Abstract
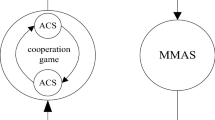
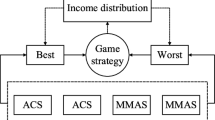
To address the lack of convergence speed and diversity of traditional ant colony algorithm when solving large-scale travelling salesmen problem (TSP), a multi-ant colony optimization based on bidirectional induction mechanism and cooperative game is proposed. First, a novel heterogeneous multi-population is introduced, different populations cooperate to enhance the algorithm’s overall performance. Second, a cooperative game in multi-population is proposed, the pheromone income is distributed to participants based on their contribution, which can balance the convergence and diversity. Third, we introduce a bidirectional induction mechanism, by expanding the difference of pheromone concentration between outstanding solutions and mediocre solutions, the convergence can be further improved. In addition, the current optimal clip will be recommended to other populations for learning, each population will continue search based on the current optimal clip, which can improve the accuracy of the solutions. If the algorithm falls into stagnation, the current optimal solution will be inducted reversely, which can help the algorithm jump out of the local optimum. Finally, the experimental results of the large-scale TSP instances show that the improved algorithm can effectively balance the convergence and diversity, and it has better stability.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Ahmmed A, Rana MAA, Haque AAMM, Mamun M Al (2008) A multiple Ant Colony System for dynamic vehicle routing problem with time window. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on convergence and hybrid information technology ICCIT 2008 2:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCIT.2008.249
Akhand MAH, Ayon SI, Shahriyar SA et al (2020) Discrete spider monkey optimization for travelling salesman problem. Appl Soft Comput J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105887
Changdar C, Mondal M, Giri PK et al (2022) A two-phase ant colony optimization based approach for single depot multiple travelling salesman problem in Type-2 fuzzy environment. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10190-9
Chen D, You XM, Liu S (2022) Ant colony algorithm with Stackelberg game and multi-strategy fusion. Appl Intell 52:6552–6574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02774-9
Chen J, You XM, Liu S, Li J (2019) Entropy-based dynamic heterogeneous ant colony optimization. IEEE Access 7:56317–56328. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2900029
Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Bahdanau D, Bengio Y (2014) On the properties of neural machine translation: encoder–decoder approaches. In: Proceedings of SSST-8, workshop on syntax, semantics and structure in statistical translation, pp 103–111. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/w14-4012
Chung J, Gulcehre C, Cho K, Bengio Y (2014) Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.3555
Das PK, Jena PK (2020) Multi-robot path planning using improved particle swarm optimization algorithm through novel evolutionary operators. Appl Soft Comput J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106312
Dorigo M, Gambardella LM (1997) Ant colony system: a cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1:53–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.585892
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A (1996) Ant system: optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans Syst Man, Cybern Part B Cybern 26:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/3477.484436
Du P, Liu N, Zhang H, Lu J (2021) An improved ant colony optimization based on an adaptive heuristic factor for the traveling salesman problem. J Adv Transp. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6642009
Gao W (2020) New ant colony optimization algorithm for the traveling salesman problem. Int J Comput Intell Syst 13:44–55. https://doi.org/10.2991/ijcis.d.200117.001
Gülcü Ş, Mahi M, Baykan ÖK, Kodaz H (2018) A parallel cooperative hybrid method based on ant colony optimization and 3-Opt algorithm for solving traveling salesman problem. Soft Comput 22:1669–1685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2432-3
Gunduz M, Aslan M (2021) DJAYA: a discrete Jaya algorithm for solving traveling salesman problem. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107275
Hoos HH, Stützle T (2000) MAX MIN ant system. Futur Gener Comput Syst 16:889–914
Huang Y, Shen XN, You X (2021) A discrete shuffled frog-leaping algorithm based on heuristic information for traveling salesman problem. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107085
Li W, Xia L, Huang Y, Mahmoodi S (2022) An ant colony optimization algorithm with adaptive greedy strategy to optimize path problems. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 13:1557–1571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03120-0
Liang S, Jiao T, Du W, Qu S (2021) An improved ant colony optimization algorithm based on context for tourism route planning. PLoS ONE 16:20281–20292. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0257317
