020) Progressive collapse design of reinforced concrete frames using structural optimization and machine learning. Structures 28(28):1252–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2020.09.039
Farahmand‐Tabar S, Ashtari P (2020) Simultaneous size and topology optimization of 3D outrigger‐braced tall buildings with inclined belt truss using genetic algorithm. Struct Des Tall Spec 29(13):e1776. https://doi.org/10.1002/tal.1776
Farahmand-Tabar S, Barghian M (2020a) Formulating the optimum parameters of modified hanger system in the cable-arch bridge to restrain force fluctuation and overstressing problems. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42:453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02513-0
Farahmand-Tabar S, Barghian M (2020b) Response control of cable-stayed arch bridge using modified hanger system. J Vib Control 26(23–24):2316–2328. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546320921635
Farahmand-Tabar S, Barghian M (2021) Seismic assessment of a cable-stayed arch bridge under three-component orthotropic earthquake excitation. Adv Struct Eng 24(2):227–242. https://doi.org/10.1177/1369433220948756
Farahmand-Tabar S, Barghian M, Vahabzadeh M (2019) Investigation of the progressive collapse in a suspension bridge under the explosive load. Int J Steel Struct 19(6):2039–2050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-019-00263-x
Farahmand-Tabar S, Barghian M (2023) Seismic evaluation of the bridge with a hybrid system of cable and arch: Simultaneous effect of seismic hazard probabilities and vertical excitations. Mech Based Des Struct Mach. https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2023.2172029
Gholizadeh S (2013) Layout optimization of truss structures by hybridizing cellular automata and particle swarm optimization. Comput Struct 125:86–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2013.04.024
Gholizadeh S, Danesh M, Gheyratmand C (2020) A new Newton metaheuristic algorithm for discrete performance-based design optimization of steel moment frames, Comp Struct 234:106250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2020.106250
Gil L, Andreu A (2001) Shape and cross-section optimization of a truss structure. Comput Struct 79(7):681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7949(00)00182-6
Gomes MH (2011) Truss optimization with dynamic constraints using a particle swarm algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 38:957–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.07.086
Hasançebi O, Erbatur F (2002) Layout optimisation of trusses using simulated annealing. Adv Eng Softw 33(7–10):681–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9978(02)00049-2
Hasançebi O, Kazemzadeh Azad S (2015) Adaptive dimensional search: a new metaheuristic algorithm for discrete truss sizing optimization. Comput Struct 154:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.03.014
Ho-Huu V, Nguyen-Thoi T, Nguyen-Thoi MH, Le-Anh L (2015) An improved constrained differential evolution using discrete variables (D-ICDE) for layout optimization of truss structures. Expert Syst Appl 42(20):7057–7069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.04.072
Kaur A, Jain S, Goel S (2020) Sandpiper optimization algorithm: a novel approach for solving real-life engineering problems. Appl Intell 50:582–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01507-3
Kaveh A, Kalatjari V (2004) Size, geometry optimization of trusses by the force method and genetic algorithm. J Appl Math Mech 84(5):347–357. https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.200310106
Kaveh A, Khayatazad M (2013) Ray optimization for size and shape optimization of truss structures. Comput Struct 117:82–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2012.12.010
Kaveh A, Zakian P (2018) Improved GWO algorithm for optimal design of truss structures. Eng Comp 34:685–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0567-1
Khalilpourazari S, Khalilpourazary S (2019) An efficient hybrid algorithm based on Water Cycle and Moth-Flame Optimization algorithms for solving numerical and constrained engineering optimization problems. Soft Comput 23:1699–1722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2894-y
Khatibinia M, Yazdani H (2018) Accelerated multi-gravitational search algorithm for size optimization of truss structures. Swarm Evol Comput 38:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2017.07.001
Lee KS, Geem ZW (2005) A new meta-heuristic algorithm for continuous engineering optimization: harmony search theory and practice. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194(36–38):3902–3933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2004.09.007
Lingyun W, Mei Z, Guangming W, Guang M (2005) Truss optimization on shape and sizing with frequency constraints based on genetic algorithm. J Constr Steel Res 25:361–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-004-0623-8
Liu S, Zhu H, Chen Z, Cao H (2019) Frequency-constrained truss optimization using the fruit fly optimization algorithm with an adaptive vision search strategy. Eng Optim 52(5):777–797. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2019.1624738
Madah H, Amir O (2017) Truss optimization with buckling considerations using geometrically nonlinear beam modeling. Comput Struct 192:233–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2017.07.023
