Abstract
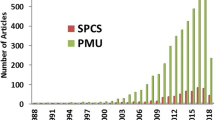
Synchronized phasor measurements provide the basis for fine-grained wide area power quality monitoring in electric grids. Time-synchronized phasor measurement units (PMUs) are deployed at different locations in the grid and report 10–60 measurements/second to energy management systems or other applications. For control applications it is crucial to receive measurement data as soon as possible after a state change in order to trigger corrective actions in time to prevent incidents in the grid.
In this paper we analyze characteristics of synchrophasor M2M communication for different network technologies, including VDSL, HSPA and LTE networks. We briefly review synchrophasor communication approaches and real-time demands. We then emulate PMU traffic and perform measurements on different networks. We show how the underlying technology influences one-way delay patterns for synchrophasor communication, which has direct implication on the achievable real-time properties.
Zusammenfassung
Synchronisierte Phasor Messungen stellen die Basis für Wide Area Monitoring Systeme in intelligenten Stromnetzen (Smart Grids) dar. Zeitsynchronisierte Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs) an verschiedenen Beobachtungspunkten senden 10–60 Messungen/Sekunde an Energiemanagementsysteme und andere Anwendungen. PMU Messergebnisse müssen den Anwendungen möglichst schnell zur Verfügung stehen. Nur dann können Anwendungen korrigierend in Prozesse eingreifen und Störungen im Stromnetz verhindern.
In diesen Beitrag analysieren wir Synchrophasor Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Kommunikationsmuster für verschiedene Technologien, einschließlich VDSL, HSPA und LTE. Wir betrachten zunächst die Echtzeitanforderungen und die verschiedenen Ansätze für PMU Kommunikation. Anschließend emulieren wir PMU Datenströme und führen damit Messungen in verschiedenen Kommunikationsnetzen durch. In unseren Ergebnissen zeigen wir, wie die zugrunde liegenden Technologien die Verzögerungszeiten (One-way Delay), und damit die Erfüllung von Echtzeitanforderungen, für die PMU Kommunikation beeinflussen.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, Y., Fischione, C. (2012): Real-time scheduling in LTE for smart grids. In 2012 5th international symposium on communications control and signal processing, ISCCSP (pp. 1–6).
Chenine, M., Nordstrom, L. (2011): Modeling and simulation of wide-area communication for centralized PMU-based applications. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv., 26(3), 1372–1380.
Hasan, R., Bobba, R., Khurana, H. (2009): Analyzing NASPInet data flows. In Power systems conference and exposition. PSCE 09 (pp. 1–6). New York: IEEE Press PES.
Kansal, P., Bose, A. (2012): Bandwidth and latency requirements for smart transmission grid applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, 3(3), 1344–1352.
IEEE (2011): Standard for synchrophasor measurements for power systems. IEEE Std C371181-2011 revis. IEEE Std C37118-2005, pp. 1–61.
IEEE (2011): Standard for synchrophasor data transfer for power systems. IEEE Std C371182-2011 Revis. IEEE Std C37118-2005, pp. 1–53.
IEC 61850 communication networks and system in substation automation. 2005–2002.
Martin, K. E. (2011): Synchrophasor standards development—IEEE C37.118 amp; IEC 61850. In 44th Hawaii international conference on system sciences, HICSS (pp. 1–8).
Cisco (2012): Whitepaper: PMU networking with IP multicast.
Fabini, J., Abmayer, M. (2013): Delay measurement methodology revisited: time-slotted randomness cancellation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., 62(10), 2839–2848.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Waltraud Müllner and Werner Wiedermann from A1 Telekom Austria AG, Philipp Svoboda and Markus Laner from the Institute of Telecommunications for providing LTE modems and SIM cards, which have facilitated measurements in mobile cellular networks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zseby, T., Fabini, J. & Rani, D. Synchrophasor communication. Elektrotech. Inftech. 131, 8–13 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00502-013-0193-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00502-013-0193-6