Mahi M, Baykan ÖK, Kodaz H (2015) A new hybrid method based on particle swarm optimization, ant colony optimization and 3-Opt algorithms for traveling salesman problem. Appl Soft Comput J 30:484–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.068
Meng J, You X, Liu S (2022) Heterogeneous ant colony optimization based on adaptive interactive learning and non-zero-sum game. Soft Comput 26:3903–3920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06833-2
Ning J, Zhang Q, Zhang C, Zhang B (2018) A best-path-updating information-guided ant colony optimization algorithm. Inf Sci (ny) 433–434:142–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.12.047
Panwar K, Deep K (2021) Transformation operators based grey wolf optimizer for travelling salesman problem. J Comput Sci 55:101454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2021.101454
Stodola P, Michenka K, Nohel J, Rybanský M (2020) Hybrid algorithm based on ant colony optimization and simulated annealing applied to the dynamic traveling salesman problem. Entropy. https://doi.org/10.3390/E22080884
Stodola P, Otřísal P, Hasilová K (2022) Adaptive Ant Colony Optimization with node clustering applied to the travelling salesman problem. Swarm Evol Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2022.101056
Tuani AF, Keedwell E, Collett M (2020) Heterogenous adaptive ant colony optimization with 3-opt local search for the travelling salesman problem. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106720
Wang S, Liu Y, Qiu Y et al (2022) Cooperative task allocation for multi-robot systems based on multi-objective ant colony system. IEEE Access 10:56375–56387. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3165198
Wang Y, Han Z (2021) Ant colony optimization for traveling salesman problem based on parameters optimization. Appl Soft Comput 107:107439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107439
Wang Y, Wang L, Chen G et al (2020) An improved ant colony optimization algorithm to the periodic vehicle routing problem with time window and service choice. Swarm Evol Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2020.100675
Wu C, Fu X, Pei J, Dong Z (2021) A Novel Sparrow Search Algorithm for the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Access 9:153456–153471. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3128433
Yang S, Huang J, Li W, Xiang X (2022) A novel discrete group teaching optimization algorithm for TSP path planning with unmanned surface vehicles. J Mar Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091305
Yi Z, Hongda Y, Mengdi S, Yong X (2022) Hybrid swarming algorithm with van der waals force. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.806177
Yingyong L, Fangying Z, Li W et al (2013) The natural restoration capability of vegetation in different site types along the expressway 25, Lu-Su section, China. Appl Mech Mater 253–255:1075–1081. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.253-255.1075
Yong W (2015) Hybrid Max–Min ant system with four vertices and three lines inequality for traveling salesman problem. Soft Comput 19:585–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1279-8
Zhang D, You X, Liu S, Yang K (2019) Multi-colony ant colony optimization based on generalized Jaccard similarity recommendation strategy. IEEE Access 7:157303–157317. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2949860
Zhang Z, Han Y (2022) Discrete sparrow search algorithm for symmetric traveling salesman problem. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108469
Zhou J, Wang C, Li Y et al (2017) A multi-objective multi-population ant colony optimization for economic emission dispatch considering power system security. Appl Math Model 45:684–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.01.001
Zhou X, Ma H, Gu J et al (2022) Parameter adaptation-based ant colony optimization with dynamic hybrid mechanism. Eng Appl Artif Intell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105139
Zhu H, You X, Liu S (2019) Multiple ant colony optimization based on pearson correlation coefficient. IEEE Access 7:61628–61638. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2915673
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61673258, Grant 61075115, and the Shanghai Natural Science Foundation under Grant 19ZR1421600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The paper and the algorithm code were written by LW. Suggestions for revising the manuscript were given by XY. The material for the experiment was prepared by SL. The final manuscript is approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
All the authors have been informed and agreed to publish this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., You, X. & Liu, S. Multi-ant colony optimization based on bidirectional induction mechanism and cooperative game. Soft Comput 27, 15075–15093 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08689-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08689-6