Miguel LFF, Miguel LFF (2013) Shape and size optimization of truss structures considering dynamic constraints through modern metaheuristic algorithms. Expert Syst Appl 39(10):9458–9467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.02.113
Mirjalili SA, Mirjalili SM, Hatamlou A (2015) Multi-Verse Optimizer: a nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput & Applic 521:1870–1877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1870-7
Mohammad Hasani Zade B, Mansouri N (2022) PPO: a new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm based on predation for optimization. Soft Comput 26:1331–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06404-x
Mohr DP, Stein I, Matzies T, Knapek CA (2014) Redundant robust topology optimization of truss. Optim Eng 15:945–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-013-9241-7
Mortazavi A (2020) Size and layout optimization of truss structures with dynamic constraints using the interactive fuzzy search algorithm. Eng Optim 53(3):369–391. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2020.1726341
Nguyen-Van S, T.Nguyen K, Hai Luong V, Lee S, X.Lieu Q (2021) A novel hybrid differential evolution and symbiotic organisms search algorithm for size and shape optimization of truss structures under multiple frequency constraints. Expert Syst Appl 184:115534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115534
Ouyang H, Wu W, Zhang C et al (2019) Improved harmony search with general iteration models for engineering design optimization problems. Soft Comput 23:10225–10260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3579-x
Ozbasaran H, Eryilmaz Yildirim M (2020) Truss-sizing optimization attempts with CSA: a detailed evaluation. Soft Comput 24:16775–16801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04972-y
Pierezan J, Coelho LdS, Mariani VC, Segundo EHdV, Prayogode D (2021) Chaotic coyote algorithm applied to truss optimization problems. Comp Struct 42:106353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2020.106353
Rahami H, Kaveh A, Gholipoura Y (2008) Sizing, geometry and topology optimization of trusses via force method and genetic algorithm. Eng Struct 30:2360–2369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.01.012
Rodriguez L, Castillo O, Garcia M, Soria J (2021) A new meta-heuristic optimization algorithm based on a paradigm from physics: string theory. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 41(1):1657–1675. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-210459
Rostami P, Marzbanrad J (2020) Multi-material topology optimization of compliant mechanisms using regularized projected gradient approach. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42:457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02549-2
Safaeian Hamzehkolaei N, MiarNaeimi F (2021) A new hybrid multi-level cross-entropy-based moth-flame optimization algorithm. Soft Comput 25:14245–14279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06109-1
Sanaei E, Babaei M (2011) Cellular Automata in Topology Optimization of Continuum Structures. Int J Eng Sci Technol 3(4):27–41. https://doi.org/10.4314/ijest.v3i4.68538
Sanaei E, Babaei M (2012) Topology optimization of structures using cellular automata with constant strain triangles. Int J Civil Eng 10(3):179–188
Shojaee S, Arjomand M, Khatibi M (2013) A hybrid algorithm for sizing and layout optimization of truss structures combining discrete PSO and convex approximation. Int J Optim Civil Eng 3(1):57–83
Stolpe M (2015) Truss topology optimization with discrete design variables by outer approximation. J Glob Optim 61:139–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-014-0142-x
Tang W, Tong L, Gu Y (2005) Improved genetic algorithm for design optimization of truss structures with sizing, shape and topology variables. Int J Numer Methods Eng 62(13):1737–1762. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1244
Tauzowski P, Blachowski B, Lógó J (2021) Topology optimization of elasto-plastic structures under reliability constraints: afirst order approach. Comp Struct 243: 106406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2020.106406
Wang D, Zhang WH, Jiang JS (2002) Combined shape and sizing optimization of truss structures. Comput Mech 29:307–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-002-0343-x
Wang D, Zhang WH, Jiang JS (2004) Truss optimization on shape and sizing with frequency constraints. AIAA J 42:1452–1456. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.1711
Weldeyesus AG, Gondzio J, He L, Gilbert M, Shepherd P, Tyas A (2019) Adaptive solution of truss layout optimization problems with global stability constraints. Struct MultidiscipOptim 60:2093–2111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02312-9
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MB devised and supervised the project. Conceptualization, material preparation, data collection Methodology, and Formal analysis were performed by SF-T. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [SF-T], and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Farahmand-Tabar, S., Babaei, M. Memory-assisted adaptive multi-verse optimizer and its application in structural shape and size optimization. Soft Comput 27, 11505–11527 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08349-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08349-9