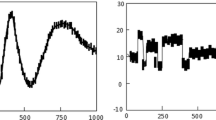
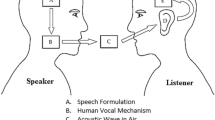
Abstract
Wavelet decomposition reconstructs a signal by a series of scaled and translated wavelets. Incorporating discrete wavelet decomposition theory with neural network techniques, wavelet networks have recently emerged as a powerful tool for many applications in the field of signal processing, such as data compression and function approximation. In this paper, four contributions are claimed: (1) From the point of view of machine learning, we analyse and construct wavelet network to achieve the compact representation of a signal. (2) A new algorithm of constructing wavelet network is proposed. The orthogonal least square (OLS) is employed to prune the wavelet network. (3) Our experiments on speech signal processing results show that the wavelet network pruned by OLS achieves the best approximation and prediction capabilities among the representative speech processing techniques. (4) Our proposed methodology has been successfully applied to speech synthesis for a talking head to read web texts.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Gao JB, Harris CJ, Gunn SR (2001) On a class of support vector kernels based on frames in function hilber spaces. Neural Comput 13:1975–1994
Gorriz JM, Puntonet CG, Salmeron M, de la Rosa JJG (2004) A new model for time-series forecasting using radial basis functions and exogenous data. Neural Comput Appl 13:101–111
Platt J (1991) A resource-allocating network for function interpolation. Neural Comput 3(2):213–225
Salmeron M, Ortega J, Puntonet CG, Prieto A (2001) Improved RAN sequential prediction using orthogonal techniques. Neurocomputing 41:153–172
Moulines E, Charpentier F (1990) Pitch synchronous waveform processing techniques for text-to-speech synthesis using diphones. Speech Commun 9:453–467
McAulay RJ, Quatieri TF (1986) Speech analysis/synthesis based on a sinusoidal representation. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 34:744–754
Mallat SG (1989) A theory of multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 11:674–693
Daubechies I (1990) The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 36:961–1005
Mallat SG, Zhong S (1992) Characterization of signals from multiscale edges. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 14(7):710–732
Zhang Q, Benveniste A (1992) Wavelet network. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 3(6):889–898
Zhang Q (1997) Using wavelet network in nonparametric estimation. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 8(2):227–236
Bishop CM (19991) Improving the generalization properties of radial basis function neural networks. Neural Comput 3(4):579–588
Chen S, Cowan CF, Grant PM (1991) Orthogonal least squares learning algorithms for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 2(2):302–309
Chen S, Chng ES, Alkadhimim K (1996) Regularized orthogonal least squares algorithm for constructing radial basis function networks. Int J Control 64(5):829–837
Chen S, Wu Y, Luk BL (1999) Combined genetic algorithm optimisation and regularised orthogonal least squares learning for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 10(5):1239–1243
Gomm JB, Yu DL (2000) Selecting radial basis function network centers with recursive orthogonal least squares training. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 11:306–314
Akaike H (1969) Fitting autoregressive models for prediction. Ann Inst Stat Math 21:243–347
Chen F, Spinko V, Shi D (2005) Real-time lip synchronization using wavelet network. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Cyberworlds, Singapore
Vapnik VN (1999) An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 10:988–999
Scholkopf B, Sung KK, Burges CJC, Girosi F, Niyogi P, Poggio T, Vapnik V (1997) Comparing support vector machines with gaussian kernels to radial basis function classifiers. IEEE Trans Signal Process 45(11):2758–2765
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, D., Chen, F., Ng, G.S. et al. The construction of wavelet network for speech signal processing. Neural Comput & Applic 15, 217–222 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-005-0016-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-005-0016-8