Abstract
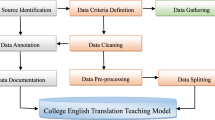
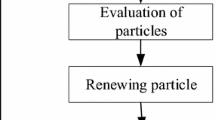
English language translation teaching plays a crucial role in today’s globalized world, particularly in countries like China, which has seen an increased emphasis on English language proficiency. However, effective teaching and assessment of students’ translation abilities remain significant challenges for educators. To address the challenges of English language translation and teaching, this paper proposes a novel approach that integrates Internet of Things (IoT), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and Neural Network algorithms to assist teachers in evaluating and assessing students’ English translation abilities by enabling them to better fulfill their teaching responsibilities. This paper first describes the computational mechanism of Neural Network algorithm using PSO, which includes the particle coding approach. An application model is designed to assess students’ capacity for learning using English translational instruction. The PSO algorithm gathers information on their learning progress, and fully utilize the analyzed results to develop learning strategies and create teaching materials for various learning types, which is helpful for the quick advancement of English translation teaching. Secondly, this paper develops a translational application model for English language as a practical framework. The proposed method utilizes the upgraded PSO-enabled Neural Network to process English language translation and teaching data by achieving network training in a global optimal state of PSO by reducing training errors. Thirdly, this paper evaluates the effectiveness of the model by comparing the average errors of the training and test samples with different numbers of particles such as 5, 10, and 20. Finally, the results demonstrate high accuracy in measuring students’ translation abilities. Furthermore, the study collects and examines three data sets, specifically English-Foreign Language Translation Corpus (EFLT), English Language Learners’ Corpus (ELLC), and English-Multilingual Parallel Corpus (EMPC), with a detection accuracy of 0.84, 0.97, and 0.65, respectively.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Ali M, Yin B, Kunar A, Sheikh AM et al (2020) Reduction of multiplications in convolutional neural networks. In: 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), pp 7406–7411. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.23919/CCC50068.2020.9188843
Aslam MS, Dai X, Hou J, Li Q, Ullah R, Ni Z, Liu Y (2020) Reliable control design for composite-driven scheme based on delay networked T-S fuzzy system. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 30(4):1622–1642
Bilal H, Yin B, Kumar A, Ali M, Zhang J, Yao J (2023) Jerk-bounded trajectory planning for rotary flexible joint manipulator: an experimental approach. Soft Comput 27(7):4029–4039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07923-5
Cao H (2022) Entrepreneurship education-infiltrated computer-aided instruction system for college Music Majors using convolutional neural network. Front Psychol 13:900195. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.900195
Cao B, Zhao J, Lv Z, Gu Y, YangHalgamuge PSK (2020) Multiobjective evolution of fuzzy rough neural network via distributed parallelism for stock prediction. iEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(5):939–952. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2972207
Cao B, Gu Y, Lv Z, Yang S, ZhaoLi JY (2021) RFID reader anticollision based on distributed parallel particle swarm optimization. IEEE Internet Things J 8(5):3099–3107. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3033473
Chen G, Chen P, Huang W, Zhai J (2022) Continuance intention mechanism of middle school student users on online learning platform based on qualitative comparative analysis method. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3215337
Elnadeef EA (2023) Transformative pedagogy towards using internet of things in teaching English at King Khalid University context from Digital Native Perspective. Int J Linguist Lit Transl 6(4):25–34. https://doi.org/10.32996/ijllt.2023.6.4.5
GraboWsKi Ł, Groom N (2022) Functionally-defined recurrent multi-word units in English-to-Polish translation: a corpus-based study. Revista Española De Lingüística Aplicada/spanish Journal of Applied Linguistics 35(1):1–29
Kumar A, Shaikh AM, Li Y et al (2021) Pruning filters with L1-norm and capped L1-norm for CNN compression. Appl Intell 51:1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01894-y
Li C (2021) A control-value theory approach to boredom in English classes among university students in China. Mod Lang J 105(1):317–334
Li L, Wu X, Kong M, Liu J, Zhang J (2023) Quantitatively interpreting residents happiness prediction by considering factor-factor interactions. IEEE Trans Computl Soc Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSS.2023.3246181
Liu Y, Zhang C (2023) Neural network algorithm based on particle swarm optimization and design of immersive intelligent English teaching in college English teaching system. In: 2023 International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE). https://doi.org/10.1109/icdcece57866.2023.10151018
Liu A, Zhai Y, Xu N, Nie W, LiZhang WY (2022a) Region-aware image captioning via interaction learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(6):3685–3696. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3107035
Liu Y, Wang K, Liu L, Lan H, Lin L (2022b) Tcgl: Temporal contrastive graph for self-supervised video representation learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:1978–1993. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3147032
Liu Y, Li Q, Cai D, Lu W (2023a) Research on the strategy of locating abnormal data in IOT management platform based on improved modified particle swarm optimization convolutional neural network algorithm. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.167406122.23888304/v1
Liu X, He J, Liu M, Yin Z, YinZheng LW (2023b) A scenario-generic neural machine translation data augmentation method. Electronics 12(10):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12102320
Muhammad Y, Jan MA, Mastorakis S, Zada B (2022) A deep learning-based smart assistive framework for visually impaired people. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Omni-layer Intelligent Systems (COINS), 2022, pp 1–6
Muhammad Y, Hassan MA, Almotairi S, Farooq K, Granelli F, Strážovská Ľ (2023) The Role of socioeconomic factors in improving the performance of students based on intelligent computational approaches. Electronics 12:1982
Pratheesh Kumar MR, Prasanna Kumaar P, Kameshwaranath R, Thasarathan R (2018) Roundness error measurement using teaching learning based optimization algorithm and comparison with particle swarm optimization algorithm. Int J Data Netw Sci. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2018.8.003
Tian J, Hou M, Bian H, Li J (2022) Variable surrogate model-based particle swarm optimization for high-dimensional expensive problems. Complex Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-022-00910-7
Wang L, Zhai Q, Yin B, et al (2019) Second-order convolutional network for crowd counting. In: Proc. SPIE 11198, Fourth International Workshop on Pattern Recognition, 111980T (31 July 2019); https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2540362
Yang S, Li Q, Li W, Li X, Liu A (2022) Dual-Level representation enhancement on characteristic and context for image-text retrieval. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(11):8037–8050. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3182426
Yao W, Guo Y, Wu Y, Guo J (2017) Experimental validation of fuzzy PID control of flexible joint system in presence of uncertainties. In: 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), pp 4192–4197. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.23919/ChiCC.2017.8028015
Yin B, Aslam MS et al (2023) A practical study of active disturbance rejection control for rotary flexible joint robot manipulator. Soft Comput 27:4987–5001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08026-x
Yin B, Khan J, Wang L, Zhang J, Kumar A (2019) Real-time lane detection and tracking for advanced driver assistance systems. In: 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), pp 6772–6777. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.23919/ChiCC.2019.8866334
Funding
This paper was funded by Teaching quality project of Anhui Provincial Department of Education in 2022 under Grant No. 2022xsxx001; Teaching quality project of Anhui University of Finance and Economics in 2022 under Grant No. acjyyb2022085.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any study with human participants or animals performed by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L. An IoT-based English translation and teaching using particle swarm optimization and neural network algorithm. Soft Comput 27, 14431–14450 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09032-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09032-9