Abstract
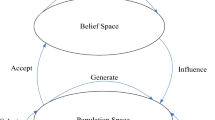
A multi-population cultural differential evolution (MCDE) algorithm is proposed. Each of the populations is managed by its private cultural differential evolution algorithm, in which a center individual is introduced into the belief space and selection function follows a new method to select the offspring for the next generation. To accelerate the convergence speed, the populations exchange their knowledge with each other every given generations. An adaptive mechanism of population diversity preservation is put forward to prevent the populations from being trapped in local optima. In the adaptive mechanism, the idea of culture fusion between populations is used to know the convergence status, so that the diversity of populations is kept along the evolutionary process. The performance evaluation on MCDE using eleven constrained optimization problems shows that MCDE is a competitive approach. MCDE is further applied to a practical optimization problem in an ammonia synthesis system with the objective to maximize the net value of ammonia. The results achieved by MCDE are compared with those by two traditional differential evolution algorithms, which indicate that MCDE has more excellent performance and better effectiveness.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durham W (1991) Coevolution: genes, culture, and human diversity. Stanford University Press, Stanford
Reynolds RG (1994) An introduction to cultural algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 3rd annual conference on evolutionary programming. World Scientific, pp 131–139
Reynolds RG, Peng B, Brewster JJ (2003) Cultural swarms: knowledge-driven problem solving in social systems. In: IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics, vol 4. IEEE Press, New York, pp 3589–3594. doi:10.1109/ICSMC.2003.1244446
Gao F, Cui G, Liu H (2006) Integration of genetic algorithm and cultural algorithms for constrained optimization. In: King I et al (eds) ICONIP 2006, Part III, LNCS, vol 4234. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 817–825. doi:10.1007/11893295_90
Lin C, Chen C, Lin C (2009) A hybrid of cooperative particle swarm optimization and cultural algorithm for neural fuzzy networks and its prediction applications. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C 39:55–68. doi:10.1109/TSMCC.2008.2002333
Ricardo LB, Carlos ACC (2004) A cultural algorithm with differential evolution to solve constrained optimization problems. In: Lemaitre C, Reyes CA, Gonzalez JA (eds) IBERAMIA 2004, LNAI, vol 3315. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 881–890. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-30498-2_88
Huang H, Gu X (2008) Neural network based on cultural algorithms and its application on modeling. Control Decis 23:477–480 (in Chinese). doi:CNKI:SUN:KZYC.0.2008-04-023. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC200804023.htm
Yuan X, Nie H, He L, Li C, Zhang Y (2008) A cultural algorithm for scheduling of hydro producer in the power market. In: Second international conference on genetic and evolutionary computing. IEEE Press, New York, pp 364–367. doi:10.1109/WGEC.2008.55
Ali M, Reynolds R, Ali R, Salhieh A (2011) Knowledge-based constrained function optimization using cultural algorithms with an enhanced social influence metaphor. Comput Intell, SCI 343:103–119. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-20206-3_7
Coelho LS, Clemente Souza RCT, Mariani VC (2009) Improved differential evolution approach based on cultural algorithm and diversity measure applied to solve economic load dispatch problems. Math Comput Simul 79:3136–3147. doi:10.1016/j.matcom.2009.03.005
Xiao B, Xiao J, Dong X, Tao Y, Lu C (2010) Research of PID parameter optimization based on cultural based ant colony algorithm for superheated steam temperature. In: 2010 29th Chinese control conference. IEEE Press, New York, pp 5171–5176
Reyes LC, Zezzatti CAOO, Santillán CG, Hernández PH, Fuerte MV (2010) A cultural algorithm for the urban public transportation. Lect Notes Comput Sci 6077:135–142. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13803-4_17
Soza C, Becerra RL, Riff MC, Coello CAC (2011) Solving timetabling problems using a cultural algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 11:337–344. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2009.11.024
Pan ZL, Chen L, Zhang GZ (2010) Cultural algorithm for minimization of binary decision diagram and its application in crosstalk fault detection. Int J Autom Comput 7:70–77. doi:10.1007/s11633-010-0070-2
Digalakis JG, Margaritis KG (2002) A multipopulation cultural algorithm for the electrical generator scheduling problem. Math Comput Simul 60:293–301. doi:10.1016/S0378-4754(02)00021-6
Alami J, Imrani AE, Bouroumi A (2007) A multipopulation cultural algorithm using fuzzy clustering. Appl Soft Comput 7:506–519. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2006.10.010
Guo YN, Cheng J, Cao Y, Lin Y (2011) A novel multi-population cultural algorithm adopting knowledge migration. Soft Comput 15:897–905. doi:10.1007/s00500-010-0556-4
Reynolds RG, Zhu S (2001) Knowledge-based function optimization using fuzzy cultural algorithms with evolutionary programming. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B 31:1–18. doi:10.1109/3477.907561
Storn R, Price K (1995) Differential evolution-a simple and efficient adaptive scheme for global optimization over continuous spaces. Technical report, TR-95-012, International Computer Science Institute
Bhat TR, Venkataramani D, Ravi V, Murty CVS (2006) An improved differential evolution method for efficient parameter estimation in biofilter modeling. Biochem Eng J 28:167–176. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2005.11.002
Chauhan N, Ravi V, Chandra DK (2009) Differential evolution trained wavelet neural networks: application to bankruptcy prediction in banks. Expert Syst Appl 36:7659–7665. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2008.09.019
Khazraee SM, Jahanmiri AH, Ghorayshi SA (2010) Model reduction and optimization of reactive batch distillation based on the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and differential evolution. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-010-0364-x
Liu Y, Qin Z, Shi Z, Lu J (2007) Center particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 70:672–679. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2006.10.002
Koziel S, Michalewicz Z (1999) Evolutionary algorithms, homomorphous mappings, and constrained parameter optimization. Evol Comput 7:19–44. doi:10.1162/evco.1999.7.1.19
Zangwill WI (1967) Nonlinear programming via penalty functions. Manag Sci 13:344–358
Runarsson TP, Yao X (2000) Stochastic ranking for constrained evolutionary optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 4:284–294. doi:10.1109/4235.873238
Janikow CZ, Michalewicz Z (1991) An experimental comparison of binary and floating point representations in genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of 4th international conference on genetic algorithms. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, pp 151–157
Shi Y, Eberhart RC (1998) Parameter selection in particle swarm optimization. Lect Notes Comput Sci 1447:591–600. doi:10.1007/BFb0040810
Storn R, Price K (1996) Minimizing the real functions of the ICEC’96 contest by differential evolution. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on evolutionary computation. IEEE Press, New York, pp 842–844. doi:10.1109/ICEC.1996.542711
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to help improve our paper. This work is supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2009AA04Z141), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 61174040), Shanghai Commission of Science and Technology (Grant no. 08JC1408200), Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (Grant no. B504), and the Specialized Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 200802510010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Test constrained optimization problems
Appendix: Test constrained optimization problems
Problem g01
Problem g02
Problem g03
Problem g04
Problem g05
Problem g06
Problem g07
Problem g08
Problem g09
Problem g10
Problem g11
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Wang, R., Zhang, L. et al. A multi-population cultural algorithm with adaptive diversity preservation and its application in ammonia synthesis process. Neural Comput & Applic 21, 1129–1140 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0749-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0749-5