Abstract
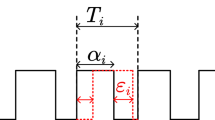
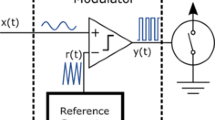
For battery powered portable devices it is required to have circuits that combine high efficiency with a small footprint. In the case of Class-D amplifiers the high efficiency can be achieved by applying pulse-width modulation (PWM) to generate the desired output signal. Classical PWM requires an output filter to suppress the idle current. In order to avoid this filter a different modulation scheme is used, which however introduces a larger amount of electromagnetic emissions. Therefore spread-spectrum techniques are applied to distribute the emissions over a wider frequency range. In this article methods are discussed that allow the use of spread-spectrum modulation without introducing audible artifacts due to the modulation.
Zusammenfassung
Für batterieversorgte mobile Geräte werden Komponenten benötigt, die einerseits eine kleine Baugröße andererseits auch einen geringen Stromverbrauch aufweisen. Im Fall von Klasse-D-Verstärkern wird die hohe Effizienz dadurch erreicht, dass man Pulsweitenmodulation (PWM) verwendet, um das gewünschte Ausgangssignal zu erhalten. Klassische PWM benötigt ein Filter am Ausgang, um Ruheströme in der Last zu vermeiden. Zur Vermeidung dieses Filters setzt man andere Modulationsverfahren ein, welche ein größeres Maß an elektromagnetischen Emissionen erzeugen. Aus diesem Grund verwendet man Spread-Spectrum-Modulation, damit diese Emissionen über einen größeren Frequenzbereich verteilt werden. In diesem Beitrag werden Spread-Spectrum-Methoden vorgestellt, die auch für Audio-Anwendungen geeignet sind.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen, K. (1997): High-fidelity pwm-based amplifier concept for active loudspeaker systems with very low energy consumption. J. Audio Eng. Soc., 45(7/8), 554–570. Online available: http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=7847.
Martin, J. (1970): Theoretical efficiencies of class-d power amplifiers. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng., 117(6), 1089–1090.
Ming, X., Chen, Z., Kun Zhou, Z., Zhang, B. (2011): An advanced spread spectrum architecture using pseudorandom modulation to improve emi in class d amplifier. IEEE Trans. Power Electron., 26(2), 638–646.
Jin, C., Tan, M. T., See, K. Y. (2013): Filterless class-d amplifier with pseudorandomized carrier frequency modulation for emi reduction. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat., 55(1), 74–80.
Wang, H., Zhang, B., Sun, J., Wang, R. (2010): Application of spread spectrum for emi reduction in class d amplifier. In 10th IEEE international conference on solid-state and integrated circuit technology (ICSICT 2010) (pp. 129–131).
IEC 61967-4, IEC.
Hardin, K., Fessler, J., Bush, D. (1994): Spread spectrum clock generation for the reduction of radiated emissions. In Electromagnetic compatibility, 1994 symposium record. IEEE international symposium on compatibility in the loop (pp. 227–231).
Karaca, T., Auer, M., Winkler, G., Deutschmann, B. (2014): Impact of spread spectrum emi-reduction on audio performance of filterless classd amplifiers. In 22nd Austrian workshop on microelectronics (Austrochip, October) (pp. 1–6).
Schreier, R. (1994): On the use of chaos to reduce idle-channel tones in delta-sigma modulators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Fundam. Theory Appl., 41(8), 539–547.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auer, M., Karaca, T. Spread spectrum techniques for Class-D audio amplifiers to reduce EMI. Elektrotech. Inftech. 133, 43–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00502-015-0384-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00502-015-0384-4